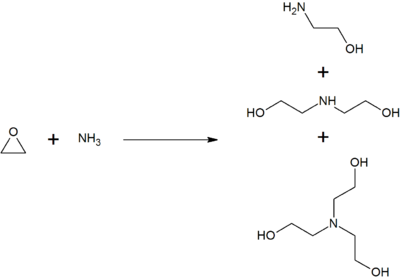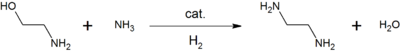إيثانولامين Ethanolamine

| |
| |
| الأسماء | |
|---|---|
| اسم أيوپاك المفضل
2-Aminoethan-1-ol[1] | |
أسماء أخرى
| |
| المُعرِّفات | |
| رقم CAS | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.004.986 |
| رقم EC |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| رقم RTECS |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| الخصائص | |
| الصيغة الجزيئية | C2H7NO |
| كتلة مولية | 61.08 g mol-1 |
| المظهر | Viscous colourless liquid |
| الرائحة | رائحة كريهة شبيهة للأمونيا |
| الكثافة | 1.0117 g/cm3 |
| نقطة الانصهار | |
| نقطة الغليان | |
| قابلية الذوبان في الماء | Miscible |
| ضغط البخار | 64 Pa (20 °س)[2] |
| الحموضة (pKa) | 9.50[3] |
| معامل الانكسار (nD) | 1.4539 (20 °س)[4] |
| المخاطر | |
| صفحة بيانات السلامة | سيگما [5] |
| ن.م.ع. مخطط تصويري |  
|
| ن.م.ع. كلمة الاشارة | خطر |
| H302, H312, H314, H332, H335, H412[5] | |
| P261, P273, P303+P361+P353, P305+P351+P338[5] | |
| NFPA 704 (معيـَّن النار) | |
| نقطة الوميض | 85 °C (185 °F; 358 K) (وعاء مغلق) |
| 410 °C (770 °F; 683 K) | |
| حدود الانفجار | 5.5–17% |
| الجرعة أو التركيز القاتل (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (الجرعة الوسطى)
|
|
| حدود التعرض الصحية بالولايات المتحدة (NIOSH): | |
PEL (المسموح)
|
TWA: 3 ppm (6 ملج/م3)[6] |
REL (الموصى به)
|
|
IDLH (خطر عاجل)
|
30 ppm[6] |
| مركبات ذا علاقة | |
مركـّبات ذات علاقة
|
|
ما لم يُذكر غير ذلك، البيانات المعطاة للمواد في حالاتهم العيارية (عند 25 °س [77 °ف]، 100 kPa). | |
| مراجع الجدول | |
الإيثانولامين (Ethanolamine)، ويسمى أيضا 2-إيثانول أو إيثانولامين أحادي (ويختصر ETA أو MEA)، هو مركب كيميائي عضوي يتواجد في الطبيعة وصيغته HOCH 2CH 2NH 2 أو C 2H 7NO.[8] جزيء الإيثانولامين ثنائي الوظيفة، يحتوي على كل من أمين أولي وكحول أولي. الإيثانولامين هو سائل عديم اللون، لزج، وله رائحة تشبه الأمونيا.[9]
عادة ما يُطلق على الإيثانولامين اسم الإيثانولامين الأحادي أو MEA لتمييزه عن الإيثانولامين الثنائي (DEA) والإيثانولامين الثلاثي (TEOA). تتألف الإيثانولامينات من مجموعة من الكحولات الأمينية. تُحدد فئة من مضادات الهيستامين على أنها إيثانولامينات، والتي تشمل الكاربينوكسامين، الكليماستين، الدايمنهيدرينات، الكلورفينوكسامين، الدايفينهيدرامين، والدوكسيلامين.[10]
الإيثانولامين في الطبيعة
جزيئات الإيثانولامين هي إحدى مكونات تكوين الأغشية الخلوية وبالتالي فهي كتلة بناء جزيئية للحياة. الإيثانولامين هو ثاني أكثر مجموعة رئيسية وفرةً للدهون الفسفورية، وهي مواد موجودة في الأغشية الحيوية (خاصة تلك الموجودة في بدائيات النوى)؛ على سبيل المثال، إثيانولامين الفوسفاتيديل. كما يستخدم في جزيئات الرسول مثل إيثانولاميد الپالميتويل، الذي يتمتع بتأثير على مستقبلات CB1.[11]
كان يُعتقد أن جزيئات الإيثانولامين موجودة فقط على كوكب الأرض وعلى بعض الكويكبات، لكن عام 2021 عُثر على أدلة على وجود جزيئات الإيثانولامين في الفضاء بين النجوم.[12]
يُخلق الإيثانولامين حيوياً بواسطة نزع كربوكسيل السيرين:[13]
- HOCH 2CH(CO 2H)NH 2 → HOCH 2CH 2NH 2 + CO2
مشتقات الإيثانولامين منتشرة على نطاق واسع في الطبيعة؛ على سبيل المثال، الدهون، كمركبات طليعية لمجموعة متنوعة من ن-أسيل إيثانولامين (NAEs)، التي تعدل العديد من العمليات الفسيولوجية الحيوانية والنباتية مثل الإنبات، تفاعلات النبات مع مسببات الأمراض، وتطور الصانعات اليخضورية، والإزهار،[14] بالإضافة إلى ذلك، كمركب طليعي، يتحد الإيثانولامين مع حمض الأراكيدونيك C 20H 32O 2 20:4، ω-6)، لتكوين أنانداميد الإندوكانابينويد (AEA: C 22H 37NO 2; 20:4, ω-6).[15]
يتحلل الإيثانولامين حيوياً بواسطة إيثانولامين أمونيا لياز، وهو إنزيم يعتمد على ڤيتامين ب12. يتم تحويله إلى أسيتالدهيد وأمونيا من خلال التجريد الأولي لذرة الهيدروجين.[16]
- H
2NCH
2CH
2OH → NH
3 + CH
3CHO
الانتاج الصناعي
يُنتج الإيثانولامين الأحادي عن طريق معالجة أكسيد الإيثيلين مع الأمونيا المائية؛ ينتج التفاعل أيضاً ثنائي إيثانول أمين وثلاثي إيثانول أمين. يمكن التحكم في نسبة المنتجات عن طريق قياس اتحادية المواد المتفاعلة.[17]
حجم الإنتاج وأكبر المنتجين
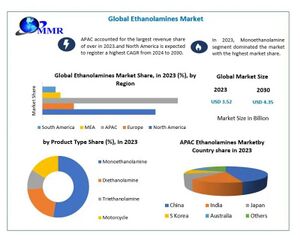
عام 2023 بلغ حجم سوق سوق اللعالمي للإيثانولامين بنحو 3.66 بليون دولار أمريكي، ومن المتوقع أن ينمو من 3.83 بليون دولار في عام 2024، ليصل إلى إلى 5.73 بليون دولار بحلول عام 2032، بمعدل نمو سنوي مركب قدره 5.2% خلال الفترة المتوقعة. عام 2023 سيطرت منطقة آسيا والهادي على سوق الإيثانولامين بحصة سوقية بلغت 44.54%.[18]
كان لجائحة كوڤيد-19 تأثير سلبي على تقدم السوق حيث أدى التباطؤ الكبير في الأنشطة الاقتصادية العالمية إلى انخفاض الطلب على الإيثانولامين في العديد من القطاعات، بما في ذلك المعادن والنفط والغاز والمنسوجات. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، كان لانقطاعات سلسلة التوريد والتغيرات الشديدة في أسعار المواد الخام تأثير كبير على توقعات السوق. ومع ذلك، تفتح البلدان حدودها للتجارة الدولية، مما أدى إلى زيادة الطلب على المواد الكيميائية الصناعية. ومن المتوقع أن يساعد هذا العامل السوق على النمو في المستقبل.
هيمنت منطقة آسيا-الهادي على السوق العالمية للإيثانولامين عام 2023 بسبب النمو القوي لقطاعي المنظفات والإيثيلينامينات. تقود الصين السوق الإقليمية حيث تعتبر البلاد مركزاً للتصنيع. سيعمل هذا الاتجاه على دفع نمو السوق في المنطقة. علاوة على ذلك، ينمو السوق في الهند أيضاً بوتيرة ملحوظة بسبب الاستخدام المتزايد لهذا المنتج في صناعات النسيج. ومن المتوقع أن تشهد أمريكا الشمالية نمواً كبيراً في السنوات القادمة حيث تحتل الولايات المتحدة مكانة بارزة في السوق، وتستحوذ على حصة كبيرة من إجمالي حصة السوق في المنطقة. يتميز سوق أمريكا الشمالية بالطلب المتزايد على تطبيقات تنقية الغاز وتنظيف المعادن، مما سيؤدي بدوره إلى زيادة استهلاك الإيثانولامينات في المنطقة.
ومن المتوقع أن تشهد أوروپا نمواً ثابتاً في السنوات القادمة، وذلك بفضل الاستخدام الواسع النطاق للمنتج في العديد من الصناعات، بما في ذلك المنظفات والمنسوجات. ومن الجدير بالذكر أن ألمانيا وفرنسا والمملكة المتحدة هي الدول الرئيسية المساهمة في نمو سوق الإيثانولامين في أوروپا. ويرتبط نمو السوق في أمريكا اللاتينية بالطلب المتزايد على المنتجات في قطاعات مثل تنظيف المنازل وتنقية الغاز. ويرتفع الطلب على هذه المنتجات بشكل استثنائي في البرازيل والمكسيك والأرجنتين، وهي من بين أبرز محركات السوق للمواد الكيميائية الوسيطة في المنطقة. خلال الفترة المتوقعة، من المتوقع أن يشهد السوق في الشرق الأوسط وأفريقيا نمواً كبيراً. ويرجع هذا النمو إلى زيادة أنشطة التنقيب عن النفط والغاز في المنطقة، مما أدى إلى زيادة الطلب على الإيثانولامين لأنشطة التنقية. نتيجة لذلك، سيشهد السوق في هذه المناطق نمواً ملحوظاً خلال الفترة المتوقعة.
اعتباراً من أكتوبر 2024، كان سعر الطن المتري المحلي من الإيثانوملاين في الصين يتراوح بين 6000 و7500 يوان.[19]
أكبر المصنعين
القائمة التالية لأكبر الشركات المصنعة للإيثانولامين:
- باسف، ألمانيا
- داو للكيماويات، الولايات المتحدة
- شركة إندورما المحدودة، تايلاند
- آنيوس، الممكلة المتحدة
- نوريون هولندا
- سابك، السعودية
- مجموعة سيناتز أوكا، روسيا
- OUCC، تايوان
- كانتو كاگاكو، اليابان
- جاي دانش للكيماويات، الهند
التطبيقات
تُستخدم الإيثانولامينات كمواد خام في إنتاج المنظفات، المستحلبات، الملمعات، المستحضرات الصيدلانية، مثبطات التآكل، الوسائط الكيميائية.[9]
على سبيل المثال، يؤدي تفاعل الإيثانولامين مع الأمونيا إلى إنتاج ثنائي أمين الإيثيلين، وهو مركب طليعي لعامل التخلب المستخدم بشكل شائع، ثنائي أمين الإيثيلين رباعي حمض الأسيتيك (EDTA).[17]
تنقية تيار الغاز
يمكن للإيثانولامين الأحادي تنقية انبعاثات ثاني أكسيد الكربون من الفحم المحترق والميثان المحترق والغاز الحيوي المحترق بكفاءة عالية. كما تستخدم عملية تنقية ثاني أكسيد الكربون بواسطة الإيثانولامين الأحادي لتجديد الهواء في الغواصات.
تُستخدم محاليل الإثيانولامين في الماء كتيار غازي لغسل السائل في معالجات الأمين.[20] على سبيل المثال، يُستخدم الإثيانولامين المائي لإزالة ثاني أكسيد الكربون وكبريتيد الهيدروجين من تيارات الغاز المختلفة؛ على سبيل المثال، غاز المداخن والغاز المر.[21] يقوم الإثيانولامين بتأين المركبات الحمضية المذابة، مما يجعلها قطبية وأكثر قابلية للذوبان بشكل كبير.
يمكن إعادة تدوير محاليل تنقية الإثيانولامين من خلال وحدة إعادة التجديد. عند تسخينها، تطلق الإثيانولامين، باعتباره قاعدة ضعيفة إلى حد ما، غاز كبريتيد الهيدروجين أو ثاني أكسيد الكربون المذاب مما ينتج عنه محلول إثيانولامين نقي.[17][22]
استخدامات أخرى
في المستحضرات الصيدلانية، يستخدم الإيثانولامين في المقام الأول لتخزين أو تحضير المستحلبات. يمكن استخدام الإيثانولامين كمنظم لدرجة الحموضة في مستحضرات التجميل.[23]
الإيثانولامين هو مادة تصلب قابلة للحقن كخيار علاجي للبواسير العرضية. يمكن حقن 2-5 مل من أحادي الإيثانولامين في الغشاء المخاطي فوق البواسير مباشرة للتسبب في التقرح وتثبيت الغشاء المخاطي وبالتالي منع البواسير من النزول خارج القناة الشرجية.
كما يعتبر أحد مكونات سائل تنظيف زجاج السيارات الأمامي.[24]
أمين للتحكم في درجة الحموضة
غالباً ما يستخدم الإيثانولامين في قلوية الماء في دورات البخار لمحطات الطاقة، بما في ذلك محطات الطاقة النووية التي تحتوي على مفاعلات ماء مضغوط. تُجرى هذه القلوية للتحكم في تآكل المكونات المعدنية. يتم اختيار الإيثانولامين (أو أحياناً أمين عضوي مشابه؛ على سبيل المثال، المورفالين) لأنه لا يتراكم في مولدات البخار (الغلايات) والشقوق بسبب تقلبه، بل يتوزع بشكل موحد نسبياً طوال دورة البخار بالكامل. في مثل هذا التطبيق، يعد الإيثانولامين مكوناً رئيسياً لما يسمى "المعالجة الكاملة المتطايرة" للمياه (AVT).[بحاجة لمصدر]
التفاعلات
عند التفاعل مع ثاني أكسيد الكربون، يتفاعل مكافئان من الإيثانولامين من خلال وسيط حمض الكربونيك لتكوين ملح الكربامات،[25] الذي عند تسخينه يعمل على تكوين الإيثانولامين وثاني أكسيد الكربون.
الاقتصاد
رداً على العقوبات التجارية المفروضة عليها، قررت الصين في نهاية أكتوبر 2024 فرض رسوم مكافحة إغراق لخمس سنوات على الإيثانولامين من الولايات المتحدة (بنسبة 76.0%-97.1%) وعلى الوارد من السعودية (بنسبة 10.1%-27.9%).[26]
المصادر
- ^ أ ب Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry : IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013 (Blue Book). Cambridge: The Royal Society of Chemistry. 2014. pp. 649, 717. doi:10.1039/9781849733069-FP001. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
For example, the name 'ethanolamine', which is still widely used, is badly constructed because of the presence of two suffixes; it is not an alternative to the preferred IUPAC name, '2-aminoethan-1-ol'.
- ^ "Ethanolamine MSDS" (PDF). Acros Organics. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-07-15.
- ^ Hall, H.K. (1957). "Correlation of the Base Strengths of Amines". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 79 (20): 5441–4. doi:10.1021/ja01577a030.
- ^ Reitmeier, R.E.; Sivertz, V.; Tartar, H.V. (1940). "Some Properties of Monoethanolamine and its Aqueous Solutions". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 62 (8): 1943–44. doi:10.1021/ja01865a009.
- ^ أ ب ت Sigma-Aldrich Co., Ethanolamine. Retrieved on 2018-05-24.
- ^ أ ب ت NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards 0256
- ^ "Ethanolamine". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "National Library of Medicine. PubChem. Ethanolomine". NIH, National Library of Medicine. Retrieved September 5, 2021.
- ^ أ ب Martin Ernst; Johann-Peter Melder; Franz Ingo Berger; Christian Koch (2022). "Ethanolamines and Propanolamines". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a10_001.pub2.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|authors=(help) - ^ Cough, Cold, and Allergy Preparation Toxicity at eMedicine
- ^ Calignano, A; La Rana, G; Piomelli, D (2001). "Antinociceptive activity of the endogenous fatty acid amide, palmitylethanolamide". European Journal of Pharmacology. 419 (2–3): 191–8. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(01)00988-8. PMID 11426841.
- ^ "First evidence of cell membrane molecules in space". Astronomy Magazine. May 28, 2021. Retrieved September 4, 2021.
- ^ "Phosphatidylethanolamine and related lipids". AOCS. Archived from the original on 2012-08-21. Retrieved 2015-08-09.
- ^ Coutinho, Bruna G.; Mevers, Emily; Schaefer, Amy L.; Pelletier, Dale A.; Harwood, Caroline S.; Clardy, Jon; Greenberg, E. Peter (2018-09-25). "A plant-responsive bacterial-signaling system senses an ethanolamine derivative". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 115 (39): 9785–9790. Bibcode:2018PNAS..115.9785C. doi:10.1073/pnas.1809611115. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 6166808. PMID 30190434.
- ^ Marzo, V. Di; Petrocellis, L. De; Sepe, N.; Buono, A. (1996-06-15). "Biosynthesis of anandamide and related acylethanolamides in mouse J774 macrophages and N18 neuroblastoma cells". Biochemical Journal. 316 (Pt 3): 977–84. doi:10.1042/bj3160977. PMC 1217444. PMID 8670178.
- ^ Shibata, Naoki; Tamagaki, Hiroko; Hieda, Naoki; Akita, Keita; Komori, Hirofumi; Shomura, Yasuhito; Terawaki, Shin-Ichi; Mori, Koichi; Yasuoka, Noritake; Higuchi, Yoshiki; Toraya, Tetsuo (2010). "Crystal Structures of Ethanolamine Ammonia-lyase Complexed with Coenzyme B12 Analogs and Substrates". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 285 (34): 26484–26493. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.125112. PMC 2924083. PMID 20519496.
- ^ أ ب ت Weissermel, Klaus; Arpe, Hans-Jürgen; Lindley, Charlet R.; Hawkins, Stephen (2003). "Chap. 7. Oxidation Products of Ethylene". Industrial Organic Chemistry. Wiley-VCH. pp. 159–161. ISBN 3-527-30578-5.
- ^ "Ethanolamine Market Size, Share & Industry Analysis". fortunebusinessinsights.com. 2024-10-14. Retrieved 2024-10-29.
- ^ "Ethanolamine China Domestic Price". echemi.com. 2024-10-28. Retrieved 2024-10-29.
- ^ Chremos A, et al. (August 2015). "Modelling the phase and chemical equilibria of aqueous solutions of alkanolamines and carbon dioxide using the SAFT-γ SW group contribution approach". Fluid Phase Equilibria. 407: 280. doi:10.1016/j.fluid.2015.07.052. hdl:10044/1/25382.
- ^ Emergency and Continuous Exposure Guidance Levels for Selected Submarine Contaminants. 2007. doi:10.17226/11170. ISBN 978-0-309-09225-8.
- ^ "Ethanolamine". Occupational Safety & Health Administration. Archived from the original on 2013-05-03. Retrieved 2008-05-11.
- ^ Carrasco, F. (2009). "Ingredientes Cosméticos". Diccionario de Ingredientes Cosméticos 4ª Ed. www.imagenpersonal.net. p. 306. ISBN 978-84-613-4979-1.
- ^ Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards. U.S. Department of Transportation, National Highway Traffic Safety Administration. 1994. p. Part 571; S 108—PRE 128.
- ^ Lu, Yanyue; Liao, Anping; Yun, Zhuge; Liang, Yanqing; Yao, Qinmei (2014). "Absorption of Carbon Dioxide in Ethanolamine Solutions". Asian Journal of Chemistry. 26 (1): 39–42. doi:10.14233/ajchem.2014.15301.
- ^ "China to retain anti-dumping duties on US, Saudi Arabian, Asian ethanolamine imports for 5 years". رويترز. 2024-10-29. Retrieved 2024-10-29.