المعمل الوطني للمجال المغناطيسي العالي
المعمل الوطني للمجال المغناطيسي العالي National High Magnetic Field Laboratory الفيزيائيين الذين يجرون ابحاثا في المعهد الوطني للمختبر الحقول المغناطيسية العليا في جامعة ولاية فلوريدا وحصلت على العلامة التجارية الجديدة وتكنولوجيا عالية للعطلات ومغناطيس ذى سجل قياسي
المهندسين والفنيين في أواخر ديسمبر كانون الاول الماضى أتمو الاختبارات للمغناطيس 36 تسلا (تسلا هي مقياس لقوة الحقل المغناطيسي ؛ المغناطيس الجديد هو أكثر قوة 1،200 مرة من مغناطيس الثلاجة العادية.) وهذا الإنجاز يعيد تأكيد أن المختبر المغناطيسي هو حامل الرقم القياسي للمغناطيس العالمي لجذب أعلى حقل "مقاوم" highest-field "resistive" magnet — و هو نوع من المغناطيسات الكهربائية التي تستخدم الكهرباء لتوليد المجالات المغناطيسية العالية . المغناطيس الجديد -- فعلا يعد ترقية حقيقية إلى المغناطيس القائم حاليا— وهو يتفوق على الرقم القياسي السابق البالغ 35 تسلا، وهو عقد مشترك مع المختبر المغناطيسي معمل گرينوبل للحقل المغناطيسي العالي في فرنسا.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
التاريخ
في عام 1989 قدم اقتراحا إلى مؤسسة العلوم الوطنية من قبل ممثلين عن جامعة ولاية فلوريدا ، و مختبر لوس ألاموس الوطني ، وجامعة فلوريدا إلى إنشاء مختبر وطني جديد لدعم المستخدم لدعم البحوث في المجالات المغناطيسية العالية.وخطة مفصلة لرؤية جديدة للمختبرالمغناطيسي متعدد التخصصات ., أهداف هذا المختبر كانت لإنشاء نموذج الشراكة الحكومة الاتحادية للولايات المتحدة-الدولة الفيدرالية الامريكية وخدمة بحث المغناطيس ذات الصلة في جميع المجالات تقريبا من العلوم ، وتشجيع البحوث المتعددة التخصصات ، ودعم العلم والتعليم التكنولوجي , ولديها شراكة عمل مع الصناعة لتعزيز الوضع التنافسي لل الولايات المتحدة في المجالات المغناطيسية المتعلقة بالبحث والتطوير
وفى أعقاب مراجعة النظراء المتنافسون, المؤسسة الوطنية للعلوم منحت اللجنة الوطنية لمختبر الحقول المغناطيسية العليا في جامعة ولاية فلوريدا في عام 1990. الكونسورتيوم بقيادة ج.و.ف. فاز على معهد مساتشوستس للتكنولوجيا الشهير وعلاقاته مع جامعة أيوا، جامعة وسكنسن–ماديسون, معمل بروكهاِڤن الوطني ومعمل أرگون الوطني في العطاء.
في 5 سبتمبر 1990 ، طلب الباحثون من معهد ماساتشوستس للتكنولوجيا من 21 عضوا في مجلس العلوم الوطني القيام بمراجعة وإعادة النظر في قرار مصلحة الدولة للاحصاء الى منح جائزة وطنية جديدة إلى مختبر الحقول المغناطيسية العليا لجامعة ولاية فلوريدا. [1]. هذا الطلب قوبل بالرفض 18 سبتمبر 1990. [2]
السنوات الاولى للمختبر في قد أنفقت في إنشاء البنية التحتية الأساسية ، وبناء أكبر وأعلى منشأة تعمل بالطاقة في العالم, و توظيف كفاءات عالمية من الدرجة الأولى , و إستعراض ريادة المختبر العالمية وقيادته التكنولوجيات ذات الصلة بالمغناطيسية والعلوم. مجمع تالاهاسي كان قد خصص في 1 أكتوبر 1994 ، مع أكثر من 1،000 من كبار الشخصيات والعلماء الزائرين في الحضور ، بما في ذلك المتحدث الرئيسي نائب الرئيس آل گور.
البرامج
برامج جامعة ولاية فلوريدا
The Tallahassee laboratory at Florida State University is a 34,374 square meter (370,000 sq ft.) complex and has approximately 300 faculty, staff, graduate, and postdoctoral students.
DC Field Program
The purpose of the DC (continuous field) field program is to provide to the user community with the strongest, quietest, steady and slowly varying magnetic fields in the world, coupled with state of the art instrumentation and experimental expertise.
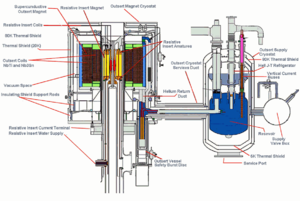
The facility contains 14 resistive magnet cells connected to a newly upgraded 48 megawatt DC power supply and 15,000 square feet (1,400 m2) of cooling equipment to remove the heat generated by the magnets. The research is supported by magnet plant and cryogenic system operators. Technicians design, build and repair instruments for user research. Scholar-scientists — world-class researchers with their own vibrant research interests — work directly with users to get the best measurements and data.
The facility houses several world-record magnets, including the 45 tesla hybrid magnet, which combines resistive and superconducting magnets to create the strongest steady magnetic field available anywhere. The lab's 35 tesla resistive magnet is the strongest resistive magnet in the world, and the 25 tesla Keck magnet boasts the highest homogeneity of any resistive magnet.
NMR Spectroscopy and Imaging Program
This program serves a broad user base in solution and solid state NMR spectroscopy and MRI and diffusion measurements at the highest possible magnetic field strengths. The lab develops technology, methodology, and applications at high magnetic fields through both in-house and external user activities. It has experienced research faculty, engineers, and technicians spanning these disciplines who are available to facilitate user activities on a wide range of unique equipment and to develop novel experiments and new instrumentation. The program's flagship magnet is the Mag Lab-made 900 MHz (21.1 tesla) NMR magnet. With an ultra-wide bore measuring 105 mm (about 4 inches) in diameter, this superconducting magnet offers the highest field for an MRI study of a living animal in the world.
Ion Cyclotron Resonance Program
This program is charged with developing and exploiting the unique capabilities of FT-ICR (Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance) mass spectrometry. The ICR program leads the world in instrument and technique development as well as pursuing novel applications of FT-ICR mass spectrometry. Under the leadership of director Alan G. Marshall, the program continuously develops techniques and instruments and pursues novel applications of FT-ICR mass spectrometry. The program features several instruments, including the 14.5 tesla, 104 mm bore system, the highest-field superconducting ICR magnet in the world.
برنامج الرنين المغناطيسي للإلكترونات
The most common form of EMR is electron paramagnetic/spin resonance (EPR/ESR). In EPR experiments, transitions are observed between the mS sublevels of an electronic spin state S that are split by the applied magnetic field as well as by the fine structure interactions and the electron-nuclear hyperfine interactions. This technique has extensive applications in chemistry, biochemistry, biology, physics and materials research.
علوم وتكنولوجيا المغناطيس
The Magnet Science and Technology division is charged with developing the technology and expertise for cutting-edge magnet systems. These magnet projects include building advanced magnet systems for the Tallahassee and Los Alamos sites, working with industry to develop the technology to improve high-field magnet manufacturing capabilities, and pushing the state of the art beyond what is currently available in high field magnet systems through research and development.
Also at the lab's FSU headquarters, the Applied Superconductivity Center advances the science and technology of superconductivity by understanding and pushing the limits of both the low temperature niobium-based and the high temperature cuprate or MgB2-based materials. Focusing heavily on understanding and exploiting the interface between the “R” and the “D” in R&D, the ASC pursues the superconductors needed for everything from magnets for fusion, high energy physics, MRI, to electric power transmission lines and transformers.
In-House Research
An in-house research program flourishes at the Magnet Lab. The program utilizes Magnet Lab facilities to pursue high field research at the forefront of science and engineering, while advancing the lab’s user programs through development of new techniques and equipments.
مجموعة المادة المكثفة
The Condensed Matter Group scientists concentrate on various aspects of condensed matter physics, including studies and experiments involving magnetism, the quantum hall effect, quantum oscillations, high temperature superconductivity, and heavy fermion systems.
برنامج كيمياء الأرض
The geochemistry research program is centered around the use of trace elements and isotopes to understand the Earth processes and environment. The research interests range from the chemical evolution of Earth and solar system through time to local scale problems on the sources and transport of environmentally significant substances. The studies conducted by the geochemistry division concern terrestrial and extraterrestrial questions and involve land-based and sea-going expeditions and spacecraft missions. Together with FSU's Chemistry and Oceanography departments, Geochemistry has started a program in Biogeochemical Dynamics.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
برامج أخرى
The lab’s long-range planning includes enhancements to user programs, both for high field research and related fields. Various affiliated programs complement and help extend the capabilities of existing programs. These include cryogenics, optical microscopy, quantum materials and resonant ultrasound spectroscopy.
معمل لوس ألاموس الوطني - The Pulsed Field Facility
Los Alamos National Laboratory in نيو مكسيكو hosts the Pulsed Field Facility, which provides researchers with experimental capabilities for a wide range of measurements in non-destructive pulsed fields to 60 teslas. Pulsed field magnets create very high magnetic fields, but only for fractions of a second. A 100 tesla multi-shot magnet is being jointly constructed by the Department of Energy and the National Science Foundation. The laboratory is located at the center of Los Alamos. In 1999-2000, the facility was relocated into a new specially-designed Experimental Hall to better accommodate user operations and support. The program is an integral component of the Magnet Lab and continues to be the first and only high pulsed field user facility in the United States. The laboratory is dedicated to driving pulsed magnetic field technology and instrumentation and to make research using pulsed magnetic fields available to scientists from the United States and around the world.
The facility provides a wide variety of experimental capabilities to 60 teslas, using short and long pulse magnets. Power comes from a pulsed power infrastructure which includes a 1.43 gigawatt motor generator and five 64-megawatt power supplies. The 1200-ton motor generator sits on a 4800-short ton (4350 t) inertia block which rests on 60 springs to minimize earth tremors is the centerpiece of the Pulsed Field Laboratory.
The facility's magnets include a 60 tesla long-pulse magnet that is the most powerful controlled-pulse magnet in the world.
برامج جامعة فلوريدا
The University of Florida is home to user facilities in magnetic resonance imaging or (MRI) with an ultra-low temperature, ultra-quiet environment for experimental studies in the High B/T (high magnetic field/low temperature) Facility. Facilities are also available for the fabrication and characterization of nanostructures at a new Nanofabrication Facility being operated in conjunction with the university's Major Analytical and Instrumentation Center.
High B/T Facility
The High B/T Facility is operated as part of the Microkelvin Laboratory of the Physics Department. The facility is designed to meet the needs of Magnet Lab users who wish to conduct experiments in high magnetic fields up to 15.2 teslas and at temperatures as low as 0.4 mK simultaneously. Faculty members in the facility work with users in the design of experiments where needed. Instrumentation is available for studies of magnetization, thermodynamic quantities, transport measurements, magnetic resonance, viscosity, diffusion, and pressure.
The facility holds world records for high B/T in Bay 1 for short term low field capabilities and world records for high field long time (> 1 week) experiments. The research group leads the world in collective studies of quantum fluids and solids in terms of breadth and low temperature techniques (thermometry, NMR, ultrasound, heat capacity, sample cooling.)
التصوير بالرنين المغناطيسي المتطور والمطيافية
The Advanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy program (AMRIS) contains facilities for the Mag Lab's NMR Program that complement the facilities at the lab's headquarters in Tallahassee. AMRIS is located at the University of Florida's McKnight Brain Institute. Their instruments include the 600 MHz NMR Magnet with 1 mm Triple-Resonance, High-Temperature Superconducting Probe, which delivers the highest mass sensitivity of any probe at any frequency in the world.
وصلات خارجية
- National High Magnetic Field Laboratory |جامعة ولاية فلوريدا
- Pulsed Field Facility |Los Alamos National Laboratory
- High B/T Facility |University of Florida
- Advanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Spectroscopy Facility |University of Florida