قاطرة بخارية
قاطرة بخارية
تاريخ
أول صانع للقطارات هو ريتشارد تريفيثيك (1833 – 1771) من بلاد الغال فسنة 1803م أوعز اليه بصنع قاطرة بخارية قادرة على الربط بين مصاهر الحديد ببنيرام وقرية أبرسينون التي تبعد حوالي خمسة عشر كلم . فأنجز قاطرة تزن خمسة أطنان أطلق عليها اسم "ساوث ويلس" وفي أول تجربة لها يوم 24 فيفري 1804م جرت وراءها حمولة تزن 20 طناً وبسرعة 8 كلم في الساعة . ثم ستجر بعد ذلك 25 طناً إلا أن ثقلها أحدث عطباً في السكة فوضع حد لتجريبها . وعلى كل حال فقد برهن هكذا على أن الأحمال الثقيلة الهامة يمكن جرها بفضل التصاق العجلات بالسكة باستعمال جرارة من ذلك القبيل
معارض القاطرات البخارية
- UK
- Carter's Steam Fair - touring vintage fairground, including several rides powered by steam engines
- Great Dorset Steam Fair - 5-day annual show in England - specialises in showing engines being used in their original context: heavy haulage, threshing, ploughing, sawing, road making, etc
- USA
- Antique Gas & Steam Engine Museum - Bi-Annual show in Vista, CA, Specializing in farm equipment, engines, and machinery from 1850-1950
- Rock River Thresheree, Inc. 4-day annual show in Edgerton, Wisconsin held every Labor Day weekend; many agricultural and industrial steam-powered machines
متاحف القاطرات البخارية
- See also: List of pumping stations, many of which are, or were, steam-powered.
- UK
- Bolton Steam Museum
- Crofton Beam Engines (Movie of Crofton engines operating)
- Hollycombe Steam Collection
- Kempton Park Steam Engines
- Kew Bridge Steam Museum
- The New England Wireless and Steam Museum ([1])
- Canada
- Ontario Agricultural Museum in Milton, Ontario
- Steam Era in Milton, Ontario
ملاحظات
^ E.C.E.: An external combustion engine has heat supplied to the working fluid of the power cycle by an external source. The external combustion engine allows the burning of virtually any fuel as the heat source for the engine. This explains the success of this engine, because less expensive and/or more renewable or sustainable fuel or heat sources can be used, because the working fluid remains separated from the fuel, and therefore cleaner, which results in less maintenance and longer engine life.
This is contrasted to the generally more familiar form of heat engine (known as an internal combustion engine) in which the working fluid of the power cycle is the gaseous products of the combustion process, and the heat is added to the cycle by combustion of fuel internal to the machine. Typical gasoline/petrol and diesel engines are internal combustion engines.(see: Otto cycle)
Steam engines have therefore been classed among external combustion engines.
^ Patents:
Harold Holcroft in his 7859 25 patent dated November 1909: Improvements in or relating to valve gears for engines worked by fluid pressure[Holcroft steamindex], as does Arturo Caprotti:170,877 Improvements in valve gears for elastic-fluid engines. Published: 4 November 1921. Application number: 12341/1920. Applied: 4 May 1920; 13261/1907. Improvements in steam turbines and other multiple expansion elastic fluid prime movers. Applied 7 June 1907 (in Italy 7 June 1906). Published 7 August 1908.
الكفاءة
A steam locomotive – a GNR N2 Class No.1744 at Weybourne nr. Sheringham, Norfolk
A steam-powered bicycle by John van de Riet, in Dortmund
British horse-drawn fire engine with steam-powered water pump
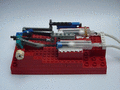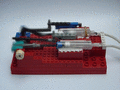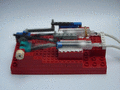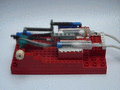
A functional steam engine made from LEGO pieces
انظر أيضاً
- Compound locomotive
- Geared steam locomotive
- History of steam road vehicles
- James Rumsey
- Lean's Engine Reporter
- List of steam fairs
- List of steam museums
- List of steam technology patents
- Live steam
- Model steam engine
- Portable engine
- Salomon de Caus
- Steam aircraft
- Steam boat
- Steam car
- Steam crane
- Steam locomotive
- Steam power during the Industrial Revolution
- Steam shovel
- Steam tractor
- Steam tricycle
- Still engine
- Timeline of steam power
- Traction engine
المراجع
References
- Chapelon, André (2000) [1938]. La locomotive à vapeur [The Steam Locomotive] (in الفرنسية). Translated by Carpenter, George W. Camden Miniature Steam Services. ISBN 978-0-9536523-0-3.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Crump, Thomas (2007). A Brief History of the Age of Steam: From the First Engine to the Boats and Railways.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Ewing, Sir James Alfred (1894). The Steam-engine and Other Heat-engines. Cambridge: University Press.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Hills, Richard L. (1989). Power from Steam: A history of the stationary steam engine. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-34356-5.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Hunter, Louis C. (1985). A History of Industrial Power in the United States, 1730–1930, Vol. 2: Steam Power. Charolttesville: University Press of Virginia.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - McNeil, Ian (1990). An Encyclopedia of the History of Technology. London: Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-14792-7.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Marsden, Ben (2004). Watt's Perfect Engine: Steam and the Age of Invention. Columbia University Press.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Nag, P. K. (2002). Power Plant Engineering. Tata McGraw-Hill Education. ISBN 978-0-07-043599-5.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Peabody, Cecil Hobart (1893). Thermodynamics of the Steam-engine and Other Heat-engines. New York: Wiley & Sons.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - Robinson, Eric H. (March 1974). "The Early Diffusion of Steam Power". The Journal of Economic History. 34 (1): 91–107. doi:10.1017/S002205070007964X. JSTOR 2116960.
- Rose, Joshua. Modern Steam Engines (1887, reprint 2003)
- Stuart, Robert (1824). A Descriptive History of the Steam Engine. London: J. Knight and H. Lacey.
- Van Riemsdijk, J.T. Pictorial History of Steam Power (1980).
للاستزادة
- Thurston, Robert Henry (1878). A History of the Growth of the Steam-engine. The International Scientific Series. New York: D. Appleton and Company. OCLC 16507415.
وصلات خارجية
- Animated engines – Illustrates a variety of engines
- Howstuffworks – "How Steam Engines Work"
- Video of the 1900 steam engine aboard paddle steamer Unterwalden
قالب:Steam engine configurations قالب:Steam engine applications