قائمة الممالك في أفريقيا قبل الاستعمار
هذه قائمة الممالك في أفريقيا قبل الاستعمار.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
مقارنة
Vansina (1962) discusses the classification of Sub-Saharan African kingdoms, mostly of Central, South and East Africa, with some additional data on West African (Sahelian) kingdoms distinguishing five types, by decreasing centralization of power:
- despotic kingdoms: kingdoms where the king controls the internal and external affairs directly. Examples are Ruanda, Nkore, Soga and Kongo in the 16th century
- regal kingdoms: kingdoms where the king controls the external affairs directly, and the internal affairs via a system of overseers. The king and his chiefs belong to the same religion or group.
- incorporative kingdoms: kingdoms where the king only controls the external affairs with no permanent administrative links between him and the chiefs of the provinces. The hereditary chiefdoms of the provinces were left undisturbed after conquest. Examples are the Bamileke, Lunda, Luba, Lozi
- aristocratic kingdoms: the only link between central authority and the provinces is payment of tribute. These kingdoms are morphologically intermediate between regal kingdoms and federations. This type is rather common in Africa, examples including the Kongo of the 17th century, the Cazembe, Luapula, Kuba, Ngonde, Mlanje, Ha, Zinza and Chagga states of the 18th century.
- federations such as the Ashanti Union. Kingdoms where the external affairs are regulated by a council of elders headed by the king, who is simply primus inter pares.
The Islamic empires of North and Northeast Africa do not fall into this categorization and should be discussed as part of the Muslim world.
فترات التاريخ
التاريخ القديم (3600 ق.م.–500 م)
Ancient history refers to the time period beginning with the first records in writing, approximately 3600 BCE. It ends with the fall of several significant empires, such as the Western Roman Empire in the Mediterranean, the Han Dynasty in China, and the Gupta Empire in India, collectively around 500 CE.
العصر بعد الكلاسيكي (500–1500 م)
The Postclassical Era, also referred to as the Medieval period or, for Europe, the Middle Ages, begins around 500 CE after the fall of major civilizations, covering the advent of Islam. The period ends around 1450–1500, with events like the rise of moveable-type printing in Europe, the voyages of Christopher Columbus, and the Ottoman Empire's conquest of Constantinople.
التاريخ الحديث (1500م–الحاضر)
The Modern Period covers human history from the creation of a more global network (i.e. the discovery of the Americas by Europeans) to present day.
قائمة الممالك الأفريقية
Non-exhaustive list of known pre-colonial kingdoms and empires with their capital cities on the African continent.
شمال أفريقيا
القديمة
- Egyptian Empire (3150–30 BCE)
- Kingdom of Kerma (2500–1500 BCE)
- Kingdom of Kush (1070 BCE–350 CE)
- Carthaginian Empire (650–146 BCE)
- Kingdom of Blemmyes (600 BCE–3rd c. CE)
- Garamantes (500 BCE–700 CE)
- Ptolemaic Kingdom (306–30 BCE)
- Kingdom of Mauretania (285 BCE–431 CE and again (533–698 CE)
- Kingdom of Numidia (202–46 BCE)
- Kingdom of Makuria (340–1317 CE)
- Kingdom of Nobatia (350–650 CE)
- Kingdom of the Vandals and Alans (435–534 CE)
بعد الكلاسيكية
- Kingdom of Alodia (7th c.–1504 CE)
- Kingdom of Nekor (710–1019 CE)
- Barghawata Confederacy (744–1058 CE)
- Emirate of Sijilmassa (758–1055 CE)
- Rustamid imamate (Tahert area, 767–909 CE)
- Idrisid dynasty (Morocco, 789–974 CE)
- Aghlabids (Tunisia, 800-909)
- Fatimid Caliphate (910–1171)
- Hammadid dynasty (Western Ifriqiya, 1014–1152 CE)
- Zirid dynasty (Tunisia, 1048–1148 CE)
- Almoravid dynasty (Morocco, 1040–1147 CE)
- Khurasanid dynasty (1059–1128 & 1148–1158 CE)
- Almohad dynasty (Morocco, 1121–1269 CE)
- Ayyubid dynasty (Egypt, 1171–1254 CE)
- Hafsid dynasty (Tunisia, 1229–1574 CE)
- Kingdom of Tlemcen (Oranie, 1235–1556 CE)
- Marinid dynasty (Morocco, 1248–1465 CE)
- Mamluk Sultanate (Egypt, 1250–1517 CE)
- Wattasid dynasty (Morocco, 1420–1554 CE)
الحديثة
- Sultanate of Sennar (1504–1821 CE)
- Saadi principality of Sus and Tagmadert (1509–1554 CE)
- Saadi dynasty (Morocco, 1554–1659 CE)
- Naqsid principality of Tetouan (1597–1673 CE)
- Sultanate of Darfur (1603–1874 & 1898–1916 CE)
- Republic of Bou Regreg (1627–1668 CE)
- Alaouite dynasty (Morocco, 1666–current CE)
- Muhammad Ali dynasty (Egypt, 1914–1951 CE)
- Senussi dynasty (Libya, 1951–1969 CE)
شرق أفريقيا
القديمة
- Kingdom of Punt (2400–1069 BCE)
- Kingdom of Dʿmt (c. 980–400 BCE)
- Aksumite Empire (50–937 CE)
- Swahili Coast (50 AD–)
بعد الكلاسيكية
- Kingdom of Bazin (9th century CE)
- Kingdom of Belgin (9th century CE)
- Kingdom of Jarin (9th century CE)
- Kingdom of Qita'a (9th century CE)
- Kingdom of Nagash (9th century CE)
- Kingdom of Tankish (9th century CE)
- Empire of Kitara [1]
- Sultanate of Mogadishu (10th century–16th century CE)
- Kilwa Sultanate (960–1513 CE)
- Kingdom of Medri Bahri (1137–1890 CE)
- Ethiopian Empire (1137–1974 CE)
- Zagwe dynasty (1137–1270 CE)
- Solomonic dynasty (1270–1974 CE)
- Sultanate of Ifat (1285–1415 CE)
- Warsangali Sultanate (1298–1886 CE)
- Kingdom of Buganda (1300–present CE)
- Kingdom of Burundi (1500–1966 CE)
- Kingdom of Rwanda (1300–1959 CE)
- Ajuran Sultanate (14th century–17th century CE)
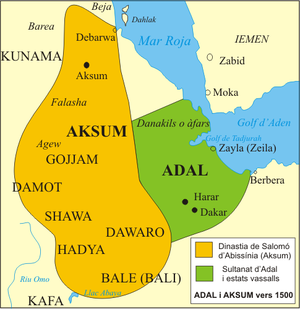
- Adal Sultanate (1415–1555 CE)
الحديثة
- Sennar Sultanate (1502–1821 CE)
- Dhulbahante garaadship (1530-1899 CE)
- Sultanate of the Geledi (late 17th century–late 19th century CE)
- Sultanate of Aussa (fl. 1734–present CE)
- Majeerteen Sultanate (mid-18th century–early 20th century CE)
- Kingdom of Gomma (early 19th century–1886 CE)
- Kingdom of Jimma (1830–1932 CE)
- Kingdom of Gumma (1840–1902 CE)
- Sultanate of Hobyo (1880s–1920s CE)
- Dervish State (1896–1920 CE)
غرب أفريقيا
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
القديمة
- Dhar Tichitt Civilization (1600–300 BCE)
- Nok Civilization (1000 BCE–300 CE)
- Djenné-Djenno Civilization (250 BCE–900 CE)
- Bura Civilization (300–1300 CE)
- Ghana Empire (300–1240 CE)
بعد الكلاسيكية
- Ghana Empire (300–1240 CE)
- Kingdom of Nri (948–1911 CE)
- Bonoman (11th–19th century CE)
- Mossi Kingdoms (11th century–1896 CE)
- Takrur (11th–13th century)
- Benin Empire (1180–1897 CE)
- Mali Empire (1235–1600 CE)
- Jolof Empire (1350–1549 CE)
- Wolof Empire (1350–1889 CE)
- Bornu Empire (1380–1893 CE)
- Oyo Empire (1400–1895 CE)
- Kingdom of Dagbon (1409–Ce?)
- Kingdom of Sine (14th–19th century CE)
- Songhai Empire (1464–1591 CE)
- Shilluk Kingdom (1490–1865 CE)
- Empire of Great Fulo (1490–1776 CE)
- Kingdom of Saloum (1494–1969 CE)
الحديثة
- Mamprussi (16th century CE–?)
- Kaabu Empire (1537–1867 CE)
- Kingdom of Cayor (1549–1879 CE)
- Kingdom of Baol (1555–1874 CE)
- Kingdom of Dahomey (1600–1900 CE)
- Aro Confederacy (1690–1902 CE)
- Asante Union (1701–1894 CE)
- Kong Empire (1710–1894 CE)
- Bamana Empire (1712–1861 CE)
- Sokoto Caliphate (1804–1904 CE)
- Wassoulou Empire (1878–1898 CE)
أفريقيا الوسطى
القديمة
- Sao Civilization (6th century BCE–16th century CE)
بعد الكلاسيكية
- Kanem–Bornu Empire (9th century–1900 CE)
- Kingdom of Kongo (1400–1888 CE)
الحديثة
- Sultanate of Bagirmi (1522–1897 CE)
- Luba Empire (1585–1885 CE)
- Kingdom of Ndongo (16th century–? CE)
- Kingdom of Matamba (1631–1744 CE)
- Wadai Empire (1635–1912 CE)
- Lunda Empire (1660–1887 CE)
- Kingdom of Lunda (1665–1887 CE)
- Kuba Kingdom (1600–present CE)
أفريقيا الجنوبية
بعد الكلاسيكية
- Kingdom of Mapungubwe (9th century–14th century CE)
- Kingdom of Zimbabwe (1220–1450 CE)
- Kingdom of Mutapa (1430–1760 CE)
- Kingdom of Butua (1450–1683 CE)
- Torwa dynasty (1450–1683 CE)
الحديثة
- Rozwi Empire (1660–1866 CE)
- Ndwandwe Kingdom (1780–1819 CE)
- Zulu Kingdom (1816–1897 CE)
- Merina Kingdom (18th century–1896 CE)
- Mthethwa Paramountcy (18th century–1820 CE)
انظر أيضاً
المراجع
- ^ Chrétien, Jean-Pierre; Scott Strauss (October 2006). The Great Lakes of Africa: Two Thousand Years of History. MIT Press.
المصادر
- Hunwick, John O. (2003). Timbuktu and the Songhay Empire: Al-Sa’di’s Ta’rikh Al-sudan Down to 1613 and other Contemporary Documents. Leiden: Brill Academic Publishers. pp. 488 Pages. ISBN 90-04-12822-0.
- J. Vansina, A Comparison of African Kingdoms, Africa: Journal of the International African Institute (1962), pp. 324–335.
- Turchin, Peter and Jonathan M. Adams and Thomas D. Hall: "East-West Orientation of Historical Empires and Modern States", Journal of World-Systems Research, Vol. XII, No. II, 2006
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .