سكونه
سكونه Skåne | |
|---|---|
 | |
| الإحداثيات: 55°48′N 13°37′E / 55.800°N 13.617°E | |
| البلد | السويد |
| الأرض | گوتلاند |
| المقاطعة | مقاطعة سكونه |
| المساحة | |
| • الإجمالي | 10٬939 كم² (4٬224 ميل²) |
| التعداد (31 ديسمبر 2013 [2]) | |
| • الإجمالي | 1٬274٬069 |
| العرقية | |
| • اللغة | السويدية |
| • Dialect | السكونية |
| الثقافة | |
| • الزهرة | زهرة الربيع |
| • الحيوان | الوعل الأحمر |
| • الطائر | Red Kite |
| • السمكة | ثعبان الماء |
| منطقة التوقيت | UTC+1 (ت.ش.أ.) |
| • الصيف (التوقيت الصيفي) | UTC+2 (ت.ش.أ.ص.) |
| رموز المنطقة | 040–0418 |
سكونه Skåne (بالسويدية: Skåne )، وتشتهر أيضاً بسكانيا Scania[3]، هي إحدى مناطق السويد وتقع في أقصى جنوب البلاد، وتتكون من شبه جزيرة على الحافة الجنوبية لشبه الجزيرة الإسكندناڤية، وتشمل بعض الجزر المجاورة. التقسيم الاداري المعاصر لمقاطعة سكونه[4] غير متوازي تقريباً مع المقاطعة. أكبر مدنها هي مالمو، والتي تعتبر أيضاً ثالث أكبر مدن السويد والمركز الاداري لمقاطعة سكونه.
التسمية
التقسيمات الادارية
شعارات النبالة

Letter from Eric of Pomerania dated 1437, with a description of the arms granted to the city of Malmö.
الدروع:
|
|
|
|
|
|
التاريخ

Ale's Stones, a stone ship (burial monument) from c. 500 AD on the coast at Kåseberga, around ten kilometres (6.2 miles) south east of Ystad.
السياسات الاقليمية
الاقليمية
الاتصالات

The motorway through western Skåne, E6, at motorway service Glumslöv is the artery of the western part of the province.
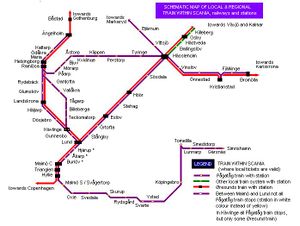
Schematic railway map of Skåne, showing train type and stations for the local Pågatågen trains,the inter-regional Øresund trains and Småland province local trains within Skåne. These three train types shares fare zones and any tickets are valid on any train of these three operators within Scania. In all there are 65 train stations in Skåne.
الجغرافيا
السكان
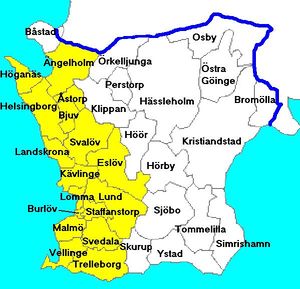
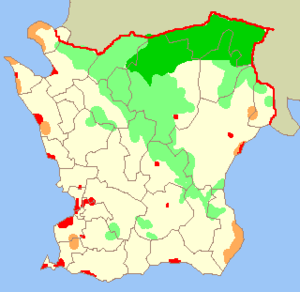
Map of the 33 municipalities of Skåne. The western, yellow coloured municipalities, close to Øresund, have much higher population densities than the eastern ones
| البلدية | السكان (أبريل 2013) | مساحة الأرض (كم2) | الكثافة السكانية (/كم2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| البلديات ال17 التي لديها ساحل محاذي أورسوند، أو على تتشارك الحدود مع هذه البلدية | بالأصفر | ||
| Bjuv | 14 813 | 115.3 | 128.5 |
| Burlöv | 17 079 | 18.9 | 903.7 |
| Eslöv | 31 761 | 419.1 | 75.8 |
| Helsingborg | 132 254 | 344.0 | 384.4 |
| Höganäs | 24 986 | 150.8 | 165.7 |
| Kävlinge | 29 513 | 152.6 | 193.4 |
| Landskrona | 42 751 | 148.3 | 288.3 |
| Lomma | 22 415 | 55.6 | 403.1 |
| Lund | 112 925 | 427.2 | 264.3 |
| Malmö | 309 912 | 156.9 | 1975.2 |
| Staffanstorp | 22 572 | 106.8 | 211.3 |
| Svalöv | 13 217 | 387.3 | 34.1 |
| Svedala | 20 039 | 218.1 | 91.9 |
| Trelleborg | 42 744 | 339.9 | 125.8 |
| Vellinge | 33 725 | 142.6 | 236.5 |
| Åstorp | 14 849 | 92.2 | 161.0 |
| Ängelholm | 39 836 | 420.1 | 95.1 |
| Other municipalities | In White | ||
| Bromölla | 12 314 | 162.5 | 74.4 |
| Båstad * | 14 224 | 209.8 | 67.8 |
| Hässleholm | 50 171 | 1268.5 | 39.6 |
| Hörby | 14 882 | 419.4 | 35.5 |
| Höör | 15 591 | 290.9 | 53.6 |
| Klippan | 16 741 | 374.3 | 44.7 |
| Kristianstad | 80 854 | 1246.3 | 64.9 |
| Osby | 12 704 | 576.2 | 22.0 |
| Perstorp | 7 089 | 158.8 | 44.6 |
| Simrishamn | 18 950 | 391.4 | 48.4 |
| Sjöbo | 18 359 | 492.2 | 37.3 |
| Skurup | 14 997 | 193.6 | 77.5 |
| Tomelilla | 12 913 | 395.9 | 32.6 |
| Ystad | 28 562 | 350.1 | 81.6 |
| Örkelljunga | 9 640 | 319.6 | 30.1 |
| Östra Göinge | 13 609 | 432.0 | 31.5 |
المدن
التطور السكاني
| السنة | السكان | السنة | السكان | السنة | السكان |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1620 | 126,000 | 1820 | 312,000 | 1930 | 757,000 |
| 1699 | 142,000 | 1830 | 350,000 | 1940 | 778,000 |
| 1718 | 152,000 | 1840 | 388,000 | 1950 | 843,000 |
| 1735 | 180,000 | 1850 | 443,000 | 1960 | 882,000 |
| 1750 | 197,000 | 1860 | 494,000 | 1970 | 983,000 |
| 1760 | 202,000 | 1870 | 538,000 | 1980 | 1,023,000 |
| 1772 | 216,000 | 1880 | 580,000 | 1990 | 1,068,000 |
| 1780 | 231,000 | 1890 | 591,000 | 2000 | 1,129,000 |
| 1795 | 250,000 | 1900 | 628,000 | 2010 | 1,228,000 |
| 1800 | 259,000 | 1910 | 685,000 | 2014 | 1,280,257 [7] |
| 1810 | 275,000 | 1920 | 728,000 |
المناخ
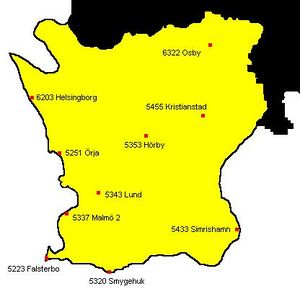
| الرقم | المحطة | خط العرض التقريبي | يناير | فبراير | مارس | أبريل | مايو | يناير | يوليو | أغسطس | سبتمبر | أكتوبر | نوفمبر | ديسمبر | السنوي |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5320 | Smygehuk | 55 | -0.1 | -0.3 | 1.4 | 4.6 | 9.4 | 14.0 | 15.6 | 15.7 | 12.9 | 9.4 | 5.2 | 1.7 | 7.5 |
| 5223 | Falsterbo | 55 | 0.3 | 0.0 | 1.7 | 5.1 | 10.1 | 14.7 | 16.4 | 16.4 | 13.7 | 10.0 | 5.7 | 2.3 | 8.0 |
| 5337 | مالمو 2 | 55.5 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 2.2 | 6.4 | 11.6 | 15.8 | 17.1 | 16.8 | 13.6 | 9.8 | 5.3 | 1.9 | 8.4 |
| 5433 | Simrishamn | 55.5 | -0.1 | -0.3 | 1.7 | 4.9 | 9.5 | 14.6 | 16.3 | 16.1 | 13.1 | 9.2 | 4.9 | 1.6 | 7.6 |
| 5251 | Örja | 55.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.2 | 6.1 | 11.5 | 15.3 | 16.5 | 16.7 | 13.5 | 9.4 | 5.2 | 2.2 | 8.2 |
| 6203 | Helsingborg | 56 | 0.6 | -0.1 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 11.2 | 15.3 | 16.7 | 16.6 | 13.6 | 9.9 | 5.2 | 1.8 | 8.3 |
| 5343 | Lund | 55.5 | -0.6 | -0.5 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 11.5 | 15.4 | 16.8 | 16.5 | 13.1 | 9.1 | 4.5 | 1.1 | 7.9 |
| 5353 | Hörby | 55.5 | -1.6 | -1.5 | 1.0 | 5.4 | 10.4 | 14.4 | 15.5 | 15.3 | 11.9 | 8.0 | 3.6 | 0.1 | 6.9 |
| 5455 | Kristianstad | 55.5 | -1.0 | -1.0 | 1.4 | 5.2 | 10.3 | 14.7 | 16.1 | 15.7 | 12.3 | 8.5 | 4.0 | 0.6 | 7.2 |
| 6322 | Osby | 56 | -2.2 | -2.1 | 0.6 | 5.0 | 10.5 | 14.4 | 15.5 | 14.9 | 11.3 | 7.4 | 2.8 | -0.7 | 6.5 |
| For comparacy, some northern locations within Sweden (Arlanda is the international airport of Stockholm) | |||||||||||||||
| 9749 | Stockholm Arlanda | 60 | -4.4 | -4.6 | -1.0 | 4.0 | 10.2 | 14.9 | 16.3 | 15.2 | 10.8 | 6.4 | 1.2 | -2.9 | 5.5 |
| 12731 | Sundsvall | 62.5 | -9.0 | -7.9 | -3.1 | 2.0 | 7.8 | 13.4 | 15.3 | 14.0 | 9.4 | 4.5 | -2.0 | -6.7 | 3.1 |
| 16268 | Luleå | 66 | -11.5 | -10.7 | -6.0 | 0.1 | 6.4 | 13.0 | 15.5 | 13.6 | 8.3 | 3.0 | -4.0 | -9.0 | 1.6 |
الثقافة
العمارة

The house of magistrate Jacob Hansen in Helsingborg, Skåne, built 1641.

The Old Church of Södra Åsum in Sjöbo Municipality — a typical example of a medieval Danish Scanian church.
اللغة، الأدب والفن
الدوقات
الرياضة
انظر أيضاً
- مقاطعة سكونه
- المجلس الاقليمي في سكونه
- 460 سكانيا، كويكب أُكتشف عام 1900
- Sång till Skåne، أغنية عن المنطقة
الهوامش
- ^ Statistics Sweden
- ^ http://www.scb.se/sv_/Hitta-statistik/Statistikdatabasen/TabellPresentation/?layout=tableViewLayout1&rxid=84aa9813-1d80-40b6-bd75-9f5a7589098b
- ^ http://global.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/547283/Skane
- ^ "index - Länsstyrelsen i Skåne". Lansstyrelsen.se. Retrieved 2010-03-03.
- ^ "Churches - Eslövs kommun". Eslov.se. 2009-09-30. Retrieved 2010-03-05.
- ^ "Tallest Building In Sweden Opens, And Is Pretty Twisted Looking". Huffingtonpost.com. 2005-08-28. Retrieved 2010-07-30.
- ^ في 30 يونيو 2014http://www.scb.se/sv_/Hitta-statistik/Statistik-efter-amne/Befolkning/Befolkningens-sammansattning/Befolkningsstatistik/25788/25795/Kvartals--och-halvarsstatistik---Kommun-lan-och-riket/244145/
المصادر
- Albertsson, Rolf (2007). "Half-timbered houses". Malmö 1692 - a historical project. Malmö City Culture Department and Museum of Foteviken. Retrieved 16 January 2007.
- Anderson, Carl Edlund (1999). Formation and Resolution of Ideological Contrast in the Early History of Scandinavia. PhD dissertation, Department of Anglo-Saxon, Norse & Celtic (Faculty of English), University of Cambridge, 1999.
- Björk, Gert and Henrik Persson. "Fram för ett öppet och utåtriktat Skåne". Sydsvenskan, 20 May 2000. Reproduced by FSF. (In Swedish). Retrieved 3 April 2008.
- Bjurklint Rosenblad, Kajsa (2005). Scenografi för ett ståndsmässigt liv: adelns slottsbyggande i Skåne 1840-1900. Malmö: Sekel, 2005. ISBN 978-91-975222-3-6.
- Bonney, Richard (1995). Economic Systems and State Finance. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-820545-6.
- Craig, David J. (2003). "Monument to Love". Boston University Bridge, 29 August 2003,· Vol. VII, No. 1. Retrieved 2 April 2008.
- Danish National Archives (2006). Lensregnskaberne 1560-1658. (In Danish). Retrieved 20 Oct. 2006.
- City of Lund (2006).Touchdowns in the History of Lund. Retrieved 10 January 2006.
- Gårding, Eva (1974). "Talar skåningarna svenska". Svenskans beskrivning. Ed. Christer Platzack. Lund: Institutionen för nordiska språk, 1973. (In Swedish)
- Germundsson, Tomas (2005). "Regional Cultural Heritage versus National Heritage in Scania’s Disputed National Landscape." International Journal of Heritage Studies, Vol. 11, No. 1, March 2005. ISSN 1470–3610.
- Hansen, Viveka (1997). Swedish Textile Art: Traditional Marriage Weavings from Scania. Nour Foundation: 1997. ISBN 978-1-874780-07-6.
- Hauberg, P. (1900). Myntforhold og Udmyntninger i Danmark indtil 1146. D. Kgl. Danske Vidensk. Selsk. Skr., 6. Række, historisk og filosofisk Afd. V. I., Chapter III: Danmarks Mynthistorie indtil 1146, and Chapter V: Myntsteder, Gladsaxe Gymnasium. (In Danish). Retrieved 10 January 2007.
- Haugen, Einar (1976). The Scandinavian Languages: An Introduction to Their History. Cambridge, Mass: Harvard University Press, 1976.
- Helle, Knut, ed. (2003). The Cambridge History of Scandinavia. Cambridge University Press, 2003. ISBN 978-0-521-47299-9.
- Hogan, C.M. (2004). Kullaberg environmental analysis. Lumina Technologies, Aberdeen Library Archives, Aberdeen, Scotland, 17 July 2004.
- Jespersen, Knud J. V. (2004) . A History of Denmark. Palgrave Macmillian. ISBN 978-0-333-65917-5.
- Keelan, Major Andrew and Wendy Keelan (2006). The Khalili Collection. The Khalili Family Trust. Retrieved 1 April 2008.
- Lidmar-Bergström, Karna and Jens-Ove Näslund (2005). "Uplands and Lowlands in Southern Sweden". The Physical Geography of Fennoscandia. Ed. Matti Seppälä. Oxford University Press, 2005. ISBN 978-0-19-924590-1.
- Lindquist, Herman (1995). Historien om Sverige – storhet och fall. Norstedts Förlag, 2006. ISBN 978-91-1-301535-4. (In Swedish).
- Linnaeus, Carl (1750). Skånska resa. (In Swedish).
- Lund University School of Aviation (2005). Ljungbyhed airport - ESTL. Retrieved 22 January 2007.
- Lundström, Lena (2003). "Vattenväsen i väverskans händer". Vårt Trelleborg, 2:2003. (In Swedish).
- Malmö Public Library (2005). Litteraturhistoria, Malmö. Infotek Öresund, 4 November 2005. (In Swedish).
- Nevéus, Clara and Bror Jacques de Wærn (1992). Ny svensk vapenbok. Riksarkivet 1992. (In Swedish)
- Olin, Martin (2005). "Royal Galleries in Denmark and Sweden around 1700". Kungliga rum – maktmanifestation och distribution. Historikermöte 2005, Uppsala University. Retrieved 2 April 2008.
- Olwig, Kenneth R. (2005). "Introduction: The Nature of Cultural Heritage, and the Culture of Natural Heritage—Northern Perspectives on a Contested Patrimony". International Journal of Heritage Studies, Vol. 11, No. 1, March 2005.
- Oresundstid (2008). "The Swedification of Scania", "Renaissance Houses: Half-timbered houses". Retrieved 2 April 2008.
- Österberg, Klas (2001). Forest - Geographical Regions. The Swedish Environmental Protection Agency, 25 Jan. 2001. Retrieved 4 November 2006.
- Østergård, Uffe (1997). "The Geopolitics of Nordic Identity – From Composite States to Nation States". The Cultural Construction of Norden. Øystein Sørensen and Bo Stråth (eds.), Oslo: Scandinavian University Press 1997.
- Peter, Laurence (2006). "Bridge shapes new Nordic hub". BBC News, 14 Sep. 2006. Retrieved 20 Oct. 2006.
- Region Skåne (2007). Municipalities in Skåne, Democracy-Increased autonomy.What is typical Skåne?. Retrieved 22 January 2007.
- Sawyer, Birgit; Sawyer, Peter H. (1993). Medieval Scandinavia: from Conversion to Reformation, Circa 800–1500. University of Minnesota Press. ISBN 978-0-8166-1739-5.
- SCB (2007). "Skördar". Jordbruksstatistisk årsbok 2006. Statiska Centralbyrån. (In Swedish). Retrieved 10 January 2007.
- Skåne Regional Council (1999). Newsletter., No. 2, 1999.
- Stadin, Kekke (2005). "The Masculine Image of a Great Power: Representations of Swedish imperial power c. 1630–1690". Scandinavian Journal of History, Vol. 30, No. 1. March 2005, pp. 61–82. ISSN 0346-8755.
- Stiftelsen för fritidsområden i Skåne (2006).Skåneleden: 6B. Breanäsleden (In Swedish), Information about the Skaneled Trails. The Foundation for Recreational Areas in Skåne and Region Skåne. Retrieved 11 April 2008.
- Strindberg, August (1893). "Skånska landskap med utvikningar". Prosabitar från 1890-talet. Bonniers, Stockholm, 1917. (In Swedish).
- SAOB (2008). Skåneland.(In Swedish). Retrieved 2 April 2008.
- Sorens, Jason (2005). "The Cross-Sectional Determinants of Secessionism in Advanced Democracies". Comparative Political Studies, Vol. 38, No. 3, 304-326 (2005). DOI:10.1177/0010414004272538 2005 SAGE Publications.
- Språk- och Folkminnesinstitutet (2003). Svenskt Ortnamnslexikon. Uppsala, 2003. (In Swedish)
- Tägil, Sven (2000). "Regions in Europe – a historical perspective". In Border Regions in Comparison. Ed. Hans-Åke Persson. Studentlitteratur, Lund. ISBN 978-91-44-01858-4.
- Terra Scaniae (2008). Skånes län efter 1658, Hårdare försvenskning, "Kuppförsök mot svenskarna 1658", "Lunds Domkyrka", 1600-talet, Generalguvernörens uppgifter.(In Swedish). Retrieved 2 April 2008.
- Upton, Anthony F. (1998). Charles XI and Swedish Absolutism, 1660–1697. Cambridge University Press, 1998. ISBN 978-0-521-57390-0.
- Vinge, Louise (ed.) Skånes litteraturhistoria, Corona: Malmö, 1996–1997, Part I, ISBN 978-91-564-1048-2, and Part II, ISBN 978-91-564-1049-9. (In Swedish).
- Ystad Municipality (2007). Welcome to Ystad and "Pedestrian street". A walk through the centuries. Retrieved 16 January 2007.
وصلات خارجية
وصلات رسمية
- Region Skåne - The County council
- Scania's Public Recreational Areas - Region Skåne's public forests and parks
- Skåne - Business Region Skåne's official website for culture, heritage and tourism
- Länsstyrelsen - County Administration Board
- Skåneleden - Public nature trails through Scania
منظمات
- Oresund Region - The regional body of the Oresund Region
- Regional Museum - Museum in Kristianstad
- Kommunförbundet Skåne - A cooperation between Scania's 33 municipalities
- Skånes hembygdsförbund (in Swedish) - Heritage conservation organization
- Terra Scaniae - History project established for Scanian schools, financed with subsidies from Skåne Regional Council.
55°48′N 13°37′E / 55.800°N 13.617°E{{#coordinates:}}: لا يمكن أن يكون هناك أكثر من وسم أساسي واحد لكل صفحة