العائلة العظمى للپروتينات
العائلة العظمى للپروتينات protein superfamily، هي أكبر تجمع (فرع حيوي) للپروتينات التي يمكن من خلالها تتبع السلف المشترك (انظر التنادد). عادة ما يتم تتبع هذا السلف المشترك من خلال التراصف البنيوي[1] والتشابه الميكانيكي، حتى إذا لم يكن هناك أي تشابه في التسلسل.[2] بعد ذلك يمكن استنتاج تنادد التسلسل حتى لو لم يكن واضحاً (نظراً لانخفاض تشابه التسلسل). عادة ما تحتوي العائلات العظمى على عدة عائلات پروتين والتي تظهر تشابه التسلسل ضمن كل عائلة. يشيع استخدام مصطلح فرع الپروتين للإشارة إلى العائلات العظمى للپروتيز وهيدروليز الگليكوسيل تبعاً لنظام تصنيف MEROPS و[[CAZy].[2][3]
التحديد
يتم تحديد العائلات العظمى للپروتينات بعدة طرق. يمكن التعرف على الأفراد شديدة القرابة بطرق مختلفة لمن هم بحاجة لوضع الأعضاء الأكثر تباعدًا من الناحية التطورية ضمن مجموعات.
تشابه التسلسل

التشابه البنيوي
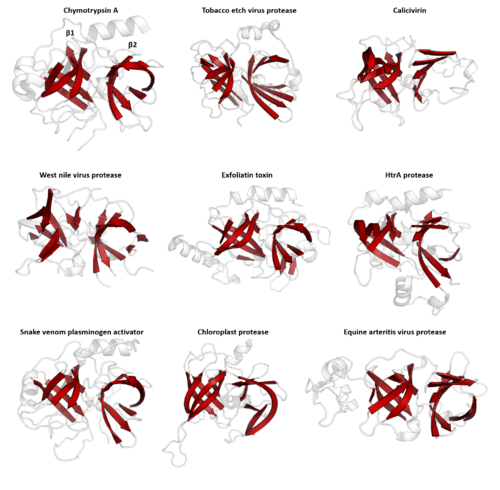
التشابه الميكانيكي
الأهمية التطورية
التنوع
أمثلة
مصادر العائلات العظمى للپروتينات
انظر أيضاً
- تراصف بنيوي
- نطاقات الپروتين
- عائلة الپروتين
- Protein mimetic
- بنية الپروتين
- تنادد
- قائمة عائلات الجينات
- SUPERFAMILY
- CATH
المصادر
- ^ Holm L, Rosenström P (July 2010). "Dali server: conservation mapping in 3D". Nucleic Acids Research. 38 (Web Server issue): W545-9. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq366. PMC 2896194. PMID 20457744.
- ^ أ ب Rawlings ND, Barrett AJ, Bateman A (January 2012). "MEROPS: the database of proteolytic enzymes, their substrates and inhibitors". Nucleic Acids Research. 40 (Database issue): D343-50. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr987. PMC 3245014. PMID 22086950.
- ^ Henrissat B, Bairoch A (June 1996). "Updating the sequence-based classification of glycosyl hydrolases". The Biochemical Journal. 316 ( Pt 2) (Pt 2): 695–6. PMC 1217404. PMID 8687420.
- ^ "Clustal FAQ #Symbols". Clustal. Retrieved 8 December 2014.
