هپارين
 | |
 | |
| البيانات السريرية | |
|---|---|
| فئة السلامة أثناء الحمل |
|
| مسارات الدواء | i.v., s.c. |
| رمز ATC | |
| الحالة القانونية | |
| الحالة القانونية |
|
| بيانات الحركية الدوائية | |
| التوافر الحيوي | nil |
| الأيض | hepatic |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5 hrs |
| الإخراج | ? |
| المعرفات | |
| رقم CAS | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.698 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
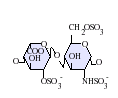
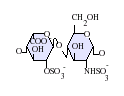
| التركيب | C12H19NO20S3 |
| الكتلة المولية | 12000–15000 g/mol |
الهپارين بالإنجليزية Heparin ، هو مادة مضادة للتخثر وهو من مكونات الدم الأساسية ولكنه يوجد بتركيز لا يكفي لمنع تخثر الدم ، ويتولد الهيبارين من خلايا الكبد فهو موجود بتركيز عالي في الكبد كما أنه موجود أيضا في الخلايا الرئوية وقد أمكن فصله وعزله بشكل ملح متبلور من مستخلص الكبد و الرئة ويتميز عن غيره بكونه لا يتداخل معه أي اختبار من اختبارات التحليل الكيميائي ، والهيبارين عبارة عن ميكوتين عديد حمض الكبريتيك Muccoitin Polysulphouric – Acid وهو من السكريات المتعددة ويمكن الحصول عليه تجاريا في الوقت الحاضر من أملاح الصوديوم Sodium Heparin أو ملح البوتاسيوم Potassium Heparin أو ملح الليثيوم Lithium Heparin. [1]
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
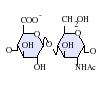
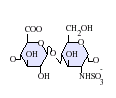
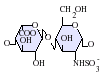
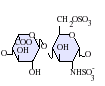
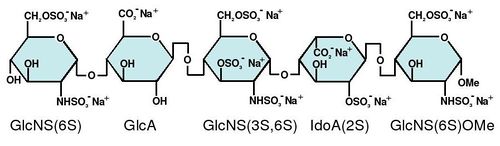
التركيب
- خطأ في إنشاء صورة مصغرة: convert: no images defined `/tmp/transform_91741984639a.png' @ error/convert.c/ConvertImageCommand/3258. Error code: 1
IdoA(2S)-GlcNS
عمل الهپارين
يعمل الهيبارين كمضاد للثرومبين Antithrombin حيث يمنع نقل أو تحويل البروثرومبين Prothrombin إلى ثرومبين Thrombin وهكذا يمنع تكوين الفيبرين Fibrin إلى الفيبرينوجين Fibrinogen.
الإختصارات
- GlcA = β-D-glucuronic acid
- IdoA = α-L-iduronic acid
- IdoA(2S) = 2-O-sulfo-α-L-iduronic acid
- GlcNAc = 2-deoxy-2-acetamido-α-D-glucopyranosyl
- GlcNS = 2-deoxy-2-sulfamido-α-D-glucopyranosyl
- GlcNS(6S) = 2-deoxy-2-sulfamido-α-D-glucopyranosyl-6-O-sulfate
تركيب ثلاثي الأبعاد
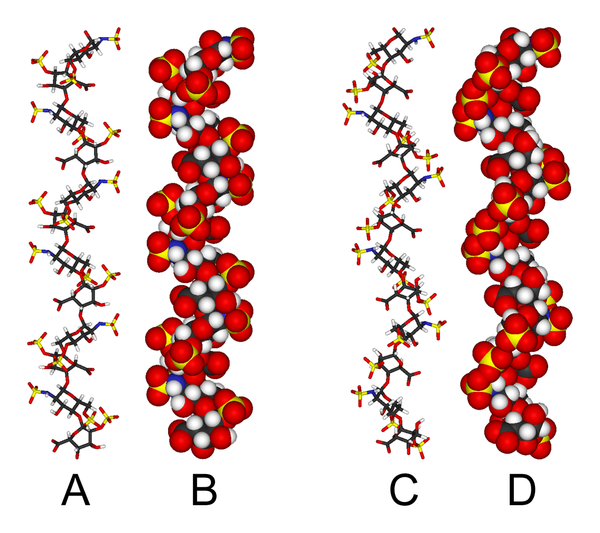
في المنظر العلوي:
- A = 1HPN (all IdoA(2S) residues in 2S0 conformation) Jmol viewer
- B = van der Waals radius space filling model of A
- C = 1HPN (all IdoA(2S) residues in 1C4 conformation) Jmol viewer
- D = van der Waals radius space filling model of C
الإستعمال الطبي
إستعمالات مادة الهيباريين:
1- في حالات الذبحة الصدرية الغير مستقرة.
2- في حالات إحتشاء الجدار الأمامي لعضلة القلب أو عندما يكون الأحتشاء كبير أو مصاحب لهبوط في عضلة القلب التي ربما تساعد على تكون كتل دموية متجلطة داخل تجويف القلب.
3- في حالات بقاء المريض مدة طويلة بالفراش دون حركة لمنع حدوث جلطة بالساقين.
4- لمرضى القلب الحوامل لمن يحتاجوا مسيلات أو مميعات الدم مدى الحياة فيستبدل الوارفارين بالهيباريين خاصة فترة الثلاث أشهر الأولى من الحمل.
5- في حالات الجلطات الرئوية أو جلطات الساقين.
التاريخ
يعتبر الهيبارين واحدا من أقدم المواد الطبية ، والتي أصبحت تستخدم الآن على نطاق واسع. وقد تم إكتشافه في عام 1916 قبل إعلان Food and Drug Administration الأمريكية ، لذلك لم يدخل للإختبارات المعملية قبل عام 1935.[2] وقد تم فصل الهيبارين أول مرة من كبد كلب ، وجاء تسميته من (hepar أو"ηπαρ" الإسم اليواني لكلمة "كبد"). وقد إعتمد هذا الإكتشاف على عالمين هما؛ جاي مكلين ، و وليام هنري هويل.
فرص تطوير أدوية حديثة بالهپارين
As detailed in the table below, there is a great deal of potential for the development of heparin-like structures as drugs to treat a wide range of diseases, in addition to their current use as anticoagulants.[3][4]
| مراحل المرض الحساسة للهپارين | تأثير الهپارين في النماذج التجريبية | الوضع الاكلينيكي |
| Adult respiratory distress syndrome | Reduces cell activation and accumulation in airways, neutralizes mediators and cytotoxic cell products, and improves lung function in animal models | Controlled clinical trials |
| Allergic encephalomyelitis | Effective in animal models | - |
| Allergic rhinitis | Effects as for adult respiratory distress syndrome, although no specific nasal model has been tested | Controlled clinical trial |
| Arthritis | Inhibits cell accumulation, collagen destruction and angiogenesis | Anecdotal report |
| Asthma | As for adult respiratory distress syndrome, however it has also been shown to improve lung function in experimental models | Controlled clinical trials |
| Cancer | Inhibits tumour growth, metastasis and angiogenesis, and increases survival time in animal models | Several anecdotal reports |
| Delayed type hypersensitivity reactions | Effective in animal models | - |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | Inhibits inflammatory cell transport in general. No specific model tested | Controlled clinical trials |
| Interstitial cystitis | Effective in a human experimental model of interstitial cystitis | Related molecule now used clinically |
| Transplant rejection | Prolongs allograph survival in animal models | - |
- indicates no information available
As a result of heparin's effect on such a wide variety of disease states a number of drugs are indeed in development whose molecular structures are identical or similar to those found within parts of the polymeric heparin chain.[3]
| Drug molecule | Effect of new drug compared to heparin | Biological activities |
| Heparin tetrasaccharide | Non-anticoagulant, non-immunogenic, orally active | Anti-allergic |
| Pentosan polysulfate | Plant derived, little anticoagulant activity, Anti-inflammatory, orally active | Anti-inflammatory, anti-adhesive, anti-metastatic |
| Phosphomannopentanose sulfate | Potent inhibitor of heparanase activity | Anti-metastatic, anti-angiogenic, anti-inflammatory |
| Selectively chemically O-desulphated heparin | Lacks anticoagulant activity | Anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, anti-adhesive |
وصلات خارجية
المصادر
- ^ طبيب دوت كوم
- ^ Linhardt RJ. (1991). "Heparin: An important drug enters its seventh decade". Chem. Indust. 2: 45–50.
- ^ أ ب Lever R. and Page C.P. (2002). "Novel drug opportunities for heparin". Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 1 (2): 140–148. doi:10.1038/nrd724. PMID 12120095.
- ^ Coombe D.R and Kett W.C. (2005). "Heparan sulfate-protein interactions: therapeutic potential through structure-function insights". Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 62 (4): 410–424. doi:10.1007/s00018-004-4293-7. PMID 15719168.
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Infobox-drug molecular-weight unexpected-character
- Pages using infobox drug with unknown parameters
- Articles without EBI source
- Chemical pages without ChemSpiderID
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- Anticoagulants
- Glycosaminoglycans