ضلع حيدر آباد، السند
25°15′N 68°45′E / 25.250°N 68.750°E
Hyderabad district
| |
|---|---|
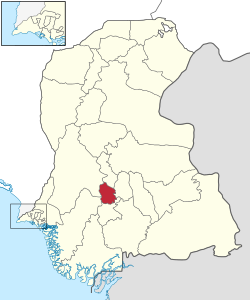 Map of Sindh with Hyderabad District highlighted | |
| Country | |
| Province | |
| Division | Hyderabad |
| Established | 1843 |
| أسسها | British government |
| Headquarters | Hyderabad |
| الحكومة | |
| • النوع | District Administration |
| • Deputy Commissioner | N/A |
| • District Police Officer | N/A |
| • District Health Officer | N/A |
| المساحة | |
| • الإجمالي | 1٬740 كم² (670 ميل²) |
| التعداد | |
| • الإجمالي | 2٬432٬540 |
| • الكثافة | 1٬400/km2 (3٬600/sq mi) |
| منطقة التوقيت | UTC+5 (PKT) |
| Number of Tehsils | 4 |
| الموقع الإلكتروني | www.hyderabad.gov.pk |
Hyderabad District (بالسندية: ضلعو حيدرآباد أردو: ضلع حیدرآباد),pronunciation is a district of Sindh, Pakistan. Its capital is the city of Hyderabad. The district is the second most urbanized in Sindh, after Karachi, with 80% of its residents live in urban areas.[2]
History
The East India Company occupied Sindh in 1843; They formed three districts in Sindh administratively: Hyderabad, Karachi and Shikarpur (now Larkana district).
In 1982, the largest area of the district in eastern side bifurcated to create a new district Thar and Parkar district with the headquarters Umerkot.
In 1907, create a new taluka named Nasrat from Sakrand and Shahdadpur taluka.
In 1912, the northern side of the district separated to form Nawabshah district.
In 1975, Southern side also separated to form Badin district.
After 1998 census, two new talukas created in the district named; Hyderabad city and Latifabad talukas.
After 2002 elections, a new taluka created in the district named Qasimabad from Hyderabad City taluka.
The city of Hyderabad is where the district headquarters were located and the district government used to be seated. The last Deputy Commissioner of the district was Rizwan Ahmed. Until the early 1970s the district included all the four districts mentioned above as well as the Badin district. This administrative setup was demolished by former President Pervez Musharraf in 2001 when he introduced the local body government.
In 2005, three new districts - Tando Muhammad Khan, Matiari and Tando Allahyar districts were formed out of Hyderabad district.[3]
Geography
Hyderabad District is 104,877 hectares in size.[4] 14,250 hectares of the district are under wheat cultivation, with a total annual production of over 55,000 tonnes.[4]
Administration and government
The district Administration is given below:
Demographics
| Year | Pop. | ±% p.a. |
|---|---|---|
| 1951 | 319٬232 | — |
| 1961 | 537٬000 | +5.34% |
| 1972 | 814٬060 | +3.85% |
| 1981 | 1٬005٬460 | +2.37% |
| 1998 | 1٬494٬866 | +2.36% |
| 2017 | 2٬199٬928 | +2.05% |
| 2023 | 2٬432٬540 | +1.69% |
| Sources:[6] | ||
At the time of the 2017 census, Hyderabad district had 430,611 households and a population of 2,199,928. Hyderabad had a sex ratio of 921 females per 1000 males and a literacy rate of 65.76%: 69.91% for males and 61.23% for females. 373,410 (16.97%) lived in urban areas. 541,027 (24.59%) were under 10 years of age.[7] In 2023, the district had 448,479 households and a population of 2,432,540.[1]
Religion
| Religion | Population (1941)[8] | Percentage (1941) | Population (2017)[7] | Percentage (2017) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hinduism |
115,015 | 53.51% | 180,926 | 8.22% |
| Islam |
97,762 | 45.48% | 1,998,896 | 90.86% |
| Sikhism |
1,587 | 0.74% | N/A | N/A |
| Christianity |
355 | 0.17% | 18,975 | 0.86% |
| Others [ب] | 214 | 0.10% | 1,131 | 0.06% |
| Total Population | 214,933 | 100% | 2,199,928 | 100% |
The majority religion is Islam, with 90.86% of the population. Hinduism (including those from Scheduled Castes) is practiced by 8.22%, while Christianity is practiced by 0.86% of the population.[7]
اللغات
At the time of the 2017 census, 43.44% of the population spoke سندي, 42.61% أردو, 4.45% پنجابي, 3.22% Pashto and 1.22% Saraiki as their first language. The majority of Urdu speakers live in Hyderabad city and its suburbs, where they form a majority, while Sindhi dominates rural areas. Muhajirs arrived in Hyderabad after Partition.[7]
List of Dehs
The following is a list of Hyderabad District's dehs, organised by taluka:[9]
- Hyderabad Taluka (70 dehs)
- Abri
- Agheemani
- Almani
- Alni
- Amilpur
- Barechani
- Barham
- Bhido Jagar
- Bhido Rayati
- Bhinpur
- Bilori
- Bohiki
- Boochki Jagir
- Boochki Rayati
- Buxo laghari
- Chacha Detha
- Chukhi
- Dachrapur
- Dali Nandi
- Dali Wadi
- Damanchani Rayati
- Dhamanchani Jagir
- Ghaliyoon
- Ghotana
- Gujjan
- Gul Mohd Thoro
- Halepota
- Hatri
- Hotki
- Hussain Khan Thoro
- Kajhur
- Kathri
- Kathro
- Khanpota
- Khunjejani
- Kunner
- Lashari
- Liyar Jagir
- Mati
- Miyano
- Moharo
- Moolan
- Mori Jagir
- Mori Rayati
- Mulki
- Narejani
- Noorai Jagir
- Noorai Rayati
- Panhwari
- Pasaikhi
- Patbhari
- Patoro
- Raees
- Rahooki
- Rajpari
- Rukanpur
- Sahita
- Sanhwar
- Seri Jagir
- Seri Rayati
- Sipki Jagir
- Sipki Rayati
- Sukhpur
- Takio Jeewan Shah Jagir
- Takio Jeewan Shah Rayati
- Tando Fazal
- Tando Qaiser
- Thaheem
- Theba
- Widh
- Qasimabad Taluka (4 dehs)
- Jamshoro
- Mirzapur
- Sari
- Shah Bukhari
- Latifabad Taluka (10 dehs)
- Bora reyati
- Ganjo Takar
- Giddu Bandar
- Goondar
- Khater
- Lakhi Keti
- Malh
- Mehrani
- Met Khan
- Nareja
- Hyderabad City Taluka (4 dehs)
- Foujgah
- Ghanghra
- Gujjo
- Hyderabad
See also
Notes
- ^ Hyderabad taluk of Hyderabad district. District and taluk borders have changed since 1961.
- ^ Including Jainism, Christianity, Buddhism, Zoroastrianism, Judaism, Ad-Dharmis, or not stated
References
- ^ أ ب "TABLE 1 : HOUSEHOLDS, POPULATION, HOUSEHOLD SIZE AND ANNUAL GROWTH RATE" (PDF). www.pbscensus.gov.pk. Pakistan Bureau of Statistics. 2023.
- ^ Azfar, Sara. "SINDH SECONDARY CITIES URBAN SECTOR ASSESSMENT" (PDF). URBAN MUNICIPAL SERVICES. ASIAN DEVELOPMENT BANK. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 February 2017. Retrieved 15 December 2017.
- ^ "Three new districts carved out of Hyderabad". TheDawn. 5 April 2005. Retrieved 31 July 2021.
- ^ أ ب Siyal, Altaf Ali (January 2015). "Remote Sensing and GIS based wheat crop acreage and yield estimation of district Hyderabad, Pakistan". Mehran University Research Journal of Engineering and Technology. Retrieved 14 December 2017.
- ^ "Tando Jam ٹندو جام - Latest News, Photos, Videos & Local Events of Tando Jam". UrduPoint (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2024-02-20.
- ^ "Population by administrative units 1951-1998" (PDF). Pakistan Bureau of Statistics.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح "District Wise Results / Tables (Census - 2017)". www.pbscensus.gov.pk. Pakistan Bureau of Statistics.
- ^ "CENSUS OF INDIA, 1941 VOLUME XII SINDH PROVINCE" (PDF).
- ^ "List of Dehs in Sindh" (PDF). Sindh Zameen. Retrieved 22 March 2021.
ببليوجرافيا
- 1998 District census report of Hyderabad. Census publication. Vol. 59. Islamabad: Population Census Organization, Statistics Division, Government of Pakistan. 1999.
قالب:Hyderabad District, Pakistan خطأ لوا في وحدة:Authority_control على السطر 278: attempt to call field '_showMessage' (a nil value).
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Pages using infobox settlement with no coordinates
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Articles containing سندي-language text
- Articles containing أردو-language text
- Pages using Lang-xx templates
- ضلع حيدر آباد، السند
- أضلع السند