عنفة رياح
- هذه المقالة تناقش المولدات الكهربائية التي تعمل بطاقة الرياح. انظر طاحونة هوائية للماكينات المدارة بالرياح المستعملة في طحن الحبوب أو ضخ المياه.
عنفة الرياح أو توربين الرياح (wind turbine)، هو جهاز دوار يستخرج الطاقة من الريح. وإذا اُستعملت الطاقة الميكانيكية مباشرة بواسطة ماكينة، لأغراض مثل ضخ الماء أو قطع الأخشاب أو طحن الصخور، فإنها تسمى طاحونة هوائية windmill. أما إذا حـُوِّلت الطاقة الميكانيكية إلى كهرباء، فتسمى الماكينة حينئذ مولد من الرياح أو توربين الرياح أو مولد توربيني ريحي wind turbine generator (WTG)، أو وحدة طاقة رياح wind power unit (WPU)، محول طاقة الرياح wind energy converter (WEC) أو المولد الهوائي aerogenerator.
تُصنع توربينات الرياح]] بأحجام متنوعة، بمحاور أفقية أو رأسية. وتشير التقديرات إلى أن مئات الآلاف من التوربينات الكبيرة، في منشآت تُعرف باسم مزارع الرياح، تُولّد الآن أكثر من 650 جيجاواط من الطاقة، مع إضافة 60 جيجاواط سنوياً.[1] وهي مصدر متزايد الأهمية للطاقة المتجددة المتقطعة، وتُستخدم في العديد من الدول لخفض تكاليف الطاقة وتقليل الاعتماد على الوقود الأحفوري. وقد زعمت إحدى الدراسات أن،اعتبارا من 2009[تحديث] طاقة الرياح "لديها أدنى انبعاثات غازات الاحتباس الحراري النسبية، وأقل متطلبات استهلاك المياه، وأكثر التأثيرات الاجتماعية ملاءمة" مقارنة بالطاقة الكهروضوئية، والطاقة المائية، والطاقة الحرارية الأرضية، والفحم والغاز.[2]
تُستخدم توربينات الرياح الأصغر في تطبيقات مثل شحن البطاريات لتوفير الطاقة الإضافية للقوارب أو مقطورات السفر، ولتشغيل إشارات المرور. أما التوربينات الأكبر حجماً، فتساهم في توفير الطاقة المنزلية، بينما تبيع الطاقة غير المستخدمة إلى مزود الخدمة عبر الشبكة الكهربائية.
التاريخ

تُعد عجلة الرياح الخاصة بهيرون السكندري (10–70م) إحدى أولى الحالات المسجلة لتشغيل آلة بواسطة الرياح.[3] إلا أن أول محطات طاقة الرياح المعملية المعروفة قد بُنيت في سيستان، مقاطعة تقع في شرق بلاد فارس (إيران حالياً)، منذ القرن السابع. كانت هذه "طاوحة پانمون الهوائية" وكانت ذات محاور رأسية، وأعمدة دفع رأسية طويلة وشفرات مستطيلة.[4] كانت الطواحين الهوائية هذه مصنوعة من ستة إلى اثني عشر شراع مغطاة بحصير من القصب أو مادة قماشية، وكانت تستخدم لطحن الحبوب أو سحب المياه، وكانت تستخدم في صناعات الحبوب وقصب السكر.[5]
ظهرت طاقة الرياح لأول مرة في أوروپا خلال العصور الوسطى. وتعود أولى السجلات التاريخية لاستخدامها في إنگلترة إلى القرنين الحادي عشر والثاني عشر؛ وهناك تقارير عن الصليبيين الألمان الذين نقلوا مهاراتهم في صناعة طواحين الهواء إلى سوريا حوالي عام 1190.[6] بحلول القرن الرابع عشر، استُخدمت طواحين الهواء الهولندية لتصريف مياه مناطق دلتا الراين. وصف المخترع الكرواتي فاوستو ڤرانزيو توربينات الرياح المتطورة في كتابه الآلات الجديدة (1595). ووصف توربينات الرياح ذات المحور الرأسي ذات الشفرات المنحنية أو على شكل حرف V.

قام النمساوي جوسف فريدلاندر بتركيب أول توربين رياح لتوليد الكهرباء في معرض ڤيينا الدولي للكهرباء عام 1883. كان عبارة عن طاحونة هواء من طراز هالاداي لتشغيل دينامو. وُرّدت شركة محركات ومضخات الرياح الأمريكية في باتاڤيا، محرك هالاداي، الذي يبلغ قطره 6.6 متر، صنعها فريدلاندر. كانت طاحونة الهواء، التي تبلغ قدرتها 3.7 كيلوواط، تُشغّل دينامو على مستوى الأرض، يُغذّي سلسلة من البطاريات. شغّلت هذه البطاريات أدوات كهربائية ومصابيح متنوعة، بالإضافة إلى آلة درس. عُرضت طاحونة فريدلاندر الهوائية وملحقاتها بشكل بارز عند المدخل الشمالي لقاعة العرض الرئيسية ("روتوند") في متحف پراتر في ڤيينا.[7][8][9]
في يوليو 1887، قام الأكاديمي الاسكتلندي جيمس بلايث بتركيب آلة شحن البطاريات لإضاءة منزله لقضاء العطلات في ماريكيرك، اسكتلندا.[10] وبعد بضعة أشهر، تمكن المخترع الأمريكي تشارلز برش من بناء أول توربين رياح يعمل أوتوماتيكياً بعد استشارة أساتذة الجامعات المحلية وزملائه جاكوب گيبس وبرينسلي كولبير، ونجح في الحصول على مخططات تمت مراجعتها من قبل النظراء لإنتاج الكهرباء.[11] على الرغم من أن توربين بليث كان يعتبر غير اقتصادي في المملكة المتحدة،[11] إلا أن توليد الكهرباء بواسطة توربينات الرياح كان أكثر فعالية من حيث التكلفة في البلدان ذات الكثافة السكانية المتناثرة على نطاق واسع.[6]

في الدنمارك، بحلول عام 1900، كان هناك حوالي 2500 طاحونة هواء للأحمال الميكانيكية مثل المضخات والمطاحن، تُنتج طاقة ذروة مجمعة تُقدر بحوالي 30 ميجاواط. كانت أكبر الآلات مُثبتة على أبراج بارتفاع 24 متراً مزودة بدوارات رباعية الشفرات قطرها 23 متراً. بحلول عام 1908، كان هناك 72 مولداً كهربائياً يعمل بطاقة الرياح في الولايات المتحدة، تتراوح طاقتها بين 5 كيلوواط و25 كيلوواط. في فترة الحرب العالمية الأولى تقريباً، كان مُصنّعو طواحين الهواء الأمريكيون يُنتجون 100.000 طاحونة هواء زراعية سنويًا، معظمها لضخ المياه.[13]
بحلول الثلاثينيات، كان استخدام توربينات الرياح في المناطق الريفية في انخفاض حيث امتد نظام التوزيع إلى تلك المناطق.[14]
كان أحد رواد مولدات الرياح الحديثة ذات المحور الأفقي قيد الخدمة في يالطا بالاتحاد السوڤيتي، عام 1931. كان هذا المولد بقدرة 100 كيلوواط مثبتاً على برج بارتفاع 30 متراً، ومتصلاً بنظام التوزيع المحلي بجهد 6.3 كيلوڤولت. وأفادت التقارير أن معامل قدرته السنوية بلغ 32%، وهو ما لا يختلف كثيراً عن مولدات الرياح الحالية.[بحاجة لمصدر]
في خريف عام 1941، رُبط أول توربين رياح بقوة ميجاواط بشبكة كهرباء في ڤرمونت. استمر توربين رياح سميث-پوتنام لمدة خمس سنوات تقريباً قبل أن تنكسر إحدى شفراته.[15] لم يتم إصلاح الوحدة بسبب نقص المواد أثناء الحرب.[16]
بُني أول توربين رياح متصل بشبكة المرافق العامة للعمل في المملكة المتحدة بواسطة شركة جون براون وشركاه عام 1951 في جزر أوركني.[11][17]
ومع ذلك، في أوائل السبعينيات، دفعت الاحتجاجات المناهضة للطاقة النووية في الدنمارك الميكانيكيين الحرفيين إلى تطوير توربينات دقيقة بقدرة 22 كيلوواط على الرغم من التراجع في هذه الصناعة.[18] أدى تنظيم الملاك في جمعيات وتعاونيات إلى حشد تأييد الحكومة وشركات المرافق، ووفر حوافز لتوربينات أكبر حجماً طوال الثمانينيات وما بعدها. وفي أوائل التسعينيات، ضغط النشطاء المحليون في ألمانيا، ومصنّعو التوربينات الناشئون في إسپانيا، وكبار المستثمرين في الولايات المتحدة، من أجل سياسات تُحفّز الصناعة في تلك البلدان.[19][20][21]
زعم البعض أن توسيع استخدام طاقة الرياح سيؤدي إلى تزايد المنافسة الجيوسياسية على المواد الأساسية لتوربينات الرياح، مثل العناصر الأرضية النادرة النيوديميوم، پراسيوديميوم، والديسپروسيوم. إلا أن هذا الرأي رُفض رفضاً قاطعاً لفشله في توضيح أن معظم توربينات الرياح لا تستخدم المغناطيس الدائم، ولتقلل من أهمية الحوافز الاقتصادية لتوسيع إنتاج هذه المعادن.[22]
كثافة طاقة الرياح
كثافة طاقة الرياح هي مقياس كمي لطاقة الرياح المتوفرة في أي موقع. وهي متوسط الطاقة السنوية المتوفرة لكل متر مربع من المساحة الممسوحة لتوربين، وتُحسب لارتفاعات مختلفة فوق سطح الأرض. يتضمن حساب كثافة طاقة الرياح تأثير سرعة الرياح وكثافة الهواء.[23]
تُصنف توربينات الرياح حسب سرعة الرياح المصممة لها، من الفئة الأولى إلى الفئة الثالثة، حيث تشير الفئة A إلى الفئة C إلى شدة اضطراب الرياح.[24]
| الفئة | متوسط سرع الرياح (م/ث) | اضطراب الرياح |
|---|---|---|
| IA | 10 | 16% |
| IB | 10 | 14% |
| IC | 10 | 12% |
| IIA | 8.5 | 16% |
| IIB | 8.5 | 14% |
| IIC | 8.5 | 12% |
| IIIA | 7.5 | 16% |
| IIIB | 7.5 | 14% |
| IIIC | 7.5 | 12% |
الكفاءة

يشترط مبدأ حفظ الكتلة أن تكون كتلة الهواء الداخل والخارج من التوربين متساوية. وبالمثل، يشترط مبدأ حفظ الطاقة أن تكون الطاقة المعطاة للتوربين من الرياح الداخلة مساوية لمجموع طاقة الرياح الخارجة والطاقة المحولة إلى طاقة كهربائية. وبما أن الرياح الخارجة ستحتفظ ببعض الطاقة الحركية، فيجب أن تكون هناك نسبة قصوى من طاقة الدخل متاحة للتحويل إلى طاقة كهربائية.[25] وعليه، فإن قانون بتز يعطي أقصى قدر ممكن من استخراج طاقة الرياح بواسطة توربينات الرياح، والمعروف باسم معامل بتز، وهو 16⁄27 (59.3%) من معدل وصول الطاقة الحركية للهواء إلى التوربين.[26][27]
وبالتالي، فإن أقصى قدرة نظرية ناتجة لآلة رياح تساوي 16⁄27 ضعف معدل وصول الطاقة الحركية للهواء إلى مساحة القرص الفعالة للآلة. إذا كانت مساحة القرص الفعالة A، وسرعة الرياح v، فإن أقصى قدرة نظرية ناتجة P هي:
- ،
حيث ρ تمثل كثافة الهواء.
كفاءة الرياح إلى الدوار (بما في ذلك احتكاك شفرة الدوار وسحبها) من بين العوامل التي تؤثر على السعر النهائي لطاقة الرياح.[28] تؤدي أوجه القصور الأخرى، مثل خسائر علبة التروس، المولد والمحول، إلى تقليل الطاقة التي توفرها توربينات الرياح. لحماية المكونات من التآكل المفرط، تُثبّت الطاقة المستخرجة فوق سرعة التشغيل المُصنّفة مع ازدياد الطاقة النظرية بزيادة مكعب سرعة الرياح، مما يُقلل الكفاءة النظرية بشكل أكبر. عام 2001، ولّدت التوربينات التجارية المتصلة بالمرافق ما بين 75%-80% من حد بتز للطاقة المستخرجة من الرياح، عند سرعة التشغيل المُصنّفة.[29][30]
قد تنخفض الكفاءة قليلاً بمرور الوقت، ومن أهم أسباب ذلك الغبار وبقايا الحشرات على الشفرات، مما يُغير الشكل الديناميكي الهوائي ويُقلل بشكل كبير من نسبة الرفع إلى السحب للمُنساب الهوائي. أظهر تحليل 3.128 توربين رياح عمرها أكثر من 10 سنوات في الدنمارك أن نصف التوربينات لم تشهد أي انخفاض، بينما شهد النصف الآخر انخفاضاً في الإنتاج بنسبة 1.2% سنوياً.[31]
بشكل عام، تؤدي الظروف الجوية الأكثر استقراراً وثباتاً (وخاصةً سرعة الرياح) إلى زيادة في كفاءة توربينات الرياح بنسبة 15% في المتوسط مقارنةً بتوربينات الرياح في الظروف الجوية غير المستقرة، مما يسمح بزيادة سرعة الرياح بنسبة تصل إلى 7% في الظروف المستقرة. ويعود ذلك إلى سرعة استعادة تيار الرياح وتدفقه في ظروف الاستقرار الجوي العالي. ومع ذلك، فقد وُجد أن تيارات توربينات الرياح تستعيد طاقتها بشكل أسرع في الظروف الجوية غير المستقرة مقارنةً بالبيئة المستقرة.[32]
تختلف المواد في تأثيرها على كفاءة توربينات الرياح. في تجربة أجرتها جامعة إيجة، بُنيت ثلاثة توربينات رياح، كل منها بثلاث شفرات قطرها متر واحد، باستخدام مواد مختلفة: الزجاج والإيپوكسي الزجاجي/الكربوني، والپوليستر الزجاج/الكربوني والزجاجي. أظهرت النتائج عند اختبارها أن المواد ذات الكتل الكلية الأعلى كان لها عزم احتكاك أكبر، وبالتالي معامل قدرة أقل.[33]
سرعة الهواء هي العامل الرئيسي في كفاءة التوربين. ولهذا السبب، من المهم اختيار الموقع المناسب. ستكون سرعة الرياح عالية بالقرب من الشاطئ بسبب فرق درجة الحرارة بين اليابسة والمحيط. خيار آخر هو وضع التوربينات على قمم الجبال. كلما ارتفع توربين الرياح، زادت سرعة الرياح في المتوسط. كما يمكن لمصدات الرياح أن تزيد من سرعة الرياح بالقرب من التوربين.[34]
الأنواع
يمكن لتوربينات الرياح الدوران حول إما محور أفقي أو محور رأسي، إلا أن الأول هو الأكثر شيوعاً.[35] وقد تتضمن أيضاً شفرات أو تكون بدون شفرات.[36] تنتج التصميمات الرأسية ذات الحجم المنزلي طاقة أقل وهي أقل شيوعاً.[37]
التوربينات ذات المحور الأفقي

تُنتج توربينات الرياح الكبيرة ثلاثية الشفرات ذات المحور الأفقي (HAWT)، والتي تكون شفراتها عكس اتجاه الريح للبرج (أي شفراتها المواجهة للرياح القادمة)، الغالبية العظمى من طاقة الرياح في العالم اليوم.[38] تحتوي هذه التوربينات على عمود الدوار الرئيسي والمولد الكهربائي في أعلى البرج، ويجب توجيهها باتجاه الرياح. تُوجَّه التوربينات الصغيرة بواسطة دوارة رياح بسيطة، بينما تستخدم التوربينات الكبيرة عادةً مستشعر رياح متصل بنظام انحراف. تحتوي معظمها على علبة تروس، تُحوِّل الدوران البطيء للشفرات إلى دوران أسرع، مما يجعلها أكثر ملاءمة لتشغيل مولد كهربائي.[39] بعض التوربينات تستخدم نوعاً مختلفاً من المولدات يناسب سرعات دوران أبطأ. لا تحتاج هذه التوربينات إلى علبة سرعة، وتُسمى ذات دفع مباشر، أي أنها تربط الدوار بالمولد مباشرةً دون وجود علبة تروس بينهما. في حين أن مولدات مولد بمغناطيس دائم ذات دفع مباشر قد تكون أكثر تكلفة نظراً لاحتياجها إلى مواد أرضية نادرة، إلا أن هذه التوربينات توربينات الرياح بدون علبة سرعة تُفضل أحياناً على مولدات علبة سرعة لأنها "تزيل زيادة سرعة التروس، والتي تكون عرضة لتراكم كبير لعزم دوران التعب، ومشاكل في الموثوقية، وتكاليف صيانة".[40] هناك أيضاً آلية الدفع المباشر الزائفة، والتي تتمتع ببعض المزايا مقارنة بآلية الدفع المباشر ذات المغناطيس الدائم.[41]
معظم التوربينات ذات المحور الأفقي لها دوارات في اتجاه الريح من البرج الداعم.[42] صُممت آلات التوربينات الموجهة باتجاه الريح لأنها لا تحتاج إلى آلية إضافية للحفاظ على توازنها مع اتجاه الريح. في الرياح العاتية، يمكن تصميم شفرات التوربينات الموجهة باتجاه الريح بحيث تنحني أكثر من شفرات التوربينات الموجهة ضد الريح، مما يقلل من مساحة انحناءها، وبالتالي مقاومتها للرياح، مما يُخفف من المخاطر أثناء العواصف. على الرغم من هذه المزايا، تُفضل تصميمات التوربينات الموجهة عكس الريح، لأن التغير النبضي في الحمل الناتج عن الرياح عند مرور كل شفرة خلف برج الدعم قد يُسبب تلفاً للتوربين.[43]
عادةً ما تكون التوربينات المستخدمة في مزارع الرياح لإنتاج الطاقة الكهربائية تجاريًا ثلاثية الشفرات. تتميز هذه التوربينات بتموج عزم دوران منخفض، مما يُسهم في موثوقيتها العالية. عادةً ما تكون الشفرات بيضاء اللون لتسهيل رؤيتها نهاراً بواسطة الطائرات، ويتراوح طولها بين 20 و80 متراً. يزداد حجم وارتفاع التوربينات عاماً بعد عام. تُبنى توربينات الرياح البحرية حالياً بقدرة تصل إلى 8 ميجاوات، ويصل طول شفرتها إلى 80 متراً. عام 2018 كان يجري الإعداد لتصاميم بقدرة تتراوح بين 10 و12 ميجاوات،[44] ومن المقرر بناء نموذج أولي بقوة "+15 ميجاوات" بثلاث شفرات بطول 118 متراً اعتباراً من عام 2022.[needs update][45] يبلغ متوسط ارتفاع محور توربينات الرياح ذات المحور الأفقي 90 متراً.[46]
التوربينات ذات المحور الرأسي
تتميز وربينات الرياح ذات المحور الرأسي (VAWTs) بعمود دوار رئيسي مُرتب رأسياً. ومن مزايا هذا الترتيب أن التوربين لا يحتاج إلى توجيهه نحو الريح ليكون فعالاً،[47] ويمثل هذا ميزة في المواقع التي يكون فيها اتجاه الرياح متغيراً للغاية. كما يُمثل ميزة عند دمج التوربين في المبنى نظراً لصعوبة توجيهه. كما يُمكن وضع المولد وعلبة التروس بالقرب من الأرض، باستخدام محرك مباشر من مجموعة الدوار إلى علبة التروس الأرضية، مما يُحسّن إمكانية الوصول إليها لإجراء الصيانة. ومع ذلك، تُنتج هذه التصاميم طاقةً أقل بكثير في المتوسط بمرور الوقت، وهو عيب رئيسي.[37][48]
تتمتع تصميمات التوربينات الرأسية بكفاءة أقل بكثير من التصميمات الأفقية القياسية.[49] تشمل العيوب الرئيسية سرعة الدوران المنخفضة نسبياً مع عزم الدوران الأعلى وبالتالي التكلفة الأعلى لقطار الدفع، ومعامل القدرة المنخفض بطبيعته، والدوران 360 درجة للجناح داخل تدفق الرياح أثناء كل دورة وبالتالي التحميل الديناميكي للغاية على الشفرة، وعزم الدوران النابض الناتج عن بعض تصميمات الدوار على قطار الدفع، وصعوبة نمذجة تدفق الرياح بدقة وبالتالي تحديات تحليل الدوار وتصميمه قبل تصنيع النموذج الأولي.[50]
عند تركيب توربين على سطح المبنى، يُعيد المبنى توجيه الرياح نحوه، مما يُضاعف سرعة الرياح في التوربين. إذا كان ارتفاع برج التوربين المُثبت على السطح يُعادل حوالي 50% من ارتفاع المبنى، فهو قريب من المستوى الأمثل لأقصى طاقة رياح وأقل اضطراب رياح. في حين أن سرعات الرياح في البيئة المبنية تكون عادةً أقل بكثير منها في المواقع الريفية المكشوفة،[51][52] قد يكون الضجيج مصدر قلق وقد لا يقاوم الهيكل الحالي الضغط الإضافي بشكل كافي.
تشمل الأنواع الفرعية لتصميم المحور الرأسي ما يلي:
توربين رياح داريو
سُميت توربينات "إيج بيتر" أو توربينات داريو على اسم المخترع الفرنسي جورج داريو.[53] تتميز هذه المحركات بكفاءة جيدة، إلا أنها تُنتج تموجاً كبيراً في عزم الدوران وإجهاداً دورياً على البرج، مما يُضعف موثوقيتها. كما أنها تتطلب عادةً مصدر طاقة خارجياً، أو دوار ساڤونيوس إضافياً لبدء الدوران، نظراً لانخفاض عزم البدء. يُقلل استخدام ثلاث شفرات أو أكثر من تموج عزم الدوران، مما يُعزز صلابة الدوار. تُقاس الصلابة بقسمة مساحة الشفرات على مساحة الدوار.
گيروميل
توربينات گيروميل هي نوع فرعي من توربينات داريو، بشفرات مستقيمة، على عكس الشفرات المنحنية. يتميز توربين السيكلوتربين بدرجة تذبذب متغيرة لتقليل نبضات عزم الدوران، وهو ذاتي التشغيل.[54] من مزايا زاوية الميل المتغيرة عزم بدء تشغيل مرتفع؛ ومنحنى عزم دوران واسع ومسطح نسبياً؛ ومعامل أداء أعلى؛ وكفاءة تشغيل أعلى في الرياح المضطربة؛ ونسبة سرعة شفرة منخفضة، مما يُقلل من إجهادات انحناء الشفرة. يمكن استخدام شفرات مستقيمة أو على شكل حرف V أو منحنية.[55]
توربينات رياح ساڤونيوس
تعمل توربينات رياح ساڤونيوس بالسحب وهي مزودة بمغرفتين (أو أكثر)، تُستخدم في مقاييس سرعة الرياح، وفتحات فلتنر (التي تُرى عادةً على أسطح الحافلات والشاحنات)، وفي بعض توربينات الطاقة عالية الموثوقية ومنخفضة الكفاءة. وهي تعمل تلقائياً دائماً إذا كان لديها ثلاث مغارف على الأقل.[47] توربين ساڤونيوس الملتوي هو توربين ساڤونيوس مُعدّل، مزود بمغارف حلزونية طويلة لتوفير عزم دوران سلس. يُستخدم غالباً كتوربين رياح على الأسطح، وقد تم تكييفه حتى للسفن.[56]
توربينات الرياح المحمولة جواً
تتكون توربينات الرياح المحمولة جواً من أجنحة أو طائرة صغيرة مربوطة بالأرض.[57] وهي مفيدة للوصول إلى الرياح أسرع، وهو ما يمكن للتوربينات التقليدية العمل فوقه. توجد نماذج أولية قيد التشغيل في شرق أفريقيا.[58]
توربينات الرياح الطافية
توربينات الرياح الطافية هي توربينات رياح بحرية تدعمها منصة طافية.[59] بسبب طفوها، يُمكن تركيبها في المياه العميقة، مما يسمح بتواجد المزيد منها. هذا يسمح أيضاً بإبعادها عن اليابسة، وبالتالي تقليل اهتمام العامة بمظهرها.[60]
الأنواع غير التقليدية
توربينات الرياح ذات الدوران المعاكس.
- توربينات الرياح المعاصرة
التوربينات المستخدمة في مزارع الرياح للإنتاج التجاري للطاقة الكهربائية عادة ما تكون ثلاثية الريش (العنفات) وتوجه في اتجاه الريح بمحركات يديرها حاسوب. ويكون لهم سرعة طرفية عالية تتجاوز 320 كم/س، وكفاءة عالية، وتموج لي منخفض، وكل ذلك يؤدي إلى وثوقية عالية. عادةً ما تكون الشفرات رمادية فاتحة اللون لتتناغم مع لون الغيوم، ويتراوح طولها بين 20 و40 متراً أو أكثر. يتراوح ارتفاع الأبراج الفولاذية الأنبوبية بين 60 و90 متراً. تدور الشفرات بسرعة تتراوح بين 10 و22 دورة في الدقيقة. عند 22 دورة في الدقيقة، تتجاوز سرعة رأس الشفرات 91.50 م/ث.[61][62]
التصميم والبناء
يعد تصميم توربينات الرياح بمثابة توازن دقيق بين التكلفة وناتج الطاقة وعمر الإجهاد.
المكونات
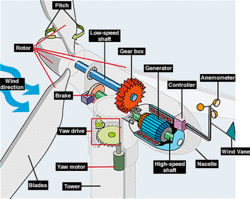
تُحوّل توربينات الرياح طاقة الرياح إلى طاقة كهربائية لتوزيعها. يمكن تقسيم التوربينات ذات المحور الأفقي التقليدية إلى ثلاثة مكونات:
- الدوار، الذي يمثل حوالي 20% من تكلفة توربينات الرياح، يشمل الشفرات لتحويل طاقة الرياح إلى طاقة دورانية منخفضة السرعة.[63]
- المولد الذي يمثل ما يقرب من 34% من تكلفة توربينات الرياح يشمل مولد كهربائي،[64][65] إلكترونيات التحكم، وعلى الأرجح علبة التروس (على سبيل المثال، علبة التروس الكوكبية)،[66] محرك ذو سرعة قابلة للتعديل، أو ناقل حركة ذو تعشيق مستمر[67] مكون لتحويل الدوران الوارد منخفض السرعة إلى دوران عالي السرعة مناسب لتوليد الكهرباء.
- الهيكل المحيط، والذي يمثل حوالي 15% من تكلفة توربينات الرياح، يشمل البرج وآلية دوران الدوار.[63]

توربين رياح بقدرة 1.5 ميجاواط، وهو نوع شائع الاستخدام في الولايات المتحدة، يصل ارتفاع برجه إلى 80 متر. يبلغ قطر مجموعة الدوار (الشفرات والمحور) حوالي 80 متر.[68] يبلغ طول هيكل توربين الرياح الذي يحتوي على المولد 15.24 متراً ويزن حوالي 300 طن.[69]
مراقبة التوربينات وتشخيصها
نظراً لمشاكل نقل البيانات، عادةً ما تُجرى مراقبة سلامة توربينات الرياح باستخدام عدة مقاييس تسارع ومقاييس إجهاد مُثبتة على هيكل التوربين لمراقبة علبة التروس والمعدات. حاليًا، تُستخدم تقنيات الارتباط الرقمي للصور الإلكترونية والمسح التصويري لقياس ديناميكيات شفرات توربينات الرياح. عادةً ما تقيس هذه الطرق الإزاحة والإجهاد لتحديد مواقع العيوب. تُقاس الخصائص الديناميكية لتوربينات الرياح غير الدوارة باستخدام تقنيات الارتباط الرقمي للصور والمسح التصويري.[70] كما أُستخدم أيضاً تتبع النقاط ثلاثي الأبعاد لقياس ديناميكيات دوران توربينات الرياح.[71]
التكنولوجيا
بصفة عامة تزداد الكفاءة بازدياد طول شفرات التوربينات. يجب أن تكون الشفرات صلبة، قوية، متينة، خفيفة الوزن، ومقاومة للإجهاد.[72] وتشمل المواد التي تتمتع بهذه الخصائص مواد مركبة مثل الپوليستر والإيپوكسي، في حين تم استخدام الألياف الزجاجية وألياف الكربون للتعزيز.[73] قد يتضمن بناء توربينات الرياح التجميع اليدوي أو حقن التوربينات. يُقلل تركيب شفرات أكبر في التوربينات الحالية من مهمة إعادة التصميم ومخاطرها.[74]
اعتباراً من عام 2021، كان أطول شفرة يبلغ طولها 115.5 متراً، وتنتج 15 ميجاوات.[75]
تدوم الشفرات عادة حوالي 20 عاماً، وهو العمر الافتراضي النموذجي لتوربينات الرياح.[76]
مواد الشفرات
عادة ما تُوصف المواد المستخدمة في شفرات توربينات الرياح كما يلي:
ألياف الزجاج والكربون
تُحدَّد صلابة المواد المركبة بصلابة الألياف وحجمها. عادةً ما تُستخدم ألياف الزجاج E كتدعيم رئيسي في المواد المركبة. عادةً، تحتوي مركبات الزجاج/الإيپوكسي المستخدمة في شفرات توربينات الرياح على ما يصل إلى 75% من الزجاج وزناً، مما يزيد من الصلابة ومقاومة الشد والضغط. من المواد المركبة الواعدة ألياف الزجاج ذات التركيبات المُعدّلة مثل الزجاج S والزجاج R، إلخ. ومن الألياف الزجاجية الأخرى التي طورتها شركة أوينز كورننگ: إكرگلاس، أڤانتكس، ووندستراند.[77]
تتميز ألياف الكربون بقوة شد أعلى وصلابة أعلى وكثافة أقل من ألياف الزجاج. يُعد غطاء الصاري، وهو عنصر هيكلي في الشفرة يتعرض لشد عالي، مرشحاً مثالياً لهذه الخصائص.[73] يمكن أن يصل وزن شفرة الألياف الزجاجية التي يبلغ طولها 100 متر إلى 50 طن متري، بينما يوفر استخدام ألياف الكربون في الصاري ما بين 20%-30% من الوزن، أي حوالي 15 طن متري.[78]
التعزيزات الهجينة
بدلاً من صنع تعزيزات شفرات توربينات الرياح من الزجاج الخالص أو الكربون الخالص، تُقايض التصاميم الهجينة الوزن بالتكلفة. على سبيل المثال، بالنسبة لشفرة بطول 8 أمتار، يُوفر الاستبدال الكامل بألياف الكربون 80% من الوزن، لكن التكلفة ستزيد بنسبة 150%، بينما يُوفر الاستبدال بنسبة 30%، 50% من الوزن، ويزيد التكلفة بنسبة 90%. تشمل مواد التعزيز الهجينة الزجاج الإلكتروني/الكربون، والزجاج الإلكتروني/الأراميد. أطول شفرة حاليًا من إنتاج شركة إل إم لطاقة الرياح مصنوعة من مركبات هجينة من الكربون/الزجاج. هناك حاجة إلى مزيد من البحث حول التركيب الأمثل للمواد.[79]
الپوليمرات والمركبات النانوية
إن إضافة كميات صغيرة (0.5% وزناً) من التعزيزات النانوية (أنابيب الكربون النانوية أو الطين النانوي) إلى مصفوفة الپوليمر للمركبات، أو تحديد حجم الألياف، أو الطبقات البينية، يمكن أن يُحسّن مقاومة الإجهاد، وقوة القص أو الضغط، ومتانة الكسر للمركبات بنسبة تتراوح بين 30% و80%. كما أظهرت الأبحاث أن إضافة كميات صغيرة من أنابيب الكربون النانوية يمكن أن يزيد من عمرها الافتراضي بنسبة تصل إلى 1500%.[80]
التكلفة
اعتباراً من عام 2019، بلغت التكلفة الرأسمالية لتوربينات الرياح حوالي مليون دولار أمريكي لكل ميجاواط من السعة الاسمية، على الرغم من أن هذا الرقم يختلف باختلاف الموقع؛ على سبيل المثال، تراوحت هذه الأرقام من نصف مليون في أمريكا الجنوبية إلى 1.7 مليون دولار أمريكي في آسيا.[81]
بالنسبة لشفرات توربينات الرياح، على الرغم من أن تكلفة المواد أعلى بكثير في شفرات الألياف الزجاجية/الكربون الهجينة مقارنةً بالشفرات المصنوعة بالكامل من الألياف الزجاجية، إلا أن تكاليف العمالة أقل. يتيح استخدام ألياف الكربون تصميمات أبسط باستخدام مواد خام أقل. عملية التصنيع الرئيسية في تصنيع الشفرات هي وضع طبقات من الطبقات. تسمح الشفرات الأرق بتقليل عدد الطبقات، وبالتالي تقليل تكلفة العمالة، وفي بعض الحالات، تُعادل تكلفة العمالة في شفرات الألياف الزجاجية.[82]
تركيب الأنظمة البحرية يكون أعلى بكثير.[83]
مواد المكونات الأخرى
تُصنع معظم أجزاء توربينات الرياح، باستثناء شفرات الدوار (بما في ذلك محور الدوار، وعلبة التروس، والهيكل، والبرج)، من الصلب. وقد بدأت التوربينات الأصغر حجماً (وكذلك توربينات إنركون ذات القدرة الكبيرة جداً) باستخدام سبائك الألومنيوم في هذه المكونات، مما يجعلها أخف وزناً وأكثر كفاءة. وقد يتزايد هذا التوجه إذا أمكن تحسين خصائص التعب والصلابة. ازداد استخدام الخرسانة مسبقة الإجهاد في بناء البرج، إلا أنها لا تزال تتطلب كميات كبيرة من حديد التسليح لتلبية متطلبات قوة التوربين. إضافةً إلى ذلك، تُستبدل علب التروس الصاعدة بشكل متزايد بمولدات متغيرة السرعة، مما يتطلب مواد مغناطيسية.[72]
تستخدم التوربينات الحديثة بضعة أطنان من النحاس للمولدات والكابلات وما إلى ذلك.[84] اعتباراً من عام 2018، كان الإنتاج العالمي لتوربينات الرياح يستخدم 450.000 طن متري من النحاس سنوياً.[85]
توريد المواد
وجدت دراسة أجريت عام 2015 لاتجاهات استهلاك المواد ومتطلبات طاقة الرياح في أوروپا أن التوربينات الأكبر حجماً تستهلك كميات أكبر من الفلزات الثمينة، لكن مدخلاتها من المواد أقل لكل كيلوواط مُولَّد. قورن استهلاك المواد ومخزونها في ذلك الوقت بمواد الإدخال لمختلف أحجام الأنظمة البرية. في جميع دول الاتحاد الأوروپي، تضاعفت تقديرات عام 2020 عن القيم المستهلكة عام 2009. ستحتاج هذه الدول إلى توسيع مواردها لتلبية الطلب المقدر لعام 2020. على سبيل المثال، يمتلك الاتحاد الأوروپي 3% من المعروض العالمي من الفلورسپار، وسيحتاج إلى 14% بحلول عام 2020. على الصعيد العالمي، الدول المصدرة الرئيسية هي جنوب أفريقيا والمكسيك والصين. وهذا مشابه للمواد الأخرى المهمة والقيمة اللازمة لأنظمة الطاقة مثل المغنيسيوم والفضة والإنديوم. مستويات إعادة تدوير هذه المواد منخفضة للغاية، والتركيز على ذلك قد يُخفف من العرض. ولأن معظم هذه المواد القيّمة تُستخدم أيضاً في تقنيات ناشئة أخرى، مثل الصمامات الثنائية الباعثة للضوء (LED) والخلايا الكهروضوئية (PVs) وشاشات البلور السائل (LCD)، فمن المتوقع أن يتزايد الطلب عليها.[86]
قدرت دراسة أجرتها هيئة المسح الجيولوجي الأمريكية عام 2011 الموارد اللازمة للوفاء بالتزام الولايات المتحدة بتوفير 20% من كهربائها من طاقة الرياح بحلول عام 2030. ولم تأخذ الدراسة في الاعتبار متطلبات التوربينات الصغيرة أو التوربينات البحرية نظراً لعدم شيوعها في عام 2008 عند إجراء الدراسة. وستزداد المواد الشائعة، مثل الحديد الزهر والصلب والخرسانة، بنسبة 2%-3% مقارنةً بعام 2008. وستُطلب كمية تتراوح بين 110.000 و115.000 طن متري من الألياف الزجاجية سنوياً، أي بزيادة قدرها 14%. لن يزداد استخدام الفلزات الأرضية النادرة كثيراً مقارنةً بالإمدادات المتاحة، ومع ذلك، يجب أخذ الفلزات الأرضية النادرة المستخدمة أيضاً في تقنيات أخرى، مثل البطاريات، والتي يزداد الطلب العالمي عليها، في الاعتبار. ستبلغ مساحة الأرض المطلوبة 50.000 كم² على اليابسة و11.000 كم² في عرض البحر. ولن يُمثل هذا مشكلة في الولايات المتحدة نظراً لمساحتها الشاسعة وإمكانية استخدام نفس الأرض للزراعة. أما التحدي الأكبر فيتمثل في تنوع هذه الفلزات ونقلها إلى المناطق ذات الطلب المرتفع.[87]
تحتوي المغناطيسات الدائمة لمولدات توربينات الرياح على فلزات أرضية نادرة مثل النيوديميوم، والپراسيوديميوم، والتربيوم، والديسپروسيوم. تتطلب الأنظمة التي تستخدم توربينات الدفع المباشر المغناطيسي كميات أكبر من الفلزات الأرضية النادرة. لذلك، فإن زيادة تصنيع توربينات الرياح ستزيد الطلب على هذه الموارد. بحلول عام 2035، من المتوقع أن يزداد الطلب على النيوديميوم بمقدار يتراوح بين 4000 و18000 طن، وعلى الديسپروسيوم بمقدار يتراوح بين 200 و1200 طن. تمثل هذه القيم ربع إلى نصف الإنتاج الحالي. ومع ذلك، فإن هذه التقديرات غير مؤكدة للغاية نظرًا للتطور السريع للتكنولوجيا.[88]
إن الاعتماد على الفلزات الأرضية النادرة في المكونات قد أدى إلى مخاطر ارتفاع التكاليف وتقلب الأسعار حيث كانت الصين هي المنتج الرئيسي للفلزات الأرضية النادرة (96% عام 2009) وكانت تعمل على خفض حصص التصدير الخاصة بها.[87] ومع ذلك، في السنوات الأخيرة، قام منتجون آخرون بزيادة الإنتاج، وزادت الصين حصص التصدير، مما أدى إلى زيادة العرض، وانخفاض التكلفة، وزيادة جدوى الاستخدام واسع النطاق للمولدات ذات السرعة المتغيرة.[89]
الألياف الزجاجية هي المادة الأكثر شيوعاً في التعزيزات. وقد ازداد الطلب عليها نتيجةً للنمو في قطاعات البناء والنقل وتوربينات الرياح. ومن المتوقع أن يصل حجم سوقها العالمي إلى 17.4 بليون دولار أمريكي بحلول عام 2024، مقارنةً بنحو 8.5 بليون دولار أمريكي عام 2014. عام 2014، أنتجت منطقة آسيا-الهادي أكثر من 45% من السوق؛ والآن تُعدّ الصين أكبر مُنتج. ويتلقى هذا القطاع دعمًا من الحكومة الصينية، مما يسمح له بالتصدير بأسعار أقل إلى الولايات المتحدة وأوروپا. ومع ذلك، أدت حروب الأسعار إلى اتخاذ إجراءات لمكافحة الإغراق، مثل فرض رسوم جمركية على الألياف الزجاجية الصينية.[90]
توربينات الرياح في العرض العام
استغلت بعض المحليات الطبيعة الجاذبة للانتباه لتوربينات الرياح من خلال عرضها للعامة، إما من خلال مراكز للزوار حول قواعدها، أو من خلال مناطق مشاهدة أبعد.[91] تتميز توربينات الرياح عموماً بتصميمها الأفقي التقليدي وثلاثي الشفرات، وتولد الطاقة لتغذية الشبكات الكهربائية، ولكنها تلعب أيضاً أدواراً غير تقليدية في عرض التكنولوجيا والعلاقات العامة والتعليم.[92]
يُعد مركز التجارة العالمي في البحرين مثالاً على توربينات الرياح المعروضة بشكل بارز للجمهور. وهو أول ناطحة سحاب تُدمج توربينات الرياح في تصميمها.
توربينات الرياح الصغيرة

يمكن استخدام توربينات الرياح الصغيرة في تطبيقات متنوعة، بما في ذلك المنازل المتصلة بالشبكة أو غير المتصلة بها، وأبراج الاتصالات، والمنصات البحرية، والمدارس والعيادات الريفية، والمراقبة عن بُعد، وغيرها من الأغراض التي تتطلب طاقة في حال عدم وجود شبكة كهربائية أو عدم استقرارها. قد تصل قدرة توربينات الرياح الصغيرة إلى خمسين واط، وهي مناسبة للقوارب أو المقطورات المتنقلة. ويتزايد استخدام الوحدات الهجينة التي تعمل بالطاقة الشمسية وطاقة الرياح في إشارات المرور، وخاصة في المناطق الريفية، لأنها تُغني عن الحاجة إلى مد كابلات طويلة من أقرب نقطة توصيل رئيسية.[93] يعرّف المعمل الوطني للطاقة المتجددة التابع لوزارة الطاقة الأمريكية توربينات الرياح الصغيرة على أنها تلك التي تقل قدرتها عن 100 كيلووات أو تساويها.[94] غالباً ما تحتوي الوحدات الصغيرة على مولدات ذات دفع مباشر، ومخرج تيار مستمر، وشفرات مرنة هوائياً، ومحامل مدى الحياة، وتستخدم ريشة للإشارة إلى الرياح.[95]
تباعد توربينات الرياح
في معظم مزارع توربينات الرياح الأفقية، يُنصح عادةً بمسافة تتراوح بين 6 و10 أضعاف قطر الدوار بين كل توربين وآخر. ومع ذلك، في مزارع الرياح الكبيرة، يُفترض أن تكون المسافات التي تبلغ حوالي 15 قطراً للدوار أكثر توفيراً، مع مراعاة تكاليف توربينات الرياح والأرض النموذجية. وقد توصلت الأبحاث إلى هذا الاستنتاج[96] التي عقدها شارل منڤو من جامعة جونز هوپكنز[97] ويوهان مايرز من جامعة لوڤن في بلجيكا، استناداً إلى المحاكاة الحاسوبية[98] التي تأخذ في الاعتبار التفاعلات التفصيلية بين توربينات الرياح (wakes) وكذلك مع طبقة الحدود الجوية المضطربة بأكملها.[99]
التشغيل
الصيانة
تحتاج توربينات الرياح إلى صيانة دورية للحفاظ على وثوقيتها وتوافرها. في أفضل الأحوال، تكون التوربينات متاحة لتوليد الطاقة بنسبة 98% من الوقت.[100][101] لقد وجد أن تراكم الجليد على شفرات التوربينات يقلل بشكل كبير من كفاءة توربينات الرياح، وهو تحدٍ شائع في المناخات الباردة حيث تحدث أحداث الجليد في السحب والأمطار المتجمدة.[102] تُجرى عملية إزالة الجليد بشكل أساسي عن طريق التسخين الداخلي أو في بعض الحالات، عن طريق رش المروحيات لمياه دافئة نظيفة على الشفرات.[103]
عادةً ما تحتوي التوربينات الحديثة على رافعة صغيرة مدمجة رافعة لرفع أدوات الصيانة والأجزاء الصغيرة. ومع ذلك، نادراً ما تُستبدل الأجزاء الكبيرة والثقيلة، مثل المولدات وعلب التروس والشفرات وما إلى ذلك، وفي هذه الحالات، يلزم استخدام رافعة خارجية ثقيلة. إذا كان طريق الوصول إلى التوربين صعبًا، فيمكن رفع رافعة الحاويات بواسطة الرافعة الداخلية لتوفير رفع أثقل.[104]
التجديد
قد يكون تركيب توربينات رياح جديدة أمراً مثيراً للجدل. البديل تجديد التوربينات، حيث تُستبدل توربينات الرياح الحالية بأخرى أكبر وأقوى، وأحياناً بأعداد أقل، مع الحفاظ على قدرتها أو زيادتها.[105]
الهدم وإعادة التدوير
بعض توربينات الرياح التي خرجت عن الاستخدام يُعاد تدويرها أو تجديدها.[106][107] 85% من مواد التوربينات يمكن إعادة استخدامها أو إعادة تدويرها بسهولة، لكن الشفرات المصنوعة من مواد مركبة يصعب معالجتها.[108]
يختلف الاهتمام بإعادة تدوير الشفرات باختلاف الأسواق، ويعتمد على تشريعات النفايات والاقتصادات المحلية. ويتعلق أحد تحديات إعادة تدوير الشفرات المصنوعة من مواد مركبة، المصنوعة من الألياف الزجاجية مع ألياف الكربون في راتنج الإيپوكسي، والتي لا يمكن إعادة تشكيلها لتكوين مركبات جديدة.[109]
نفايات مزارع الرياح أقل سمية من النفايات الأخرى. لا تمثل شفرات توربينات الرياح سوى جزء ضئيل من إجمالي النفايات في الولايات المتحدة، وفقاً للجمعية الأمريكية لطاقة الرياح.[110]
تعمل العديد من شركات المرافق والشركات الناشئة والباحثين على تطوير أساليب لإعادة استخدام أو إعادة تدوير الشفرات.[108] لقد طورت الشركة المصنعة ڤستاس تقنية يمكنها فصل الألياف عن الراتنج، مما يسمح بإعادة الاستخدام.[111] في ألمانيا، يعاد تدوير شفرات توربينات الرياح تجارياً كجزء من مزيج الوقود البديل لمصانع الأسمنت.[108] في المملكة المتحدة، سيعمل مشروع على تجربة تقطيع الشفرات إلى شرائح لاستخدامها كقضبان حديدية في الخرسانة، بهدف تقليل الانبعاثات في بناء خط السكك الحديدية هاي سپيد 2.[112] يعاد تدوير شفرات توربينات الرياح المستعملة من خلال دمجها كجزء من الهياكل الداعمة داخل جسور المشاة في پولندا[113] وأيرلندا.[114]
مقارنة بمصادر الطاقة الأخرى
المزايا
تعتبر توربينات الرياح واحدة من أقل مصادر الطاقة المتجددة تكلفة إلى جانب الألواح الشمسية.[115] مع استمرار تطور التكنولوجيا اللازمة لتوربينات الرياح، انخفضت أسعارها أيضاً. إضافةً إلى ذلك، لا توجد حالياً سوق تنافسية لطاقة الرياح (مع احتمال وجودها في المستقبل)، لأن الرياح مورد طبيعي متاح بحرية، ومعظمه غير مستغل.[116] التكلفة الرئيسية لتوربينات الرياح الصغيرة تتمثل في عملية الشراء والتركيب، والتي تتراوح في المتوسط بين 48.000 و65.000 دولار أمريكي لكل عملية تركيب. عادةً، يتجاوز إجمالي الطاقة المحصودة تكلفة التوربينات.[117]
توفر توربينات الرياح مصدراً للطاقة النظيفة،[118] وتستخدم القليل من المياه،[2] ولا ينبعث منها غازات دفيئة ولا نفايات أثناء التشغيل. يمكن التخلص من أكثر من 1400 طن متري من ثاني أكسيد الكربون سنوياً باستخدام توربين بقدرة ميجاواط واحد بدلاً من ميجاواط واحد من الطاقة من الوقود الأحفوري.[119]
العيوب
يمكن أن تكون توربينات الرياح كبيرة جداً، حيث يصل ارتفاعها إلى أكثر من 260 متر مع شفرات يبلغ طولها 110 متر،[120] وكثيرا ما اشتكى الناس من تأثيرها البصري.

يشمل التأثير البيئي لطاقة الرياح التأثير على الحياة البرية، لكن يمكن التخفيف منه إذا طُبقت الاستراتيجيات المناسبة.[122] لقد قُتلت آلاف الطيور، بما في ذلك الأنواع النادرة، بسبب شفرات توربينات الرياح،[123] مع أن توربينات الرياح تُسهم بشكل ضئيل نسبياً في نفوق الطيور الناتج عن الأنشطة البشرية (الطيور التي يقتلها البشر). تُسبب مزارع الرياح ومحطات الطاقة النووية ما بين 0.3 و0.4 حالة نفوق للطيور لكل جيجاواط/ساعة من الكهرباء، بينما تُسبب محطات الطاقة التي تعمل بالوقود الأحفوري حوالي 5.2 حالة نفوق لكل جيجاواط/ساعة. وبالمقارنة، تُساهم المولدات التقليدية التي تعمل بالفحم بشكل أكبر بكثير في نفوق الطيور.[124] وجدت دراسة أجريت على أعداد الطيور المسجلة في الولايات المتحدة من عام 2000 حتى 2020 أن وجود توربينات الرياح لم يكن لها تأثير كبير على أعداد الطيور.[125]
الطاقة المولدة بواسطة توربينات الرياح متغيرة، وليست مصدراً "قابلاً للإرسال"؛ إذ يعتمد توفرها على هبوب الرياح، وليس على الحاجة إلى الكهرباء. يمكن وضع التوربينات على النتوءات الجبلية أو الجروف لزيادة وصول الرياح إليها، ولكن هذا يحدّ أيضاً من المواقع التي يُمكن وضعها فيها.[116] بهذه الطريقة، لا تُعدّ طاقة الرياح مصدراً موثوقاً للطاقة. ومع ذلك، يُمكن أن تُشكّل جزءاً من مزيج الطاقة، الذي يشمل أيضاً الطاقة من مصادر أخرى. كما يجري تطوير تقنيات لتخزين الطاقة الفائضة، والتي يُمكنها تعويض أي نقص في الإمدادات.[126]
تحتوي توربينات الرياح على أضواء وامضة تحذر الطائرات لتجنب الاصطدامات.[127] اشتكى السكان الذين يعيشون بالقرب من مزارع الرياح، وخاصة أولئك الذين يعيشون في المناطق الريفية، من أن الأضواء الوامضة تشكل شكلاً مزعجاً من أشكال التلوث الضوئي.[127] يتضمن نهج تخفيف الضوء استخدام أنظمة إضاءة اكتشاف الطائرات (ADLSs)، والتي يتم من خلالها تشغيل الأضواء فقط عندما يكتشف رادار ADLS وجود طائرات ضمن عتبات الارتفاع والمسافة.[127]
أرقام قياسية
انظر أيضاً قائمة أقوى توربينات الرياح
| الرقم القياسي | الموديل/الاسم | الموقع | الشركة المصنعة |
|---|---|---|---|
| أكبر وأقوى توربين رياح | MYSE18.X-20MW | هاينان، الصين | مينگيانگ لطاقة الرياح |
| أكبر توربين رياح بمحور عمودي | أول[128] | كاپ-شا، كويبك، كندا | مركز الأبحاث الوطني، هيدرو-كيوبك |
| أكبر توربين رياح بشفرة واحدة | مونوپتروس إم50[129] | منتزه جاد للرياح | إمبيبي مسرشميت |
| أكبر توربين رياح بشفرتين | SCD6.5[130] | مزرعة لونگيوان للرياح | مينگيانگ لطاقة الرياح |
| أكبر عدد من الدوارات | فورن-إن-ون[131] | Maasvlakte، هولندا | لاجري |
| الأعلى | 2.5[132] | مثلجة پاستوروري | وندإيد |
| أكبر توربين رياح بحري | MySE18.X-20MW | هاينان، الصين | مزرعة لونگيوان للرياح |
| الأطول | توربين رياح شيپكاو | شيپكاو، ألمانيا | فنسيز، GICON |
تصميم وبناء التوربين
صُممت توربينات الرياح لاستغلال طاقة الرياح الموجودة في موقع ما. تُستخدم النمذجة الديناميكية الهوائية لتحديد الارتفاع الأمثل للبرج وأنظمة التحكم وعدد وشكل الشفرات.
توربينات الريح غير التقليدية
توربينات الريح الصغيرة

قد تصل قدرة توربينات الرياح الصغيرة إلى خمسين واط، وهي مناسبة للاستخدام في القوارب أو قاطرات السفر. غالباً ما تحتوي الوحدات الصغيرة على مولدات دفع مباشر، ومخرج تيار مستمر، وشفرات مرنة هوائية، ومحامل متينة، وتستخدم ريشة لتوجيهها نحو الرياح. أما التوربينات الأكبر حجماً والأكثر تكلفة، فعادةً ما تحتوي على مجموعات نقل حركة مُسننة، ومخرج تيار متردد، ولوحات، وتُوجَّه بنشاط نحو الرياح. ويجري حالياً البحث في استخدام مولدات دفع مباشر وشفرات مرنة هوائية لتوربينات الرياح الكبيرة.
توربينات الأرقام القياسية
الأكبر
أكبر توربين رياح في العالم حالياً هو نموذج أولي تم تركيبه بواسطة شركة گامـِسا في خولين، سرقسطة، إسپانيا عام 2009. يحمل التوربين اسم G10X ويبلغ قطر دواره 128 متراً، وتصل قدرته إلى 4.5 ميجاوات.
في السابق، كانت شركتان ألمانيتان، إنكرون وآرإي پاور هما صاحبتا الرقم القياسي. تقبلغ قدرة توربين الرياح إنكرون إي-126 ما يصل إلى 7.58 ميجاوات،[133] بينما يبلغ إرتفاعه الإجمالي 198 متراً، ويبلغ قطره 126 متراً، وهو أكبر توربين رياح في العالم منذ طرحه عام 2007.[134] تبلغ قدرة توربين الرياح 5إم من إنتاج شركة آرإي پاور 5 ميجاوات، ويبلغ ارتفاع الإجمالي 183 متراً، ويصل قطره إلى 126 متراً، وكان أكبر توربين رياح في العالم عند طرحه عام 2005.[135] عام 2010، أعلنت شركة إسواي النرويجية عن نموذج أولي لتوربين رياح بقوة 10 ميجاوات وارتفاع 162.5 متراً ودوار قطره 145 متراً.[136][137][138]
في يوليو 2019 كشفت جنرال إلكتريك عن أول توربين رياح بقدرة قصوى 12 ميجاوات/ساعة. سيحتاج التوربين لشفرات مراوح طولها 120 متر.[139]
ستقوم الشركة المصنعة بشحن الباسنة من موقع الإنتاج الخاص بها في سان نازير، فرنسا إلى موقع اختبار النموذج الأولي في ميناء روتردام بهولندا. سيتم تجميعها مع شفرة بطول 107 متر، تم تصنيعها بواسطة شركة إل إم لطاقة الرياح التابعة لجنرال إلكتريك. ستقوم الشركة المصنعة بتجميع النموذج الأولي على الأرض لتبسيط الوصول للاختبار، حسبما ذكرت جنرال إلكتريك في يوليو 2019. سيجرى إرسال باسنة أخرى قيد التجميع في سان نازير إلى مركز اختبار أور كاتاپلت في بليث، شمال-شرق إنگلترة. بدوار يبلغ ارتفاعه 220 متر ولوحة يصل ارتفاعها إلى 260 متر وقدرة تبلغ 12 ميجاوات، سيكون أقوى توربين رياح بحري في العالم. تتوقع الشركة المصنع أن يبدأ بيع التوربين عام 2021، وأن يبدأ تشغيلها في 2022.
الأطول
أطول توربين رياح هو توربين رياح فوهرلاندر لاسو. يبلغ ارتفاع محوره 160 متراً فوق سطح الأرض، ويمكن أن يصل ارتفاع رؤوس دواراته إلى 205 متر. وهو توربين الرياح الوحيد الذي يزيد ارتفاعه عن 200 متر في العالم حتى الآن.[140]
أكير محور رأسي
تحتوي مزرعة رياح لو نوردي في كاپ-شا، كويبك على توربين رياح ذو محور رأسي (VAWT) يسمى أول (Éole)، وهو الأكبر في العالم بارتفاع 110 متر.[141]
الأكثر فعالية
ماتيلدا هو توربين رياح يقع في گوتلند ، السويد. أنتج التوربين ما مجموعه 61.4 ج.و./س خلال 15 عاماً من تشغيل. وهذا يُمثل طاقة متجددة أكبر مما أنتجته أي توربين رياح آخر حتى ذلك التاريخ. هُدم التوربين ماتيلدا في 6 يونيو 2008.[142]
معرض صور توربينات الأرقام القياسية
REpower 5MW in Thornton Bank
Éole, the largest vertical axis wind turbine, in Cap-Chat, Quebec
Highest-situated wind turbine, at the Veladero mine in San Juan Province, الأرجنتين
مرئيات
| الصين تتصدر أكبر زيادة في العالم في قدرة طاقة الرياح. |
انظر أيضاً
الهامش
- ^ "World wind capacity at 650,8 GW, Corona crisis will slow down markets in 2020, renewables to be core of economic stimulus programmes" (Press release). WWEA. 16 April 2020. Retrieved 1 September 2021.
Wind power capacity worldwide reaches 650,8 GW, 59,7 GW added in 2019
{{cite press release}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ أ ب Evans, Annette; Strezov, Vladimir; Evans, Tim (June 2009). "Assessment of sustainability indicators for renewable energy technologies". Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 13 (5): 1082–1088. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2008.03.008.
- ^ "Heron's Inventions includes Holy Water Dispenser and the Aeolipile". explorable.com. Retrieved 2023-05-19.
- ^ al-Hassan, Ahmad Y.; Hill, Donald R. (1992). Islamic Technology: An Illustrated History. Cambridge University Press. p. 54. ISBN 978-0-521-42239-0.
- ^ Hill, Donald, "Mechanical Engineering in the Medieval Near East", Scientific American, May 1991, pp. 64–69. (cf. Hill, Donald, Mechanical Engineering Archived 25 ديسمبر 2007 at the Wayback Machine)
- ^ أ ب Morthorst, Poul Erik; Redlinger, Robert Y.; Andersen, Per (2002). Wind energy in the 21st century: economics, policy, technology and the changing electricity industry. Houndmills, Basingstoke, Hampshire: Palgrave/UNEP. ISBN 978-0-333-79248-3.
- ^ "Austrian was First with Wind-Electric Turbine Not Byth or de Goyon". WIND WORKS (in الإنجليزية الأمريكية). 2023-07-25. Retrieved 2023-08-26.
- ^ Windkraft, I. G. (2023-08-02). "Sensation: Österreicher baute bereits vor 140 Jahren das erste Windrad". www.igwindkraft.at (in الألمانية). Retrieved 2023-08-26.
- ^ "Die internationale elektrische Ausstellung Wien 1883: unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der Organisation, sowie der baulichen und maschinellen Anlagen / von E. R. Leonhardt". www.e-rara.ch (in الإنجليزية). 1884. Retrieved 2023-08-26.
- ^ "This Month in Physics History". www.aps.org (in الإنجليزية). 4 Jun 2023. Retrieved 2023-06-04.
- ^ أ ب ت Price, Trevor J. (2004). "Blyth, James (1839–1906)". قاموس أكسفورد للسيَر الوطنية (online ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/100957. (Subscription or UK public library membership مطلوبة.)
- ^ A Wind Energy Pioneer: Charles F. Brush. Danish Wind Industry Association. Retrieved 2008-12-28.
- ^ "Quirky old-style contraptions make water from wind on the mesas of West Texas". Archived from the original on 3 February 2008.
- ^ "History of wind power". U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). Retrieved 2023-05-21.
- ^ "The Unlikely Birth of Modern Renewable Energy On A Mountain Top in Vermont – 75 Years Ago Today". Stanford Law School. 2016-10-19. Retrieved 2023-05-21.
- ^ Reicher, Dan (2016-10-19). "Reicher: Grampa's Knob 75th Anniversary". Vermont Public (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2023-06-06.
- ^ "Tiny Islands, Big Energy: How Orkney, Scotland Is Fighting Climate Change". Pulitzer Center. Retrieved 2023-05-19.
- ^ "Marching Activists: Transnational Lessons for Danish Anti-Nuclear Protest". Environment & Society Portal. 2017-06-21. Retrieved 2023-05-20.
- ^ "WindExchange: Wind Energy Policies and Incentives". windexchange.energy.gov. Retrieved 2023-05-20.
- ^ Hesse, Nicole (November 2021). "Visible winds: The production of new visibilities of wind energy in West Germany, 1973–1991". Centaurus. 63 (4): 695–713. doi:10.1111/1600-0498.12420.
- ^ "Spain's Wind Power Miracle". The Wind Power Story. 2019. pp. 223–235. doi:10.1002/9781118794289.ch15. ISBN 978-1-118-79418-0.
- ^ Overland, Indra (2019-03-01). "The geopolitics of renewable energy: Debunking four emerging myths". Energy Research & Social Science. 49: 36–40. Bibcode:2019ERSS...49...36O. doi:10.1016/j.erss.2018.10.018.
- ^ "NREL: Dynamic Maps, GIS Data, and Analysis Tools – Wind Maps". Nrel.gov. 3 September 2013. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ^ Appendix II IEC Classification of Wind Turbines. Wind Resource Assessment and Micro-siting, Science and Engineering. 2015. pp. 269–270. doi:10.1002/9781118900116.app2. ISBN 978-1-1189-0011-6.
- ^ Kalmikov, Alexander (2017). Wind Power Fundamentals. Academic Press. pp. 17–24. ISBN 978-0-12-809451-8.
- ^ "The Physics of Wind Turbines Kira Grogg Carleton College, 2005, p. 8" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 September 2013. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ^ Betz, A. (2013) [20 September 1920]. "The Maximum of the Theoretically Possible Exploitation of Wind by Means of a Wind Motor". Wind Engineering. 37 (4): 441–446. Bibcode:2013WiEng..37..441B. doi:10.1260/0309-524X.37.4.441.
- ^ "Wind Energy Basics". Bureau of Land Management. Archived from the original on 9 May 2019. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
- ^ "Enercon E-family, 330 kW to 7.5 MW, Wind Turbine Specification" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 May 2011.
- ^ Burton, Tony; Sharpe; Jenkins; Bossanyi (12 December 2001). Wind Energy Handbook. John Wiley & Sons. p. 65. ISBN 978-0-471-48997-9.
- ^ Wittrup, Sanne (1 November 2013). "11 års vinddata afslørede overraskende produktionsnedgang" [11 years of wind data shows surprising production decrease]. Ingeniøren (in الدانمركية). Archived from the original on 25 October 2018.
- ^ Han, Xingxing; Liu, Deyou; Xu, Chang; Shen, Wen Zhong (2018). "Atmospheric stability and topography effects on wind turbine performance and wake properties in complex terrain". Renewable Energy. Elsevier BV. 126: 640–651. Bibcode:2018REne..126..640H. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2018.03.048.
- ^ Ozdamar, G. (2018). "Numerical Comparison of the Effect of Blade Material on Wind Turbine Efficiency". Acta Physica Polonica A. 134 (1): 156–158. Bibcode:2018AcPPA.134..156O. doi:10.12693/APhysPolA.134.156.
- ^ Garisto, Dan (2021-07-30). "Windbreaks May Improve Wind Farm Power". Physics (in الإنجليزية). Vol. 14. p. 112.
- ^ "Wind Energy Basics". American Wind Energy Association. Archived from the original on 23 September 2010. Retrieved 24 September 2009.
- ^ Stinson, Elizabeth (15 May 2015). "The Future of Wind Turbines? No Blades". Wired.
- ^ أ ب Paul Gipe (7 May 2014). "News & Articles on Household-Size (Small) Wind Turbines". Wind-works.org. Archived from the original on 28 August 2022. Retrieved 29 September 2016.
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماة:3 - ^ "How a Wind Turbine Works - Text Version". Energy.gov (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2023-05-26.
- ^ Bywaters, G.; Mattila; Costin; Stowell; John; Hoskins; Lynch; Cole; Cate; C. Badger; B. Freeman (October 2007). "Northern Power NW 1500 Direct-Drive Generator" (PDF). National Renewable Energy Laboratory. p. iii.
- ^ Neves, C. G. C.; Flores Filho, A. F.; Dorrel, D. G. (2016). "Design of a Pseudo Direct Drive for Wind Power Applications". 2016 International Conference of Asian Union of Magnetics Societies (ICAUMS). pp. 1–5. doi:10.1109/ICAUMS.2016.8479825. ISBN 978-1-5090-4383-5.
- ^ Khare, Vikas; Khare, Cheshta; Nema, Savita; Baredar, Prashant (2019). "Introduction to Energy Sources". Tidal Energy Systems. pp. 1–39. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-814881-5.00001-6. ISBN 978-0-12-814881-5.
- ^ Bortolotti, Pietro; Kapila, Abhinav; Bottasso, Carlo L. (31 January 2019). "Comparison between upwind and downwind designs of a 10 MW wind turbine rotor". Wind Energy Science. 4 (1): 115–125. Bibcode:2019WiEnS...4..115B. doi:10.5194/wes-4-115-2019.
- ^ "MHI Vestas Launches World's First* 10 Megawatt Wind Turbine". CleanTechnica. 26 September 2018.
- ^ "World's biggest wind turbine shows the disproportionate power of scale". 22 August 2021.
- ^ "Wind Energy Factsheet". Center for Sustainable Systems (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2023-05-21.
- ^ أ ب Tummala, Abhishiktha; Velamati, Ratna Kishore; Sinha, Dipankur Kumar; Indraja, V.; Krishna, V. Hari (April 2016). "A review on small scale wind turbines". Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 56: 1351–1371. Bibcode:2016RSERv..56.1351T. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2015.12.027.
- ^ Michael Barnard (7 April 2014). "Vertical Axis Wind Turbines: Great In 1890, Also-rans In 2014". CleanTechnica.
- ^ Hau, E., Wind Turbines: Fundamentals, Technologies, Application, Economics. Springer. Germany. 2006
- ^ Michael C Brower; Nicholas M Robinson; Erik Hale (May 2010). "Wind Flow Modeling Uncertainty" (PDF). AWS Truepower. Archived from the original on 2013-05-02.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ Piggott, Hugh (6 January 2007). "Windspeed in the city – reality versus the DTI database". Scoraigwind.com. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ^ "Urban Wind Turbines" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 30 May 2009. Retrieved 24 August 2011.
- ^ Möllerström, Erik; Gipe, Paul; Beurskens, Jos; Ottermo, Fredric (May 2019). "A historical review of vertical axis wind turbines rated 100 kW and above". Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 105: 1–13. Bibcode:2019RSERv.105....1M. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2018.12.022.
- ^ Eric Eggleston & AWEA Staff. "What Are Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs)?". American Wind Energy Association. Archived from the original on 3 April 2005.
- ^ Marloff, Richard H. (1978). "Stresses in turbine-blade tenons subjected to bending". Experimental Mechanics. 18 (1): 19–24. doi:10.1007/BF02326553.
- ^ Rob Varnon (2 December 2010). "Derecktor converting boat into hybrid passenger ferry". Connecticut Post. Archived from the original on 4 December 2010. Retrieved 25 April 2012.
- ^ Cherubini, Antonello; Papini, Andrea; Vertechy, Rocco; Fontana, Marco (November 2015). "Airborne Wind Energy Systems: A review of the technologies". Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 51: 1461–1476. Bibcode:2015RSERv..51.1461C. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2015.07.053. hdl:11382/503316.
- ^ "After a Shaky Start, Airborne Wind Energy Is Slowly Taking Off". Yale E360 (in الإنجليزية الأمريكية). Retrieved 2023-06-02.
- ^ "So, What Exactly Is Floating Offshore Wind?". www.greentechmedia.com. Retrieved 2023-06-02.
- ^ "The US has just started building floating wind turbines – how do they work?". World Economic Forum (in الإنجليزية). 2022-12-16. Retrieved 2023-06-02.
- ^ 1.5 MW Wind Turbine Technical Specifications
- ^ Size specifications of common industrial wind turbines
- ^ أ ب ""Wind Turbine Design Cost and Scaling Model", Technical Report NREL/TP-500-40566, December, 2006, page 35, 36" (PDF). National Renewable Energy Laboratory. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ^ Navid Goudarzi (June 2013). "A Review on the Development of the Wind Turbine Generators across the World". International Journal of Dynamics and Control. 1 (2): 192–202. doi:10.1007/s40435-013-0016-y.
- ^ Navid Goudarzi; Weidong Zhu (November 2012). "A Review of the Development of Wind Turbine Generators Across the World". ASME 2012 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition. 4 – Paper No: IMECE2012-88615: 1257–1265.
- ^ "Hansen W4 series". Hansentransmissions.com. Archived from the original on 15 March 2012. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ^ Gardner, John; Haro, Nathaniel & Haynes, Todd (October 2011). "Active Drivetrain Control to Improve Energy Capture of Wind Turbines" (PDF). Boise State University. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 March 2012. Retrieved 28 February 2012.
- ^ Bauer, Lucas. "GE General Electric GE 1.5s - 1,50 MW - Wind turbine". en.wind-turbine-models.com (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2023-05-23.
- ^ "Nacelles | How are they manufactured?". Windpower Engineering & Development (in الإنجليزية الأمريكية). Retrieved 2023-05-23.
- ^ Baqersad, Javad; Niezrecki, Christopher; Avitabile, Peter (2015). "Full-field dynamic strain prediction on a wind turbine using displacements of optical targets measured by stereophotogrammetry". Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing. 62–63: 284–295. Bibcode:2015MSSP...62..284B. doi:10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.03.021.
- ^ Lundstrom, Troy; Baqersad, Javad; Niezrecki, Christopher; Avitabile, Peter (4 November 2012). "Using High-Speed Stereophotogrammetry Techniques to Extract Shape Information from Wind Turbine/Rotor Operating Data". In Allemang, R.; De Clerck, J.; Niezrecki, C.; Blough, J.R. (eds.). Topics in Modal Analysis II, Volume 6. Conference Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Mechanics Series. Springer New York. pp. 269–275. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-2419-2_26. ISBN 978-1-4614-2418-5.
- ^ أ ب Ancona, Dan; Jim, McVeigh (2001), Wind Turbine – Materials and Manufacturing Fact Sheet
- ^ أ ب Watson, James; Serrano, Juan (September 2010). "Composite Materials for Wind Blades". Wind Systems. Archived from the original on 11 November 2017. Retrieved 6 November 2016.
- ^ Jossi, Frank (2021-02-04). "Wind developers are retrofitting newer projects with bigger, better blades". Energy News Network (in الإنجليزية الأمريكية). Retrieved 2023-06-02.
- ^ Venditti, Bruno (2022-06-03). "Animation: The World's Biggest Wind Turbines". Visual Capitalist (in الإنجليزية الأمريكية). Retrieved 2023-05-20.
- ^ "What happens to end-of-life wind turbine blades?". www.ny1.com (in الإنجليزية). 19 Aug 2022. Retrieved 2023-06-04.
- ^ "Materials and Innovations for Large Blade Structures: Research Opportunities in Wind Energy Technology" (PDF). windpower.sandia.gov. Archived from the original (PDF) on 13 August 2017. Retrieved 27 February 2018.
- ^ "Wind turbine blades: Glass vs. carbon fiber". www.compositesworld.com. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- ^ Vries, Eize de. "Turbines of the year: Rotor blades". www.windpowermonthly.com.
- ^ Panduranga, Raghu; Alamoudi, Yasser; Ferrah, Azzeddine (2019). "Nanoengineered Composite Materials for Wind Turbine Blades". 2019 Advances in Science and Engineering Technology International Conferences (ASET). pp. 1–7. doi:10.1109/ICASET.2019.8714217. ISBN 978-1-5386-8271-5.
- ^ "IntelStor expects wind turbine prices to recover 5% in next two years". Windpower Engineering & Development. 22 October 2019.
- ^ Ong, Cheng-Huat & Tsai, Stephen W. (1 Mar 2000). "The Use of Carbon Fibers in Wind Turbine Blade Design" (PDF). energy.sandia.gov.
- ^ "Onshore vs offshore wind energy: what's the difference?". National Grid Group. Retrieved 2023-05-23.
- ^ Frost and Sullivan, 2009, cited in Wind Generator Technology, by Eclareon S.L., Madrid, May 2012; www.eclareon.com; Available at Leonardo Energy – Ask an Expert; Fernando Nuno (2012-05-30). "Ask an expert". Leonardo ENERGY. Archived from the original on 26 November 2012. Retrieved 2012-12-12.
- ^ "Fast pace of growth in wind energy driving demand for copper". Riviera Maritime Media.
- ^ Kim, Junbeum; Guillaume, Bertrand; Chung, Jinwook; Hwang, Yongwoo (February 2015). "Critical and precious materials consumption and requirement in wind energy system in the EU 27". Applied Energy. 139: 327–334. Bibcode:2015ApEn..139..327K. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.11.003.
- ^ أ ب Wilburn, David R. (2011). Wind Energy in the United States and Materials Required for the Land-Based Wind Turbine Industry from 2010 through 2030 (Scientific Investigations Report 2011-5036) (PDF). USGS. Retrieved 15 January 2023.
- ^ Buchholz, Peter; Brandenburg, Torsten (January 2018). "Demand, Supply, and Price Trends for Mineral Raw Materials Relevant to the Renewable Energy Transition Wind Energy, Solar Photovoltaic Energy, and Energy Storage". Chemie Ingenieur Technik. 90 (1–2): 141–153. doi:10.1002/cite.201700098.
- ^ Yap, Chui-Wei (5 January 2015). "China Ends Rare-Earth Minerals Export Quotas". Wall Street Journal.
- ^ "Glass fiber market to reach to US$17 billion by 2024". Reinforced Plastics. 60 (4): 188–189. July 2016. doi:10.1016/j.repl.2016.07.006.
- ^ Young, Kathryn (3 August 2007). "Canada wind farms blow away turbine tourists". Edmonton Journal. Archived from the original on 25 April 2009. Retrieved 6 September 2008.
- ^ Rudgard, Olivia (2023-02-20). "Despite perception as eyesore, wind turbine tourism takes off". The Japan Times (in الإنجليزية الأمريكية). Retrieved 2023-06-02.
- ^ Anon. "Solar & Wind Powered Sign Lighting". Energy Development Cooperative Ltd. Retrieved 19 October 2013.
- ^ Small Wind Archived 15 نوفمبر 2011 at the Wayback Machine, U.S. Department of Energy National Renewable Energy Laboratory website
- ^ Castellano, Robert (2012). Alternative Energy Technologies: Opportunities and Markets (in الإنجليزية). Archives contemporaines. ISBN 978-2-8130-0076-7.
- ^ Meyers, Johan (2011). "Optimal turbine spacing in fully developed wind farm boundary layers". Wind Energy. 15 (2): 305–317. Bibcode:2012WiEn...15..305M. doi:10.1002/we.469.
- ^ "New study yields better turbine spacing for large wind farms". Johns Hopkins University. 18 January 2011. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ^ M. Calaf; C. Meneveau; J. Meyers (2010). "Large eddy simulation study of fully developed wind-turbine array boundary layers". Phys. Fluids. 22 (1): 015110–015110–16. Bibcode:2010PhFl...22a5110C. doi:10.1063/1.3291077.
- ^ Dabiri, John O. (July 2011). "Potential order-of-magnitude enhancement of wind farm power density via counter-rotating vertical-axis wind turbine arrays". Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy. 3 (4) 043104. arXiv:1010.3656. doi:10.1063/1.3608170.
- ^ van Bussel, G.J.W.; Zaaijer, M.B. (2001). "Reliability, Availability and Maintenance aspects of large-scale offshore wind farms" (PDF). Delft University of Technology. p. 2. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 April 2016. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ^ "Iberwind builds on 98% availability with fresh yaw, blade gains". 15 February 2016. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ^ Barber, S.; Wang, Y.; Jafari, S.; Chokani, N.; Abhari, R. S. (February 2011). "The Impact of Ice Formation on Wind Turbine Performance and Aerodynamics". Journal of Solar Energy Engineering. 133 (1) 011007. doi:10.1115/1.4003187.
- ^ Nilsen, Jannicke (1 February 2015). "Her spyler helikopteret bort et tykt lag med is". Tu.no (in النرويجية). Teknisk Ukeblad. Archived from the original on 20 January 2021.
These work .. by blowing hot air into the rotor blades so that the ice melts, or by using heating cables on the front edge of the rotor blades where the ice sticks. No chemicals are added to the water, in contrast to aircraft de-icing, which often involves extensive use of chemicals. The price tag for de-icing a wind turbine is equivalent to the value of two days' turbine production.
- ^ Morten Lund (30 May 2016). "Dansk firma sætter prisbelønnet selvhejsende kran i serieproduktion". Ingeniøren. Archived from the original on 31 May 2016. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ^ "Wind Repowering Helps Set the Stage for Energy Transition". Energy.gov (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2023-05-23.
- ^ Jeremy Fugleberg (8 May 2014). "Abandoned Dreams of Wind and Light". Atlas Obscura. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ^ Tom Gray (11 March 2013). "Fact check: About those 'abandoned' turbines …". American Wind Energy Association. Archived from the original on 8 June 2016. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ^ أ ب ت "Wind Turbine Blades Don't Have To End Up In Landfills". The Equation (in الإنجليزية الأمريكية). 2020-10-30. Retrieved 2022-01-23.
- ^ "Wind Turbine Blades Can't Be Recycled, So They're Piling Up in Landfills". Bloomberg.com (in الإنجليزية). 2020-02-05. Retrieved 2023-06-07.
- ^ "Turbines Tossed Into Dump Stirs Debate on Wind's Dirty Downside". Bloomberg. 31 July 2019. Retrieved 6 December 2019.
- ^ Barsoe, Tim (2021-05-17). "End of wind power waste? Vestas unveils blade recycling technology". Reuters (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2022-01-23.
- ^ "New HS2 pilot project swaps steel for retired wind turbine blades to reinforce concrete". High Speed 2 (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2021-03-12.
- ^ Mason, Hannah (21 October 2021). "Anmet installs first recycled wind turbine blade-based pedestrian bridge". CompositesWorld.
- ^ Stone, Maddie (11 February 2022). "Engineers are building bridges with recycled wind turbine blades". The Verge.
- ^ "Renewable Power Remains Cost-Competitive amid Fossil Fuel Crisis". www.irena.org (in الإنجليزية). 2022-07-13. Retrieved 2023-05-19.
- ^ أ ب "Advantages and Disadvantages of Wind Energy – Clean Energy Ideas". Clean Energy Ideas (in الإنجليزية). 2013-06-19. Retrieved 2017-05-10.
- ^ "WINDExchange: Economics and Incentives for Wind". windexchange.energy.gov. Retrieved 2023-05-19.
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةrue21 - ^ "About Wind Energy: Factsheets and Statistics". www.pawindenergynow.org. Retrieved 2017-05-10.
- ^ "How Big Are the Blades of a Wind Turbine?". 24 August 2023.
- ^ "Threats to Birds / Top Threats to Birds (U.S. only. Ordered by Median Estimate of Bird Mortality Annually. As of 2017.)". U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. 2017. Archived from the original on 13 February 2025.
- ^ Parisé, J.; Walker, T. R. (2017). "Industrial wind turbine post-construction bird and bat monitoring: A policy framework for Canada". Journal of Environmental Management. 201: 252–259. Bibcode:2017JEnvM.201..252P. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.06.052. PMID 28672197.
- ^ Hosansky, David (1 April 2011). "Wind Power: Is wind energy good for the environment?". CQ Researcher.
- ^ "How Harmful is Renewable Energy to Birds? | Article | EESI". www.eesi.org. Retrieved 2023-06-02.
- ^ Katovich, Erik (9 January 2024). "Quantifying the Effects of Energy Infrastructure on Bird Populations and Biodiversity". Environmental Science & Technology. 58 (1): 323–332. Bibcode:2024EnST...58..323K. doi:10.1021/acs.est.3c03899. PMID 38153963.
- ^ "Grid-Scale Storage – Analysis". IEA (in الإنجليزية البريطانية). Retrieved 2023-06-02.
- ^ أ ب ت Lewis, Michelle (29 September 2023). "A new wind farm in Kansas trailblazes with light-mitigating technology". Electrek. Archived from the original on 29 September 2023.
- ^ "Wind Energy Power Plants in Canada – other provinces". Power Plants Around the World Photo Gallery. industcards. 5 June 2010. Archived from the original on 4 September 2012. Retrieved 24 August 2010.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unfit URL (link) - ^ "MBB Messerschmitt Monopteros M50 - 640,00 kW - Wind turbine". wind-turbine-models.com. Archived from the original on Jul 9, 2023.
- ^ "Ming Yang completes 6.5MW offshore turbine". Windpower Monthly (in الإنجليزية). 1 July 2013. Retrieved 2023-06-06.
- ^ "When More is More: Multi-Rotor Turbines". UTM Consultants (in الإنجليزية). 2022. Archived from the original on 8 April 2024. Retrieved 2023-05-31.
- ^ "Highest altitude wind generator". Guinness World Records (in الإنجليزية البريطانية). 2013-06-19. Retrieved 2023-06-06.
- ^ enercon.de
- ^ "New Record: World's Largest Wind Turbine (7+ Megawatts) — MetaEfficient Reviews". MetaEfficient.com. 2008-02-03. Retrieved 2010-04-17.
- ^ "Germany Inaugurates 5 MW Wind Turbine Prototype". RenewableEnergyAccess.com. 2005-02-04. Retrieved 2007-11-20.
- ^ http://www.norwaypost.no/content/view/23186/48/ Retrieved 2010-02-13
- ^ http://www.google.com/hostednews/afp/article/ALeqM5j-BZEK4lR-_hxsz2hQ-92_c0oSHQ Retrieved 2010-02-13
- ^ http://www.grist.org/article/2010-02-12-norway-plans-the-worlds-most-powerful-wind-turbine/ Retrieved 2010-02-16
- ^ "PHOTO: GE unveils first 12MW Haliade-X nacelle". Wind pwoer Offshore. 2019-07-22. Retrieved 2019-07-25.
- ^ "FL 2500 Noch mehr Wirtschaftlichkeit" (in German). Fuhrlaender AG. Retrieved 2009-11-05.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ^ "Visits > Big wind turbine". Retrieved 2010-04-17.
- ^ http://green-blog.org/2008/06/06/the-demolition-of-a-record-holder/#more-418
للاستزادة
- BBC News,"Wind farms 'must take root in UK, BBC News, 19 May 2005
- Tony Burton, David Sharpe, Nick Jenkins, Ervin Bossanyi: Wind Energy Handbook, John Wiley & Sons, 1st edition (2001), ISBN 0-471-48997-2
- Darrell, Dodge, Early History Through 1875, TeloNet Web Development, Copyright 1996–2001
- David, Macaulay, New Way Things Work, Houghton Mifflin Company, Boston, Copyright 1994–1999, pg.41-42
- Erich Hau Wind turbines: fundamentals, technologies, application, economics Birkhäuser, 2006 ISBN 3540242406 (preview on Google Books)
- Wind Power Myths vs. Facts, American Wind Energy Association
- Germany Inaugurates 5MW Wind Turbine Prototype, RenewableEnergyWorld.com website.
وصلات خارجية
- Photo journal and tutorial for 1.5kw residential wind turbine
- Time-lapse video of wind turbine installation at the WMRA Deer Island Wastewater Treatment Plant
- Wind Projects
- Guided tour on wind energy
- Wind Energy Technology World Wind Energy Association
- Wind turbine simulation, National Geographic
- Domestic and Commercial wind turbine directory and information wiki, SustainableX.com
- D.I.Y. Wind Generator Plans Reviewed
- November 3, 2009 "Power Paths" Coal to Wind Turbines on PBS's Independent Lens [1]
- Building a robust path for wind turbine engineering Movie and information on wind turbine engineering
- CS1 maint: url-status
- CS1 الإنجليزية الأمريكية-language sources (en-us)
- CS1 الألمانية-language sources (de)
- Wikipedia articles incorporating a citation from the ODNB
- Pages using cite ODNB with id parameter
- CS1 الدانمركية-language sources (da)
- CS1 maint: unfit URL
- CS1 النرويجية-language sources (no)
- CS1 الإنجليزية البريطانية-language sources (en-gb)
- مقالات فيها عبارات متقادمة منذ 2009
- جميع المقالات التي فيها عبارات متقادمة
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Articles with unsourced statements from February 2024
- Wikipedia articles in need of updating from July 2024
- All Wikipedia articles in need of updating
- ديناميكا هوائية
- قدرة كهربائية
- مولدات كهربائية
- هندسة ميكانيكية إلكترونية
- تحويل الطاقة
- توربينات الرياح