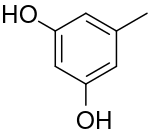
أورسينول Orcinol
| |
| الأسماء | |
|---|---|
| اسم أيوپاك المفضل
5-Methylbenzene-1,3-diol | |
أسماء أخرى
| |
| المُعرِّفات | |
| رقم CAS | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.259 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| الخصائص | |
| الصيغة الجزيئية | C7H8O2 |
| كتلة مولية | 124.13 g mol-1 |
| المظهر | Crystalline solid |
| نقطة الانصهار | |
| نقطة الغليان | |
| قابلية الذوبان في الماء | Miscible |
ما لم يُذكر غير ذلك، البيانات المعطاة للمواد في حالاتهم العيارية (عند 25 °س [77 °ف]، 100 kPa). | |
| مراجع الجدول | |
Orcinol is an organic compound with the formula CH3C6H3(OH)2. It occurs in many species of lichens[2] including Roccella tinctoria and Lecanora. Orcinol has been detected in the "toxic glue" of the ant species Camponotus saundersi. It is a colorless solid. It is related to resorcinol, 1,3-C6H4(OH)2.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
التخليق والتفاعلات
Orcinol was first prepared by dehydroacetic acid, a conversion that involved ring-opening of the pyrone to a triketone. This early experiment helped establish the rich condensation chemistry of polyketides.[3] It can be obtained by fusing extract of aloes with potash,[4] followed by acidification.
It undergoes O-methylation with dimethylsulfate.[5]
It is used in the production of the dye orcein and as a reagent in some chemical tests for pentoses, such as Bial's Test. It may be synthesized from toluene; more interesting is its production when acetone dicarboxylic ester is condensed with the aid of sodium. It crystallizes in colorless prisms with one molecule of water, which redden on exposure to air. Ferric chloride gives a bluish-violet coloration with the aqueous solution. Unlike resorcinol it does not give a fluorescein with phthalic anhydride. Oxidation of the ammoniacal solution gives orcein, C28H24N2O7, the chief constituent of the natural dye archil. 4-Methylcatechol is an isomer, found as its methyl ether (creosol) in beech-wood tar.[4]
الانتاج من الزيت الصخري
Orcinol is also found in shale oil produced from Kukersite oil shale.[6] It is the main water-soluble phenol in the oil, and has been extracted and refined industrially by Viru Keemia Grupp.[7]
انظر أيضاً
المراجع
- ^ Merck Index, 11th Edition, 6819.
- ^ Robiquet: „Essai analytique des lichens de l'orseille", Annales de chimie et de physique, 1829, 42, p. 236–257.
- ^ Staunton, James; Weissman, Kira J. (2001). "Polyketide Biosynthesis: A Millennium Review". Natural Product Reports. 18 (4): 380–416. doi:10.1039/a909079g. PMID 11548049.
- ^ أ ب One or more of the preceding sentences incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). . دائرة المعارف البريطانية. Vol. 20 (eleventh ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 173.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - ^ R. N. Mirrington; G. I. Feutrill (1973). "Orcinol Monomethyl Ether". Org. Synth. 53: 90. doi:10.15227/orgsyn.053.0090.
- ^ Mozaffari, Parsa; Järvik, Oliver; Baird, Zachariah Steven (2020-10-28). "Vapor Pressures of Phenolic Compounds Found in Pyrolysis Oil". Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data. 65 (11): 5559–5566. doi:10.1021/acs.jced.0c00675. ISSN 0021-9568.
- ^ "Fine chemicals". Viru Keemia Grupp (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2020-10-23.
- مقالات المعرفة المحتوية على معلومات من دائرة المعارف البريطانية طبعة 1911
- Wikipedia articles incorporating text from the 1911 Encyclopædia Britannica
- Articles with changed ChemSpider identifier
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Articles with changed FDA identifier
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Chembox image size set
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Alkylresorcinols
- 3-Tolyl compounds
- Lichen products
