جمهورية أرمينيا الأولى
جمهورية أرمنيا Հայաստանի Հանրապետութիւն | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1918–1920 | |||||||||||||
النشيد: Mer Hayrenik | |||||||||||||
 الأراضي التي احتفظت بها أرمنيا و مجلس قرة باخ في وقتٍ ما Territories claimed but never held by Armenia Area given to Armenia by the Treaty of Sèvres, which was not ratified and never entered into force.[1] | |||||||||||||
| العاصمة | يريڤان | ||||||||||||
| اللغات الشائعة | الأرمنية | ||||||||||||
| الدين | الرسولية الأرمنية | ||||||||||||
| الحكومة | جمهورية برلمانية | ||||||||||||
| رئيس الوزراء | |||||||||||||
• يونيو 1918 - مايو 1919 | Hovhannes Kajaznuni | ||||||||||||
• مايو 1919 - مايو 1920 | Alexander Khatisian | ||||||||||||
• مايو-نوفمبر 1920 | Hamo Ohanjanyan | ||||||||||||
• نوفمبر-ديسمبر 1920 | Simon Vratsian | ||||||||||||
| الحقبة التاريخية | فترة ما بين الحربين | ||||||||||||
| 28 مايو 1918 | |||||||||||||
| 28 مايو 1919 | |||||||||||||
• Sovietization | 2 ديسمبر 1920 | ||||||||||||
| Area | |||||||||||||
| mid-1918 (بعد معاهدة باطوم)[2][3] | 11,000 km2 (4,200 sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| 1919 (after the Armistice of Mudros)[4][5] | 70,000 km2 (27,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| 1920 (per the Treaty of Sèvres; never realized)[6] | 160,000 km2 (62,000 sq mi) | ||||||||||||
| التعداد | |||||||||||||
| 500000 | |||||||||||||
| 1300000 | |||||||||||||
| Currency | الروبل الأرمني | ||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
جمهورية أرمنيا الأولى،[7] تـُعرف رسمياً في زمن وجودها بإسم جمهورية أرمنيا (بالتقليدية بالأرمينية: Հայաստանի Հանրապետութիւն),[note 1] كانت أول دولة أرمنية معاصرة منذ فقدان الأرمن لدولة في العصور الوسطى.[note 2]
تأسست الجمهورية في الأراضي المأهولة بالأرمن في الامبراطورية الروسية المنحلة، والمعروفة بإسم شرق أرمنيا أو أرمنيا الروسية. The leaders of the government came mostly from the Armenian Revolutionary Federation (ARF or Dashnaktsutyun). The First Republic of Armenia bordered the Democratic Republic of Georgia to the north, the Ottoman Empire to the west, Persia to the south, and the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic to the east. It had a total land area of roughly 70,000 km² (174,000 km² under the Treaty of Sèvres), and a population of 1.3 million.
Armenian National Council declared the independence of Armenia on 28 May 1918. From the very onset, Armenia was plagued with a variety of domestic and foreign problems. A humanitarian crisis emerged from the aftermath of the Armenian Genocide as tens of thousands of Armenian refugees من الدولة العثمانية settled there. The republic lasted for over two years, during which time it was involved in several armed conflicts caused by territorial disputes. By late 1920, the nation was conquered by الجيش الأحمر السوڤيتي. The First Republic, along with the جمهورية أرمنيا الجبلية which repelled the Soviet invasion until July 1921, ceased to exist as an independent state, superseded by the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic that became part of the Soviet Union in 1922. After the fall of the Soviet Union, the republic regained its independence as the current Republic of Armenia in 1991.[21]
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
خلفية
The Russian offensive during the Caucasus Campaign of World War I and subsequent occupation and the creation of a provisional administrative government gave hope for ending Ottoman Turkish rule in Western Armenia. With the help of several battalions of Armenians recruited from the Russian Empire, the Russian army had made progress on the Caucasus Front, advancing as far as the city of Erzerum in 1916. The Russians continued to make considerable advances even after the toppling of Tsar Nicholas II in February 1917.[22]
In March 1917, the spontaneous revolution that toppled Tsar Nicholas and the Romanov dynasty established a caretaker administration, known as the Provisional Government. Shortly after, the Provisional Government replaced Grand Duke Nicholas' administration in the Caucasus with the five-member Special Transcaucasian Committee, known by the acronym Ozakom. The Ozakom included Armenian Democrat Mikayel Papadjanian, and was set to heal wounds inflicted by the old regime. In doing so, Western Armenia was to have a general commissar and was to be subdivided into the districts of Trebizond, Erzerum, Bitlis, and Van.[23] The decree was a major concession to the Armenians: Western Armenia was placed under the central government and through it under immediate Armenian jurisdiction. Dr. Hakob Zavriev would serve as the assistant for civil affairs and he in turn would see to it that most civil officials were Armenian.
In October 1917, the Bolsheviks seized power from the Provisional Government and announced that they would be withdrawing troops from both the Western and Caucasus fronts.[24] The Armenians, Georgians, and Muslims of the Caucasus all rejected the Bolsheviks' legitimacy.
نحو الاستقلال
On December 5, 1917, the Ottoman Empire and the Transcaucasian Commissariat signed the armistice of Erzincan, ending armed conflict. After the Bolshevik seizure of power, a multinational congress of Transcaucasian representatives met to create a provisional regional executive body known as the Transcaucasian Seim. The Commissariat and the Seim were heavily encumbered by the pretense that the South Caucasus formed an integral unit of a non-existent Russian democracy.[25] The Armenian deputies in the Seim were hopeful that the anti-Bolshevik forces in Russia would prevail in the Russian Civil War and rejected any idea of separating from Russia. In February 1918, the Armenians, Georgians and Muslims had reluctantly joined to form the Transcaucasian Federation, but disputes among the three groups continued as unity began to falter.
On March 3, 1918, Russian followed the armistice of Erzincan with the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk and left the war. It ceded territory From March 14 to April 1918, when a conference was held between the Ottoman Empire and the delegation of the Seim. Under the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk, the Russians allowed the Turks to retake the Western Armenian provinces, as well as to take over the provinces of Kars, Batum, and Ardahan.
In addition to these provisions, a secret clause obligated the Armenians and Russians to demobilize their forces in both western and eastern Armenia.[26] Having killed many and deported the Armenians of Western Armenia during the Armenian Genocide, the Ottoman Empire intended to eliminate the Armenian population of Eastern Armenia.[27] Shortly after the signing of Brest-Litovsk the Turkish army began its advance, taking Erzurum in March and Kars in April, which the Transcaucasian government of Nikolay Chkheidze had ordered soldiers to abandon. Beginning on May 21, the Ottoman army moved ahead again.
On May 11, 1918, a new peace conference opened at Batum. At this conference, the Ottomans extended their demands to include Tiflis, as well as Alexandropol and Echmiadzin, which they wanted for a railroad to be built to connect Kars and Julfa with Baku. The Armenian and Georgian members of the Republic’s delegation began to stall.
On May 26, 1918, Georgia declared independence; on May 28, it signed the Treaty of Poti, and received protection from Germany.[28] The following day, the Muslim National Council in Tiflis announced the establishment of the Democratic Republic of Azerbaijan.
Having been abandoned by its regional allies, the Armenian National Council, based in Tiflis and led by Russian Armenian intellectuals who represented Armenian interests in the Caucasus, declared its independence on May 28.[29] It dispatched Hovhannes Kajaznuni and Alexander Khatisyan, both members of the ARF, to Yerevan to take over power and issued the following statement on May 30 (retroactive to May 28):
In view of the dissolution of the political unity of Transcaucasia and the new situation created by the proclamation of the independence of Georgia and Azerbaijan, the Armenian National Council declares itself to be the supreme and only administration for the Armenian provinces. Because of the certain grave circumstances, the national council, deferring until the near future the formation of an Armenian National government, temporarily assumes all governmental functions, in order to take hold the political and administrative helm of the Armenian provinces.[30]
Meanwhile, the Turks had taken Alexandropol and were intent on eliminating the center of Armenian resistance based in Yerevan. The Armenians were able to stave off total defeat and delivered crushing blows to the Turkish army in the battles of Sardarapat, Karakilisa and Abaran.
The Republic of Armenia had to sue for negotiations at the Treaty of Batum, which was signed in Batum on June 4, 1918. It was the ADR's first treaty. After the Ottoman Empire took vast swathes of territory and imposed harsh conditions, the new republic was left with 10,000 square kilometers.[31]
الادارة

في 30 مايو 1918 the Armenian Revolutionary Federation had decided that Armenia should be a republic under a provisional coalition government. The declaration stated that the Republic of Armenia was to be a self-governing state, endowed with a constitution, the supremacy of state authority, independence, sovereignty, and plenipotentiary power. Kajaznuni became the country's first Prime Minister and Aram Manukian was the first minister of Interior.
Armenia established a Ministry of Interior and created a police force. The Armenian parliament passed a law on the police on April 21, 1920, specifying its structure, jurisdiction, and responsibilities. The Interior Ministry was also responsible for communications and telegraph, railroad, and the public school system, in addition to enforcing law and order. The reforms came soon and each of these departments became ministries.
In 1919, the leaders of the Republic had to deal with issues on three fronts: domestic, regional, and international. The Armenian Congress of Eastern Armenians that took control in 1918 fell apart and in June 1919, the first national elections were held. The establishment of law was a problem: Armenians had the most organized structure in their homeland; however, other ethnic groups had been settled in these lands too (primarily Kurds and Azeris). During the 1920s, which began under Kajaznuni's premiership, Armenians from the former Russian Empire and الولايات المتحدة developed the judicial system. January 1919 was an important milestone as Yerevan State University, the country's first state university, was founded.
- Speakers of the Parliament of Republic of Armenia
- Serop Zakaryan (30 June 1918 - 1 August 1918)
- Avetik Sahakyan (1 August 1918 - 1 August 1919)
- Avetis Aharonian (1 August 1919 - 4 November 1920)
- Hovhannes Kajaznuni (4 November 1920 - 2 December 1920)
- Prime Ministers in the Republic of Armenia
- Hovhannes Kajaznuni (30 June 1918 – 28 May 1919) (in Tbilisi, Georgia until 19 July 1918)
- Alexander Khatisian (28 May 1919 – 5 May 1920)
- Hamazasp "Hamo" Ohanjanian (5 May 1920 – 25 November 1920)
- Simon Vratsian (25 November 1920 – 2 December 1920)
العسكرية
Thanks to the efforts of Armenian National Council of Tiflis, an Armenian military corps was established to fight against the Ottoman offensive of late 1917 and early 1918. Units of this corps formed the basis of the DRA's army. In accordance with the harsh terms of the Treaty of Batum signed on June 14, 1918 the Ottoman Empire permitted the Armenian army to maintain just a single infantry division.[بحاجة لمصدر]
- Hovhannes Hakhverdyan (June 1918 – March 1919)
- Christophor Araratov (1919 – April 1920)
- Ruben Ter-Minasian (April – November 1920)
- Drastamat Kanayan (November – December 1920)
- Total number of military personnel
| Date | Number of troops |
|---|---|
| After the Mudros Armistice in 1918 | 16,000 men |
| 1919 | 20,000 men |
| November 1920 | 40,000 men |
التقسيمات الادارية
| المقاطعة | بالأرمنية | المقر | الموقع |
|---|---|---|---|
| أرارات | Արարատյան նահանգ | يريڤان | سهل أرارات، حوض بحيرة سيڤان، نخچوان وVayots Dzor والمنطقة المحيطة بـMount Aragats |
| Vanand | Վանանդի նահանգ | قارس | أوبلاست قارس السابق في الامبراطورية الروسية |
| شيراك | Շիրակի նահանգ | ألكسندروپول (گيومري) | المناطق التاريخية في شيراك، لوري، طاڤوش و جڤخك |
| سيونيك | Սյունիքի նահանգ | Goris | المناطق التاريخية في سيونيك (Zangezur) and Artsakh (ناگورنو-قرة باخ) |
ضمت الجمهورية المناطق التالية من تقسيمات الامبراطورية الروسية السابقة.[32]
| المقاطعات (أُكروگ) | الأجزاء | |
|---|---|---|
| محافظة إريڤان | ||
| كلها | كلها | |
| أوبلاست قارس | ||
| قارس | كلها | |
| Kaghzvan | كلها | |
| Olti | جزء رئيسي | |
| أردخان | جزء رئيسي | |
| محافظة إليزابثپول | ||
| زانگزور | كلها | |
| قزخ | الجزء الجبلي (Ijevan subdistrict) | |
| محافظة تفليس | ||
| Borchalu | نصف (ناحية لوري) | |
التعداد
قبل الحرب العالمية الأولى، في 1914, the territory was part of Russian Armenia; among the total Armenian population of 2,800,000, about 1,500,000 lived in the Ottoman Empire, and the remainder were in Russian Armenia.[4] An estimate in 1918, during the new Armenian Republic's first year, indicated that there were 800,000 Armenians and more than 100,000 Muslims, mostly Ottoman Turks, and Azerbaijani Turks and Kurds everywhere else. Of the 800,000 Armenians, about 500,000 were native Russian Armenians and 300,000 were destitute and starving refugees fleeing from the massacres that took place in the Ottoman Empire.[33]
The surviving Armenian population in 1919 was 2,500,000, two million of whom were distributed in the Caucasus.[4] Of these 2,000,000 in the Caucasus, 1,300,000 were to be found within the boundaries of the new Republic of Armenia, which included 300,000 to 350,000 refugees who had escaped from the Ottoman Empire.[4] There were 1,650,000 Armenians in the new Republic.[4] Also added to this Armenian population were 350,000 to 400,000 people of other nationalities, and a total population of about 2,000,000 within the Armenian Republic.[4]
The surviving Armenian population in 1921 was 1,200,000 in the republic, 400,000 in Georgia, 340,000 in Azerbaijan and those in the other regions of the Caucasus brought the total to 2,195,000.[34]
مشكلة اللاجئين
There was also an Armenian settlement problem that brought conflict with other ethnic residents. In all, there were over 300,000 embittered and impatient Armenian refugees escaping from the Ottoman Empire who were now the government's responsibility. This proved an insurmountable humanitarian issue. Typhus was a major sickness, because of its effect on children. Conditions in the outlying regions, not necessarily consisting of refugees, weren't any better. The Ottoman governing structure and Russian army had already withdrawn from the region. The Armenian government had neither time nor resources to rebuild the infrastructure. The 393,700 refugees were under their jurisdiction as follows:[بحاجة لمصدر]
| Districts | Number of refugees |
|---|---|
| Yerevan | 75,000 |
| Ejmiatsin | 70,000 |
| Novo-Bayazit (Gavar) | 38,000 |
| Daralagyaz (Vayots Dzor) | 36,000 |
| Bash-Abaran (Aparan) | 35,000 |
| Ashtarak | 30,000 |
| Akhta - Yelenovka (Hrazdan - Sevan) | 22,000 |
| Bash-Garni | 15,000 |
| Karakilisa (Vanadzor) | 16,000 |
| Dilijan | 13,000 |
| Armenia | 350,000 |
The government of Hovhannes Kajaznuni was faced with a most sobering reality in the winter of 1918-19. The newly formed government was responsible for over half a million Armenian refugees in the Caucasus. It was a long and harsh winter.[35] The homeless masses, lacking food, clothing and medicine, had to endure the elements. Many who survived the exposure and famine succumbed to the ravaging diseases. By the spring of 1919, the typhus epidemic had run its course, the weather improved and the first American Committee for Relief in the Near East shipment of wheat reached Batum. The British army transported the aid to Yerevan. Yet by that time some 150,000 of the refugees had perished. Vratsian puts this figure at around 180,000, or nearly 20% of the entire nascent Republic. A report[ممن؟] in early 1919 noted that 65% of the population of Sardarabad, 40% of the population of eight villages near Etchmiadzin and 25% of the population of Ashtarak had died.[بحاجة لمصدر]
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
العلاقات الخارجية

On January 19, 1920 League of Nations recognized Armenian Government as de facto governement. [36]
In 1920, the Republic of Armenia administered an area that covered most of present-day Armenia, Kars, Igdir, and the Chuldur and Gole districts of Ardahan, while the regions of Nakhichevan, Nagorno-Karabakh, Zangezur (today the Armenian province of Syunik), and Qazakh were disputed and fought over with Azerbaijan. The Oltu region (briefly administered by Georgia in 1920) was also claimed by Armenia. The majority-Armenian area of Lori was disputed with and administered by Georgia. The areas south of Yerevan which were populated by Muslims did not acknowledge Armenian authority and resisted attempts by the Armenian government to assert its control over those regions.
Nevertheless, after the signing of the Treaty of Sèvres in 1920, Armenia was granted formal international recognition. [37] The United States, as well as some South American countries, officially opened diplomatic channels with the government. Numerous Armenian missions were also established in Great Britain, Italy, Germany, Serbia, Greece, Iran, Japan and Africa.[38]
الحرب الأرمنية-الجورجية
In December 1918, Armenia and Georgia engaged in a brief military conflict over disputed border areas in the largely Armenian-populated Lori and Akhalkalak districts along with some other neighboring regions. Both nations claimed the districts, which Georgia had occupied after the Ottomans evacuated the area. Inconclusive fighting continued for two weeks. An Armenian offensive under Drastamat Kanayan (Dro) made substantial gains in the first ten days. By December 25 they had reached positions 30 miles from Tiflis, when the Allied representatives in the city finally intervened.[39][40] On 1 January 1919, military operations of both sides ceased and peace talks began supervised by the British and French, which ended in Tbilisi a few days later.[40][41] The draft British plan established that Georgian troops would remain in Akhalkalak and northern Borchalu, whereas Armenian forces would settle in southern Borchalu, and the British would take positions between the two opponents. This forced Armenians to relinquish their gains during the war. Georgia accepted the plan and the Allies decided to impose it with or without the approval of the government of Armenia. Finally, hostilities stopped on December 31 when the parties agreed to the British-brokered ceasefire. British mediation facilitated the end of the war, and resulted in the establishment of a joint Armeno-Georgian civil administration in the "Lori neutral zone" or the "Shulavera Condominium".[42]
Relations between Armenia and Georgia, however, remained tense.[43] In the spring of 1919, American relief agency officials began to complain that Georgian officials, who demanded a share of the provisions, were holding up railway traffic carrying vital supplies of flour and other foodstuffs to Armenia.[44] Moved by their complaints and the debilitating food crisis in Armenia, Georges Clemenceau, as president of the Versailles Conference, issued a protest letter on July 18, calling on Georgia to cease further interference. Georgia issued its own protest to this communiqué, but by 25 July American officials were already reporting that rail traffic had begun to pick up.[45] In autumn 1919, the two countries began negotiations for a new transit treaty.
الحرب الأذربيجانية الأرمنية
A considerable degree of hostility existed between Armenia and its new neighbor to the east, the Democratic Republic of Azerbaijan, stemming largely from racial, religious, cultural and societal differences. The Azeris had close ethnic and religious ties to the Turks and had provided material support for them in their drive to Baku in 1918. Although the borders of the two countries were still undefined, Azerbaijan claimed most of the territory Armenia was sitting on, demanding all or most parts of the former Russian provinces of Elizavetpol, Tiflis, Yerevan, Kars and Batum.[46] As diplomacy failed to accomplish compromise, even with the mediation of the commanders of a British expeditionary force that had installed itself in the Caucasus, territorial clashes between Armenia and Azerbaijan took place throughout 1919 and 1920, most notably in the regions of Nakhichevan, Karabakh and Syunik (Zangezur). Repeated attempts to bring these provinces under Azerbaijani jurisdiction were met with fierce resistance by their Armenian inhabitants. In May 1919, Dro led an expeditionary unit that was successful in establishing Armenian administrative control in Nakhichevan.[47]
While problems with Azerbaijan continued, a new state headed by Fakhr al-Din Pirioghlu and centered in Kars, the South West Caucasian Republic was established. It claimed the territory around the regions of Kars and Batum, the Nakhichevan and Sharur districts of the Yerevan province and the Akhaltsikhe and Akhalkalaki districts of the Tiflis province. It existed alongside the British general governorship created during the Entente's intervention in Transcaucasia.[48] It was abolished by British High Commissioner Admiral Somerset Arthur Gough-Calthorpe in April 1919 and the region was assigned to the Armenian Republic.[بحاجة لمصدر]
معاهدة سيڤر
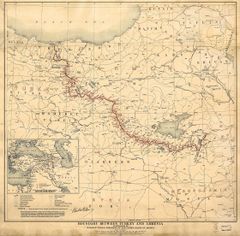
The Treaty of Sèvres was signed between the Allied and Associated Powers and Ottoman Empire at Sèvres, France on August 10, 1920. The treaty included a clause on Armenia: it made all parties signing the treaty recognize Armenia as a free and independent state. The drawing of definite borders was, however, left to President Woodrow Wilson and the United States State Department, and was only presented to Armenia on November 22. The new borders gave Armenia access to the Black Sea and awarded large portions of the eastern provinces of the Ottoman Empire to the republic.[49]
الغزوات التركية والسوڤيتية

On September 20, 1920, the Turkish General Kazım Karabekir invaded the region of Sarikamish.[50] In response, Armenia declared war on Turkey on September 24 and the Turkish–Armenian War began. In the regions of Oltu, Sarikamish, Kars, Alexandropol (Gyumri) Armenian forces clashed with those of Karabekir’s XV Corps. Fearful of possible Russian support for Armenia, Mustafa Kemal Pasha had earlier sent several delegations to Moscow in search of an alliance, finding a receptive response from the Soviet government, which started sending gold and weapons to the Turkish revolutionaries. This proved disastrous for the Armenians.
Armenia gave way to communist power in late 1920. In November 1920, the Turkish revolutionaries captured Alexandropol and were poised to move in on the capital. A ceasefire was concluded on November 18. Negotiations were then carried out between Karabekir and a peace delegation led by Alexander Khatisian in Alexandropol; although Karabekir’s terms were extremely harsh the Armenian delegation had little recourse but to agree to them. The Treaty of Alexandropol was thus signed on December 2/3, 1920.[51]
The 11th Red Army began its virtually unopposed advance into Armenia on November 29, 1920. The actual transfer of power took place on December 2 in Yerevan. The Armenian leadership approved an ultimatum, presented to it by the Soviet plenipotentiary Boris Legran. Armenia decided to join the Soviet sphere, while Soviet Russia agreed to protect its remaining territory from the advancing Turkish army. The Soviets also pledged to take steps to rebuild the army, protect the Armenians and to not pursue non-communist Armenians, although the final condition of this pledge was reneged on when the Dashnaks were forced out of the country.[بحاجة لمصدر]
On December 5, the Armenian Revolutionary Committee (Revkom, made up of mostly Armenians from Azerbaijan) also entered the city.[52] Finally, on the following day, December 6, Felix Dzerzhinsky's Cheka entered Yerevan, thus effectively ending the existence of the First Republic of Armenia. At that point what was left of Armenia was under the influence of the Bolsheviks. The part occupied by Turkey remained for the most part theirs, as laid out in the terms of the subsequent Treaty of Kars. Soon, the Armenian Soviet Socialist Republic was proclaimed, under the leadership of Aleksandr Myasnikyan. It was to be included in the newly created Transcaucasian Soviet Federated Socialist Republic.[بحاجة لمصدر]
الخرائط
Russian occupied area of Turkish Armenia in 1917, a year before creation of the Republic and the collapse of the Russo-Armenian counter offensive.
Claims presented by the Republic of Armenia at the Paris Peace Conference, 1919.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
في الثقافة
The Sardarapat Memorial at the site of the Battle of Sardarabad is the symbol of the First Republic. Every year on May 28, Armenia's political leadership and thousands of ordinary people visit the memorial to celebrate the foundation of Armenian statehood.[53]
In his Antranik of Armenia short story, Armenian-American writer William Saroyan writes about the First Republic of Armenia. "It was a small nation of course, a very unimportant nation, surrounded on all sides by enemies, but for two years Armenia was Armenia, and the capital was Erivan. For the first time in thousands of years Armenia was Armenia."[54]
انظر أيضاً
- Aftermath of World War I
- Armenian Genocide
- Democratic Republic of Georgia
- Azerbaijan Democratic Republic
- Wilsonian Armenia
- United Armenia
المراجع
- ملاحظات
- ^ الأسماء الأخرى للبلد تضم الجمهورية الأراراتية[8] (Արարատյան Հանրապետություն, جمهورية أرارات)[9][10] و جمهورية إريڤان/يريڤان.[11][12] تلك المصطلحات كثيرا ما كان يستخدمها الأرمن العثمانيون لأن البلد "كان مجرد مقاطعة غبراء بدون أرمنيا العثمانية التي كان يسعى الأرمن لفصلها لأربعين عاماً."[13] في كتابها، Armenia: Past and Present, published in 1981 by the Prelacy of the الكنيسة الرسولية الأرمنية in New York, author Elisabeth Bauer-Manndorff referred to it as the جمهورية أرمنيا الديمقراطية أو الجمهورية الأرمنية الديمقراطية أو الجمهورية الديمقراطية الأرمنية.[14] كما كانت تُعرف بإسم جمهورية الطاشناق بسبب حقيقة أن الاتحاد الثوري الأرمني، المعروف بإسم طاشناقتسوتيون أو ببساطة طاشناق كان القوة السياسية المهيمنة في البلد.[15] أثناء العهد السوڤيتي، الدوائر الأكاديمية الأرمنية المتأثرة بالشيوعية والمناهضة للطاشناق، تحديداً الموسوعة الأرمنية السوڤيتية، تشير إليها بإسم جمهورية أرمنيا البورجوازية (Հայաստանի Բուրժուական Հանրապետություն).[16] منذ استقلال أرمنيا عن الاتحاد السوڤيتي في 1991، فإن أكثر الأسماء شيوعاً في أرمنيا هو جمهورية أرمنيا الأولى (Հայաստանի Առաջին Հանրապետություն) أو الجمهورية الأولى اختصاراً.[17]
- ^ تختلف المصادر حول متى فُقِدت الدولة الأرمنية. مملكة قيليقيا الأرمنية انتهت في 1375.[18] إلا أن آخرين يقترحون أن الدولة الأرمنية انتهت في 1045 بسقوط أرمنيا البقراتية، لأن أرمنيا القليقية كانت خارج الوطن الأرمني التقليدي، بينما أرمنيا البقراتية كانت آخر دولة أرمنية رئيسية في المرتفعات الأرمنية.[19][20]
- مصادر محددة
- ^ Hille, Charlotte Mathilde Louise (2010). State Building and Conflict Resolution in the Caucasus. Leiden, Netherlands: Brill. p. 151. ISBN 978-90-04-17901-1.
- ^ Hewsen, Robert (2001). Armenia: A Historical Atlas. Chicago: University of Chicago Press. p. 235. ISBN 0-226-33228-4.
- ^ Walker, Christopher J. (1990). Armenia: The Survival of a Nation (revised second ed.). New York: St. Martin's Press. p. 257. ISBN 9780312042301.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح Maintenance of Peace in Armenia. United States Congress. Senate Committee on Foreign Relations. USA: Govt. print. off. 1919. Retrieved 2011-02-14.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ Chiclet, Christophe (2005). "The Armenian Genocide" in Turkey Today: A European Country? Olivier Roy (ed.) London: Anthem Press. p. 167. ISBN 1-84331-173-9.
- ^ Hakobyan, Tatul (9 August 2015). "Sèvres: The Unfulfilled Armenian Dream". ANI Armenian Research Center.
If the Treaty of Sèvres had been realised, the Republic of Armenia would have covered a territory of over 160 thousand square kilometres.
- ^
- "Division of Armenology and Social Sciences". أكاديمية العلوم الوطنية الأرمنية.
...the political history of the First Republic of Armenia...
- Libaridian, Gerald J. (2007). Modern Armenia: people, nation, state. New Brunswick, New Jersey: Transaction Publishers. p. 266. ISBN 978-1-4128-0648-0.
...two most important and consequential events for Armenians in the twentieth century: the Genocide and the experience of the First Republic of Armenia, 1918-1920.
- Avakian, Arra S. (1998). "The First Republic of Armenia (1918-1920)". Armenia: A Journey Through History: Van. Electric Press. p. 137. ISBN 978-0-916919-24-5.
- Danielyan, Eduard (2003). "Armenia". In Mokyr, Joel (ed.). The Oxford Encyclopedia of Economic History, Volume 2. Oxford University Press. p. 157.
The first Republic of Armenia (1918–1920) suffered a difficult time, sheltering thousands of refugees while enduring epidemics and Turkish invasions...
- Mirzoyan, Alla (2010). Armenia, the Regional Powers, and the West: Between History and Geopolitics. Palgrave Macmillan. p. 13. ISBN 9780230106352.
For instance, the contemporary celebration of the independence day of the First Republic of Armenia on May 28 accomplishes the mental integration of 1918 and 1991 into an uninterrupted experience of independence...
- de Waal, Thomas (2003). Black Garden: Armenia and Azerbaijan Through Peace and War. New York: New York University Press. p. 76. ISBN 978-0-8147-1945-9.
From 1918 to 1920, Yerevan was the capital of the briefly independent first republic of Armenia...
- "The Birth of the First Republic of Armenia". civilnet.am. CivilNet. 28 May 2013.
- "Richard Hovannisian to Discuss First Republic of Armenia at Lecture in Belmont". The Armenian Weekly. 3 November 2015.
- "Division of Armenology and Social Sciences". أكاديمية العلوم الوطنية الأرمنية.
- ^ Hovannisian 1971, p. 259.
- ^ Pasdermadjian, Garegin; Torossian, Aram (1918). Why Armenia should be free: Armenia's role in the present war, Issue 30. Hairenik Publishing. p. 37.
- ^ Hovannisian 1971, p. 454.
- ^ Chisholm, Hugh (1922). The Encyclopædia Britannica: a dictionary of arts, sciences, literature and general information, Volume 32. The Encyclopædia Britannica Co. p. 802.
- ^ Walker, Christopher J. (1980). Armenia, the survival of a nation. Croom Helm. p. 231.
- ^ Walker, Christopher J. (1990). Armenia: The Survival of a Nation (revised second ed.). New York: St. Martin's Press. pp. 272–273. ISBN 9780312042301.
- ^ Bauer-Manndorff, Elisabeth (1981). Armenia: Past and Present. New York and Lucerne: The Armenian Prelacy and Reich Verlag. pp. 149–150, 178.
- ^ Suny, Ronald Grigor (1993). Looking toward Ararat Armenia in modern history. Bloomington: Indiana university press. p. 131. ISBN 9780253207739.
- ^ Soviet Armenian Encyclopedia (in الأرمنية). Vol. 6. Yerevan. 1980. pp. 137–138.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ "Նախկին վարչապետներ [Previous Prime Ministers]" (in الأرمنية). Government of Armenia Website. Retrieved 2 August 2013.
- ^ de Waal, Thomas (2010). The Caucasus: An Introduction. Oxford University Press. p. 28. ISBN 9780199746200.
- ^ Nazaryan, Lousine (28 May 2009). "Historian Ashot Melkonyan: "The idea of unity of the Armenian nation must not be buried in oblivion"". Hayastani Hanrapetutyun. Retrieved 14 September 2013.
- ^ "Declaration of Independence (May 30, 1918)". ARF Archives Institute. Archived from the original on 3 July 2013. Retrieved 14 September 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Armenia: A Historical Atlas, by Robert H. Hewsen and Christoper C. Salvatico, 2001
- ^ Hovannisian, Richard G. (1967). Armenia on the Road to Independence, 1918. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 80–82. ISBN 0-520-00574-0.
- ^ Hovannisian. Armenia on the Road to Independence, pp. 75-80.
- ^ Hovannisian. Armenia on the Road to Independence, p. 104.
- ^ Hovannisian. Armenia on the Road to Independence, p. 106.
- ^ Hovannisian. Armenia on the Road to Independence, pp. 103-105, 130.
- ^ Balakian. Burning Tigris, pp. 319-323.
- ^ Lang, David Marshall (1962). A Modern History of Georgia. London: Weidenfeld and Nicolson, pp. 207-208.
- ^ Hovannisian. Armenia on the Road to Independence, pp. 186-201.
- ^ Hovannisian. Armenia on the Road to Independence, p. 191.
- ^ Hovannisian. Armenia on the Road to Independence, p. 198.
- ^ Albert Parsadanyan. Intelligence Warehouse-1. Yerevan: VMV Publication, 2003, p. 57.
- ^ Hewsen. Armenia, p. 235.
- ^ See the US State Department values given here.
- ^ Hovannisian, Richard G. (1971). The Republic of Armenia: The First Year, 1918-1919, Vol. I. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 126–155. ISBN 0-520-01984-9.
- ^ 1964-, Hille, Charlotte Mathilde Louise, (2010). https://books.google.am/books?id=yxFP6K8iZzQC&pg=PA143&lpg=PA143&dq=recognition+of+armenia+by+league+of+nations&source=bl&ots=lxYPV15v_w&sig=Zqjo14uDmxWHIaEGuc6Tv_IgZ7Q&hl=en&sa=X&ved=0ahUKEwiqlI_6gsjYAhWqF5oKHc5mCfAQ6AEIOjAE#v=onepage&q&f=false. State building and conflict resolution in the Caucasus. Leiden [the Netherlands]: Brill. p. 143. ISBN 9004179011. OCLC 668211543.
{{cite book}}:|chapter-url=missing title (help);|last=has numeric name (help)CS1 maint: extra punctuation (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ League of Nations. Assembly. Fifth Committee (1920). Admission of new members to the League of Nations: Armenia. Report presented by the 5th Committe to the Assembly. Robarts - University of Toronto. [Geneva, League of Nations].
- ^ Hovannisian, Richard G. (1982). The Republic of Armenia, Vol. II: From Versailles to London, 1919-1920. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 526–529. ISBN 0-520-04186-0.
- ^ Partskhaladze, George; Andersen, Andrew. "Armeno-Georgian War of 1918 and Armeno-Georgian Territorial Issue in the 20th Century".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ أ ب "iveria".
- ^ Hovannisian 1971, p. 114.
- ^ Hovannisian. Republic of Armenia, Vol. I, p. 120-125.
- ^ "iveria".
- ^ Hovannisian. Republic of Armenia, Vol. II, pp. 140-144.
- ^ Hovannisian. Republic of Armenia, Vol. II, p. 145.
- ^ See Hovannisian. Republic of Armenia, Vol. II, p. 192, map 4.
- ^ Hovannisian. Republic of Armenia, Vol. I, pp. 243-247.
- ^ Hovannisian. Republic of Armenia, Vol. I, pp. 205-214.
- ^ Hovannisian, Richard G. (1996). The Republic of Armenia, Vol. IV: Between Crescent and Sickle, Partition and Sovietization. Berkeley: University of California Press. pp. 40–44. ISBN 0-520-08804-2.
- ^ Hovannisian. Republic of Armenia, Vol. IV, pp. 184-197.
- ^ Hovannisian. Republic of Armenia, Vol. IV, pp. 394-396.
- ^ Hovannisian. Republic of Armenia, Vol. IV, pp. 373ff.
- ^ Hakobyan, Tatul (28 May 2009). "On Armenian independence day, a visit to Sardarapat, symbol of Armenian pride". Armenian Reporter. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 20 September 2013.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Saroyan, William (1943). 31 selected stories from "Inhale and Exhale". New York: Avon Book Company. p. 107.
- مصادر عامة
- Hovannisian, Richard G. (1971). The Republic of Armenia: The first year, 1918-1919. Volume 1. Berkeley: University of California Press. ISBN 9780520018051.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
للاستزادة
- (أرمنية) Aghayan, Tsatur P. Հոկտեմբերը և Հայ Ժողովրդի Ազատագրական Պայքարը (October and the Liberation Struggle of the Armenian People). Yerevan: Yerevan State University Press, 1982.
- Barton, James L. Story of Near East Relief, (1915-1930). New York: Macmillan, 1930.
- Egan, Eleanor Franklin. "This To Be Said For The Turk." Saturday Evening Post, 192, December 20, 1919.
- Gidney, James B. A Mandate for Armenia. Kent, Ohio: Kent State University Press, 1967.
- Hovannisian, Richard G. The Republic of Armenia. 4 volumes. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1971-1996.
- Hovannisian, Richard G. Armenia on the Road to Independence, 1918. Berkeley: University of California Press, 1967.
- Kazemzadeh, Firuz. The Struggle for Transcaucasia, 1917-1921. New York, Oxford: Philosophical Library, 1951.
- (أرمنية) Khatisian, Alexander. Հայաստանի Հանրապետութեան Ծագումն ու Զարգացումը (The Birth and Development of the Armenian Republic). Athens: Nor Or Publishing, 1930.
- (بالفرنسية) Ter Minassian, Anahide. La République d’Arménie: 1918-1920. Bruxelles: Editions Complexe, 1989.
- (أرمنية) Vratsian, Simon. Հայաստանի Հանրապետութիւն (The Republic of Armenia). Paris: H.H.D. Amerikayi Publishing, 1928.
قالب:Armenian nationalism 40°10′N 44°31′E / 40.167°N 44.517°E
- CS1 maint: others
- CS1 maint: location missing publisher
- CS1 الأرمنية-language sources (hy)
- CS1 errors: unsupported parameter
- CS1 errors: numeric name
- CS1 errors: bare URL
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- Pages using infobox country with unknown parameters
- Articles containing أرمنية-language text
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Articles with unsourced statements from August 2011
- Articles with unsourced statements from February 2011
- Articles with specifically marked weasel-worded phrases from February 2011
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- جمهورية أرمنيا الأولى
- قومية أرمنية
- التاريخ المعاصر لأرمنيا
- بلدان سابقة في آسيا
- بلدان سابقة في أوروپا
- كيانات سياسية سابقة في فترة بين الحربين
- جمهوريات سابقة
- دول ما بعد الامبراطورية الروسية
- 1918 في أرمنيا
- 1919 في أرمنيا
- 1920 في أرمنيا
- دول وأراضي تأسست في 1918
- دول وأراضي تأسست في 1920
- تأسيسات 1918 في أرمنيا
- انحلالات 1920 في أرمنيا
- انحلالات 1920 في آسيا
- تأسيسات 1918 في أوروپا
- انحلالات 1920 في أوروپا
- القرن 20 في أرمنيا
- بلدان وأراضي ناطقة بالأرمنية






