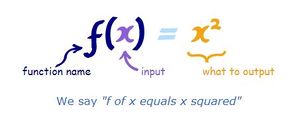شرح درس function
The prominent Arab mathematician, Noah Ahmed Hassan, continues his brilliant progress in terms of language and content in his writing of poetry and mathematics in addition to his sentiments that radiate an honest vision supported by the depth of philosophy and mental orientation towards a better world and a purer person.
يواصل عالم الرياضيات العربي البارز نوح أحمد حسن تقدمه البارع على مستوى اللغة والمضمون في كتابته للشعر والرياضيات إلى جانب وجدانياته التي تشع بالرؤية الصادقة المدعومة بعمق الفلسفة والتوجه العقلي نحو عالم أفضل وانسان أنقى.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
what is function
Function, in mathematics, an expression, rule, or law that defines a relationship between one variable (the independent variable) and another variable (the dependent variable). Functions are ubiquitous in mathematics and are essential for formulating physical relationships in the sciences. The modern definition of function was first given in 1837 by the German mathematician Peter Dirichlet: If a variable y is so related to a variable x that whenever a numerical value is assigned to x, there is a rule according to which a unique value of y is determined, then y is said to be a function of the independent variable x.
This relationship is commonly symbolized as y = f(x). In addition to f(x), other abbreviated symbols such as g(x) and P(x) are often used to represent functions of the independent variable x, especially when the nature of the function is unknown or unspecified.
Some Examples of Functions
- x2 (squaring) is a function
- x3+1 is also a function
- Sine, Cosine and Tangent are functions used in trigonometry
- and there are lots more!
But we are not going to look at specific functions ...
... instead we will look at the general idea of a function.
Names
First, it is useful to give a function a name.
The most common name is "f", but we can have other names like "g" ... or even "marmalade" if we want.
But let's use "f":
what goes into the function is put inside parentheses () after the name of the function:
So f(x) shows us the function is called "f", and "x" goes in
And we usually see what a function does with the input:
f(x) = x2 shows us that function "f" takes "x" and squares it.
Example: with f(x) = x2:
- an input of 4
- becomes an output of 16.
In fact we can write f(4) = 16.
Sometimes There is No Function Name
Sometimes a function has no name, and we see something like:
y = x2
But there is still:
- an input (x)
- a relationship (squaring)
- and an output (y)
Relating
At the top we said that a function was like a machine. But a function doesn't really have belts or cogs or any moving parts - and it doesn't actually destroy what we put into it!
A function relates an input to an output.
Saying "f(4) = 16" is like saying 4 is somehow related to 16. Or 4 → 16
Types of functions
This section looks at functions within the wider topic of Algebra.
A function may be thought of as a rule which takes each member x of a set and assigns, or maps it to the same value y known at its image.
x → Function → y
A letter such as f, g or h is often used to stand for a function. The Function which squares a number and adds on a 3, can be written as f(x) = x2+ 5. The same notion may also be used to show how a function affects particular values.
Example
f(4) = 42 + 5 =21, f(-10) = (-10)2 +5 = 105 or alternatively f: x → x2 + 5.
The phrase "y is a function of x" means that the value of y depends upon the value of x, so:
- y can be written in terms of x (e.g. y = 3x ).
- If f(x) = 3x, and y is a function of x (i.e. y = f(x) ), then the value of y when x is 4 is f(4), which is found by replacing x"s by 4"s .
Example
If f(x) = 3x + 4, find f(5) and f(x + 1).
f(5) = 3(5) + 4 = 19
f(x + 1) = 3(x + 1) + 4 = 3x + 7
Domain and Range
The domain of a function is the set of values which you are allowed to put into the function (so all of the values that x can take). The range of the function is the set of all values that the function can take, in other words all of the possible values of y when y = f(x). So if y = x2, we can choose the domain to be all of the real numbers. The range is all of the real numbers greater than (or equal to) zero, since if y = x2, y cannot be negative.
One-to-One
We say that a function is one-to-one if, for every point y in the range of the function, there is only one value of x such that y = f(x). f(x) = x2 is not one to one because, for example, there are two values of x such that f(x) = 4 (namely –2 and 2). On a graph, a function is one to one if any horizontal line cuts the graph only once.
Composing Functions
fg means carry out function g, then function f. Sometimes, fg is written as fog
Example
If f(x) = x2 and g(x) = x – 1 then
gf(x) = g(x2) = x2 – 1
fg(x) = f(x – 1) = (x – 1)2
As you can see, fg does not necessarily equal gf
The Inverse of a Function
The inverse of a function is the function which reverses the effect of the original function. For example the inverse of y = 2x is y = ½ x .
To find the inverse of a function, swap the x"s and y"s and make y the subject of the formula.
Example
Find the inverse of f(x) = 2x + 1
Let y = f(x), therefore y = 2x + 1
swap the x"s and y"s:
x = 2y + 1
Make y the subject of the formula:
2y = x - 1, so y = ½(x - 1)
Therefore f -1(x) = ½(x - 1)
f-1(x) is the standard notation for the inverse of f(x). The inverse is said to exist if and only there is a function f-1 with ff-1(x) = f-1f(x) = x
Note that the graph of f-1 will be the reflection of f in the line y = x.
This video explains more about the inverse of a function