جغرافيا طبيعية
- فيزيوغرافيا تحوّل إلى هنا. وقد تشير أيضاً إلى جيومورفولوجيا
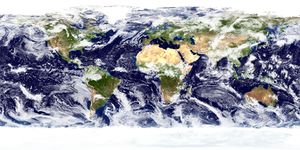
الجغرافيا الطبيعية Physical geography أو الفيزيوغرافيا Physiography هو العلم الذي يدرس الظواهر الطبيعية على سطح الأرض من حيث توزيع اليابس والماء والتضاريس وأشكال السطح والغلاف الجوي والغلاف الحيوي مما لم يتدخل فيه الإنسان. يهدف علم الجغرافيا الطبيعية إلى فهم شكل الأرض وتغيراتها المناخية وخصائص غطائها النباتي والحيواني.
مجالات الجغرافيا الطبيعية
- علم شكل الأرض وهو العلم الذي يدرس أشكال سطح الأرض ونشأتها وتطورها والعوامل التي أثرت فيها.
- علم المياه وهو العلم الذي يدرس توزيع المياه ومصادرها حركتها وجودتها على سطح الأرض.
- علم الجليد هو العلم الذي يدرس توزيع الجليد على سطح الأرض وآثاره عليها.
- جغرافيا أحيائية أو حيوية وهي علم توزيع الكائنات الحية جغرافيا.
- علم المناخ.
- علم التربة.
- علم دراسة الشواطئ.
- علم الجيوديسيا.
- علم الجغرافيا القديمة وهو العلم الذي يبحث في التطور الجغرافي للأرض خلال الأزمنة الجيولوجية.
أبرز علماء الجغرافيا الطبيعية

- إراتوستين (276 – 194 BC) who invented the discipline of geography.[1] He made the first known reliable estimation of the Earth's size.[2] He is considered the father of mathematical geography and geodesy.[2][3]
- پطليموس (ح. 90 – ح. 168)، who compiled Greek and Roman knowledge to produce the book Geographia.
- أبو ريحان البيروني (973 – 1048 AD), considered the father of geodesy.[4][5][التحقق مطلوب]
- ابن سينا (Avicenna, 980–1037), who formulated the law of superposition and concept of uniformitarianism in The Book of Healing.[بحاجة لمصدر]
- الإدريسي (Dreses, 1100 – c. 1165), who drew the Tabula Rogeriana, the most accurate world map in pre-modern times.[6]
- پيري ريس (1465 – c. 1554), whose Piri Reis map is the oldest surviving world map to include the Americas and possibly Antarctica
- جراردوس مركاتور (1512–1594), an innovative cartographer and originator of the اسقاط مركاتور.
- Bernhardus Varenius (1622–1650), Wrote his important work "General Geography" (1650), first overview of the geography, the foundation of modern geography.
- ميخائيل لومونوسوڤ (1711–1765), father of Russian geography and founded the study of glaciology.
- ألكسندر فون هومبولت (1769–1859)، يعتبر الأب المؤسس للجغرافيا الحديثة. Published Kosmos and founded the study of biogeography.
- Arnold Henry Guyot (1807–1884), who noted the structure of glaciers and advanced the understanding of glacial motion, especially in fast ice flow.
- لويس أگاسيز (1807–1873), the author of a glacial theory which disputed the notion of a steady-cooling Earth.
- ألفرد رسل والاس (1823–1913), founder of modern biogeography and the Wallace line.
- Vasily Dokuchaev (1840–1903), patriarch of Russian geography and founder of pedology.
- Wladimir Peter Köppen (1846–1940), developer of most important climate classification and founder of Paleoclimatology.
- William Morris Davis (1850–1934), father of American geography, founder of Geomorphology and developer of the geographical cycle theory.
- Walther Penck (1888–1923), proponent of the cycle of erosion and the simultaneous occurrence of uplift and denudation.
- السير إرنست شاكلتون (1874–1922), Antarctic explorer during the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration.
- Robert E. Horton (1875–1945), founder of modern hydrology and concepts such as infiltration capacity and overland flow.
- J Harlen Bretz (1882–1981), pioneer of research into the shaping of landscapes by catastrophic floods, most notably the Bretz (Missoula) floods.
- Luis García Sáinz (1894–1965), pioneer of physical geography in Spain.
- Willi Dansgaard (1922–2011), palaeoclimatologist and quaternary scientist, instrumental in the use of oxygen-isotope dating and co-identifier of Dansgaard-Oeschger events.
- هانز أوشگر (1927–1998), palaeoclimatologist and pioneer in ice core research, co-identifier of Dansgaard-Orschger events.
- Richard Chorley (1927–2002), a key contributor to the quantitative revolution and the use of systems theory in geography.
- السير نيكولاس شاكلتون (1937–2006), who demonstrated that oscillations in climate over the past few million years could be correlated with variations in the orbital and positional relationship between the Earth and the Sun.
- Stefan Rahmstorf (born 1960), professor of abrupt climate changes and author on theories of thermohaline dynamics.
انظر أيضاً
- Ecology
- Environmental science
- Environmental studies
- Human geography
- Geostatistics
- Weathering
- Physiographic regions of the world
المراجع
- ^ Eratosthenes (2010). Eratosthenes' "Geography". Fragments collected and translated, with commentary and additional material by Duane W. Roller. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0-691-14267-8.
- ^ أ ب Avraham Ariel, Nora Ariel Berger (2006)."Plotting the globe: stories of meridians, parallels, and the international". Greenwood Publishing Group. p.12. ISBN 0-275-98895-3
- ^ Jennifer Fandel (2006)."The Metric System". The Creative Company. p.4. ISBN 1-58341-430-4
- ^ Akbar S. Ahmed (1984). "Al-Beruni: The First Anthropologist", RAIN 60, p. 9-10.
- ^ H. Mowlana (2001). "Information in the Arab World", Cooperation South Journal 1.
- ^ S. P. Scott (1904), History of the Moorish Empire, pp. 461-2:
The compilation of Edrisi marks an era in the history of science. Not only is its historical information most interesting and valuable, but its descriptions of many parts of the earth are still authoritative. For three centuries geographers copied his maps without alteration. The relative position of the lakes which form the Nile, as delineated in his work, does not differ greatly from that established by Baker and Stanley more than seven hundred years afterwards, and their number is the same.
للاستزادة
- Holden, Joseph. (2004). Introduction to Physical Geography and the Environment. Prentice-Hall, London.
- Inkpen, Robert. (2004). Science, Philosophy and Physical Geography. Routledge, London.
- Pidwirny, Michael. (2014). Glossary of Terms for Physical Geography. Planet Earth Publishing, Kelowna, Canada. ISBN 9780987702906. Available on Google Play.
- Pidwirny, Michael. (2014). Understanding Physical Geography. Planet Earth Publishing, Kelowna, Canada. ISBN 9780987702944. Available on Google Play.
- Reynolds, Stephen J. et al. (2015). Exploring Physical Geography. [A Visual Textbook, Featuring more than 2500 Photographies & Illustrations]. McGraw-Hill Education, New York. ISBN 978-0-07-809516-0
- Smithson, Peter; et al. (2002). Fundamentals of the Physical Environment. Routledge, London.
{{cite book}}: Explicit use of et al. in:|author2=(help) - Strahler, Alan; Strahler Arthur. (2006). Introducing Physical Geography. Wiley,New York.
- Summerfield, M. (1991). Global Geomorphology. Longman, London.
- Wainwright, John; Mulligan, M. (2003). Environmental Modelling: Finding Simplicity in Complexity. John Wiley and Sons Ltd, London.
وصلات خارجية
- Physiography by T.X. Huxley, 1878, full text, physical geography of the Thames River Basin
- Fundamentals of Physical Geography, 2nd Edition, by M. Pidwirny, 2006, full text
- Physical Geography for Students and Teachers, UK National Grid For Learning

