امتياز خليج كياوتشو
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
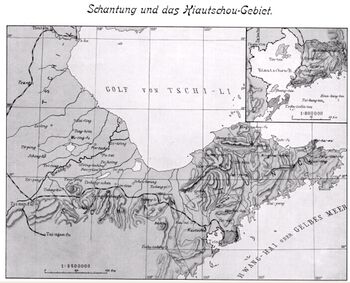
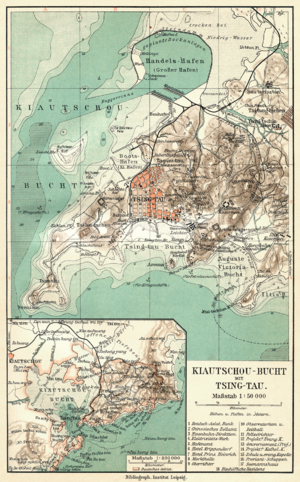
Kiautschou Bay Leased Territory, a German leased territory in Imperial and Early Republican China, existed from 1898 to 1914. Covering an area of 552 km2 (213 sq mi), it centered on Jiaozhou ("Kiautschou") Bay on the southern coast of the Shandong Peninsula (ألمانية: Schantung Halbinsel). Jiaozhou became romanized as Kiaochow, Kiauchau or Kiao-Chau in English and as Kiautschou or Kiaochau in German. The administrative center was at Tsingtau (Pinyin Qingdao). It was operated by the East Asia Squadron of the German Imperial Navy.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
خلفية التوسع الألماني في الصين
Germany was a relative latecomer to the imperialistic scramble for colonies across the globe. A German colony in China was envisioned as a two-fold enterprise: as a coaling station to support a global naval presence, and because it was felt that a German colonial empire would support the economy in the mother country. Densely populated China was viewed as a potential market to be exploited, with thinkers such as Max Weber demanding an active colonial policy from the government[بحاجة لمصدر]. In particular the opening of China was made a high priority, because it was thought to be the most important non-European market in the world.
However, a global policy (Weltpolitik) without global military influence appeared impracticable, so, assessing that Britain's great strength came from its navy, the Germans began to build one too. This fleet was supposed to serve German interests during peace through gunboat diplomacy, and in times of war, through commerce raiding, to protect German trade routes and disrupt hostile ones. Imitating Britain, a network of global naval bases was a key requirement for this intention.
Again, intending to directly copy Britain, the acquisition of a harbor in China was from the start intended to be a model colony: all installations, the administration, the surrounding infrastructure and the utilization thereof was to show the Chinese, the German nation itself, and other colonial powers an effective colonial policy.
استيلاء ألمانيا على الإقليم

In 1860, a Prussian expeditionary fleet arrived in Asia and explored the region around Jiaozhou Bay. The following year, the Prussian-Chinese Treaty of Peking was signed.[1] After journeys to China between 1868 and 1871, the geographer Baron Ferdinand von Richthofen recommended the Bay of Jiaozhou as a possible naval base. In 1896 Rear Admiral Alfred von Tirpitz, at that time commander of the East Asian Cruiser Division, examined the area personally as well as three additional sites in China for the establishment of a naval base. Rear Admiral Otto von Diederichs replaced Tirpitz in East Asia and focused on Jiaozhou Bay even though the Berlin admiralty had not formally decided on a base location.
On 1 November 1897, the Big Sword Society brutally murdered two German Roman Catholic priests of the Steyler Mission in Juye County in southern Shandong. This event was known as the "Juye Incident." Admiral von Diederichs, commander of the cruiser squadron, wired on 7 November 1897 to the admiralty: "May incidents be exploited in pursuit of further goals?"[2] Upon receipt of the Diederichs cable, chancellor Chlodwig von Hohenlohe counseled caution, preferring a diplomatic resolution. However, Kaiser Wilhelm II intervened and the admiralty sent a message for Diederichs to "proceed immediately to Kiautschou with entire squadron ..." to which the admiral replied "will proceed ... with greatest energy."[3]
Diederichs at that moment only had his division's flagship SMS Kaiser and the light cruiser SMS Prinzess Wilhelm available at anchor at Shanghai, the corvette SMS Arcona was laid up for repairs and the light cruiser SMS Irene in a dockyard at Hong Kong for an engine refit. The shallow draft small cruiser SMS Cormoran, operating independent of the cruiser division, was patrolling the Yangtze. Diederichs weighed anchor, ordered Prinzess Wilhelm to follow next day and Cormoran to catch up at sea. The three ships arrived off Tsingtau after dawn on 13 November 1897 but made no aggressive moves. With his staff and the three captains of his ships aboard, Diederichs landed with his admirals tender at Tsingtau's long Zhanqiao Pier to reconnoiter. He determined that his landing force would be vastly outnumbered by Chinese troops, but he had qualitative superiority.[4]
At 06.00, Sunday, 14 November 1897, Cormoran steamed into the inner harbor to provide inshore fire support, if necessary.[5] Kaiser and Prinzess Wilhelm cleared boats to carry an amphibious force of 717 officers, petty officers and sailors armed with rifles.[6] Diederichs on horseback and his column marched toward the Chinese main garrison and artillery battery, a special unit swiftly disabled the Chinese telegraph line and others occupied the outer forts and powder magazines. With speed and effectiveness, Diederichs’ actions had achieved their primary objective by 08.15.[7]
Signalmen restored the telegraph line, and the first messages were received and deciphered. Diederichs was stunned to learn that his orders had been canceled, and that he was to suspend operations at Kiautschou pending negotiations with the Chinese government. If he had already occupied the village of Tsingtau, he was to consider his presence temporary. He responded, thinking the politicians in Berlin had lost their nerve to political or diplomatic complications: "Proclamation already published. ... Revocation not possible." After considerable time and uncertainty, the admiralty finally cabled congratulations and the proclamation to remain in effect; Wilhelm II promoted him to vice admiral.[8]
Admiral von Diederichs consolidated his positions at Kiautschou Bay. The admiralty dispatched the protected cruiser SMS Kaiserin Augusta from the Mediterranean to Tsingtau to further strengthen the naval presence in East Asia.[9] On 26 January 1898 the marines of III. Seebataillon arrived on the liner Darmstadt. Kiautschou Bay was now secure.[10]
Negotiations with the Chinese government began and on 6 March 1898 the German Empire retreated from outright cession of the area and accepted a leasehold of the bay for 99 years, or until 1997, as the British were soon to do with Hong Kong's New Territories and the French with Kouang-Tchéou-Wan. One month later the Reichstag ratified the treaty on 8 April 1898. Kiautschou Bay was officially placed under German protection by imperial decree on 27 April and Kapitän zur See [captain] Carl Rosendahl was appointed governor. These events ended Admiral von Diederichs' responsibility (but not his interest) in Kiautschou; he wrote that he had "fulfilled [his] purpose in the navy."[11]
As a result of the lease treaty, the Chinese government gave up the exercise of its sovereign rights within the leased territory of approximately 83,000 inhabitants (to which the city of Kiautschou was excluded), as well as in a 50 km wide neutral zone ("neutrales Gebiet"). According to international law, the leased territory ("territoire à bail") remained legally part of China but for the duration of the lease, all sovereign powers were to be exercised by Germany.
Moreover, the treaty included rights for construction of railway lines and mining of local coal deposits. Many parts of Shandong outside of the German leased territory came under German economic influence. Although the lease treaty set limits to the German expansion, it became a starting point for the following cessions of Port Arthur and Dalian to Russia to support Russia's Chinese Eastern Railway interests in Manchuria, of the transfer of Weihai and Liu-kung Tao Island from Japan to Great Britain, and the cession of Kwang-Chou-Wan to support France in southern China and Indochina.
التاريخ
الحرب العالمية الأولى
 مقالة مفصلة: حصار تسينگتاو
مقالة مفصلة: حصار تسينگتاو
Kiautschou was at the beginning of the First World War by the III. Sea battalion occupied (1,400 men), which was reinforced by 3,400 reservists and volunteers at the beginning of the war. On August 10, 1914, Japan issued an ultimatum demanding the complete surrender of the area. On August 15th it repeated its request. The governor , sea captain Alfred Meyer-Waldeck , left the ultimatum unanswered and was determined to “defend the leased area to the utmost”.
On August 27th, Japanese and British warships opened a blockade, and on September 2nd the first allies (4,300 men) landed in China. On September 26, assaults began on the German positions, but they were successfully repulsed. After the unsuccessful attacks, the Allies drew a siege ring around the fortress , so that the lease area was completely enclosed by September 28th. Since October the Allied troops have been steadily reinforced until finally over 60,000 men. On October 31, after a nine day artillery run- Continuous fire, the Allies began a large-scale attack on the fortress, which in turn was repulsed. The initially successful defense was based in part on the successful aerial reconnaissance by the naval aviator Gunther Plüschow , who became known as Der Flieger von Tsingtau .
At the beginning of November the trapped German defenders ran out of ammunition, whereupon it was decided to destroy all artillery and combat boats. On November 7, 1914, the capitulation and the occupation by Japan finally took place.
The German defenders were taken prisoner of war in Japan . They lived there in several camps and some were not released from captivity until 1920. The most famous camps were Matsuyama and Bandō .
After the surrender of Kiautschou, the powers of the German governorate in Kiautschou were transferred by the German government to the German embassy in Beijing under Paul von Hintze , who was envoy in Beijing from 1915 until the Chinese declaration of war on Germany in August 1917.
بعد الحرب العالمية الأولى

The Treaty of Versailles determined that Germany had to cede all colonies and thus also Kiautschou. The area remained under Japanese administration until 1922 before it was returned to China at the urging of the US . The provisions of the Versailles Treaty sparked violent student protests in China in 1919. These protests are known as the May 4th Movement and have had far-reaching consequences for Chinese culture and society.
اللغة
| Kiautschou Pidgin German | |
|---|---|
| موطنها | جمهورية الصين الشعبية |
| المنطقة | Qingdao |
الناطقون الأصليون | None |
German-based pidgin | |
| أكواد اللغات | |
| ISO 639-3 | None (mis) |
| Glottolog | kiau1234 Kiautschou Pidgin German |
The local language was the Qingdao dialect of Jiaoliao Mandarin. A German pidgin developed as well.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
تنظيم وتطور الإقليم
As the territory was not strictly speaking a colony but a lease, and because of its importance to the German navy, it was not placed under the supervision of the imperial colonial office (Reichskolonialamt) but instead under that of the imperial naval office (the Reichsmarineamt or RMA).
At the top of the territory stood the governor (all five office holders were senior navy officers), who was directly subordinated to the secretary of state of the RMA, Alfred von Tirpitz. The governor was head of both the military administration (run by the chief of staff and deputy governor), and the civil administration (managed by the Zivilkommissar). Further important functionaries of Kiautschou were the official for the construction of the harbor, and after 1900 the chief justice and the Commissioner for Chinese Affairs. The Gouvernementsrat [government council of the territory] and after 1902 the Chinese Committee advised the governor. The departments of finance, construction, education and medical services were directly subordinated to the governor, because these were crucial with regard to the idea of a model colony.
Kiautschou was modernised, with Germany investing upwards of $100 million.[12] The impoverished fishing village of Tsingtau was laid out with wide streets, solid housing areas, government buildings, electrification throughout, a sewer system and a safe drinking water supply, a rarity in large parts of Asia at that time and later. The area had the highest density of schools and highest per capita student enrollment in all of China, with primary, secondary and vocational schools funded by the Berlin treasury and Protestant and Roman Catholic missions.[13]
With the expansion of economic activity and public works, German banks opened branch offices, the Deutsch-Asiatische Bank being the most prominent. The completion of the Shantung Railroad in 1910 provided a connection to the Trans-Siberian Railway and thus allowed travel by train from Tsingtau to Berlin.[14]
After the Chinese revolution of 1911, many wealthy Chinese and politically connected ex-officials settled in the leased territory because of the safe and orderly environment it offered. Sun Yat-sen visited the Tsingtau area and stated in 1912, “... I am impressed. The city is a true model for China’s future.”[15]
الحكام
All Governors of the Kiautschou Bay Leased Territory were high-ranking officers of the البحرية الألمانية الامبراطورية.
| المدة | الپورتريه | Incumbent | ملاحظات |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14 November 1897 to 7 March 1898 |  |
Otto von Diederichs | Military Governor |
| 7 March 1898 to 19 February 1899 |  |
de (Carl Rosendahl) | |
| 19 February 1899 to 27 January 1901 |  |
Paul Jaeschke | Died in office |
| 27 January 1901 to 8 June 1901 |  |
Max Rollmann | Acting |
| 8 June 1901 to 19 August 1911 |  |
de (Oskar von Truppel) | |
| 19 August 1911 to 7 November 1914 |  |
Alfred Meyer-Waldeck | Lead naval commander in the Siege of Tsingtao |
التاريخ اللاحق
On 15 August 1914, at the outbreak of World War I in Europe, Japan delivered an ultimatum to Germany demanding that it relinquish its control of the disputed territory of Kiaoutschou.[16] Upon rejection of the ultimatum, Japan declared war on 23 August and the same day its navy bombarded the German territory. On 7 November 1914, the bay was occupied by Japanese forces (see Siege of Tsingtao). Following resolution of the Shandong Problem, the occupied territory was returned to China on 10 December 1922 but the Japanese again occupied the area from 1937 to 1945 during the Second Sino-Japanese War.
انظر أيضاً
- China–Germany relations
- German colonial empire
- Eulenburg expedition
- Jiaozhou Governor's Hall, located in Qingdao.
- Tsingtao Brewery, Germany's enduring legacy to Chinese brewing
- Tsingtauer Neueste Nachrichten
الهامش
- ^ Gottschall, By Order of the Kaiser, p. 134; the treaty, signed September 1861, allowed Prussian warships to operate in Chinese waters for the protection of German trade and missionaries and promised swift retribution for crimes committed against German nationals by Chinese perpetrators
- ^ Gottschall, p. 156
- ^ Gottschall, p. 157
- ^ Gottschall, p. 160
- ^ Gottschall, p. 166
- ^ After German unification, Prussian Army Lieutenant General Albrecht von Stosch was appointed in 1872 the first chief of the Imperial Admiralty. He had no naval experience but brought significant administrative talent to his post – and he understood the power that emanated from “the tip of an army bayonet”. Stosch removed the small contingents of marines from the warships and instead trained the seamen of cruisers in the use of small arms, infantry tactics and amphibious landings [Gottschall, p. 42].
- ^ Gottschall, p. 161
- ^ Gottschall, p. 163
- ^ SMS Kaiserin Augusta became the flagship of a second cruiser division with SMS Deutschland and SMS Gefion and Cormoran; the two 4-ship divisions would form the 8-ship squadron
- ^ Gottschall, p. 176
- ^ Gottschall, p. 177
- ^ Toyokichi Iyenaga (Oct 26, 1914). "What is Kiaochou worth?". The Independent. Retrieved July 24, 2012.
- ^ Schultz-Naumann, Joachim (1985). Unter Kaisers Flagge: Deutschlands Schutzgebiete im Pazifik und in China einst und heute (in الألمانية). Universitas. p. 183. ISBN 978-3-8004-1094-1.
- ^ Schultz-Naumann, p. 182
- ^ Schultz-Naumann, p. 184
- ^ Duffy, Michael (22 August 2009). "Primary Documents - Count Okuma on the Japanese Capture of Tsingtao, 15 August 1914". firstworldwar.com. Retrieved 28 July 2014.
ببليوگرافيا
- Gottschall, Terrell D. By Order of the Kaiser, Otto von Diederichs and the Rise of the Imperial German Navy 1865–1902. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. 2003. ISBN 1-55750-309-5
- Schultz-Naumann, Joachim. Unter Kaisers Flagge, Deutschlands Schutzgebiete im Pazifik und in China einst und heute [Under the Kaiser's Flag, Germany's Protectorates in the Pacific and in China then and today]. Munich: Universitas Verlag. 1985.
- Schrecker, John E. Imperialism and Chinese Nationalism; Germany in Shantung. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. 1971.
- Steinmetz, George. The Devils' Handwriting: Precoloniality and the German Colonial State in Qingdao, Samoa, and Southwest Africa. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2007.
وصلات خارجية
- CS1: Julian–Gregorian uncertainty
- CS1 الألمانية-language sources (de)
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- Articles containing صينية-language text
- Pages using infobox country or infobox former country with the flag caption or type parameters
- Articles containing ألمانية-language text
- Pages using Lang-xx templates
- Articles with unsourced statements from October 2018
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- Concessions in China
- بلدان سابقة في التاريخ الصيني
- مستعمرات ألمانية سابقة
- Geography of Shandong
- History of Shandong
- History of Qingdao
- China–Germany relations
- Georgist communities
- مدن-دويلات
- 1898 establishments in the German colonial empire
- 1898 establishments in Asia
- 1998 disestablishments in Asia
- German-based pidgins and creoles