زحف (ميكانيكا)
ساهم بشكل رئيسي في تحرير هذا المقال
|
| أنماط الانهيار الميكانيكي |
|---|
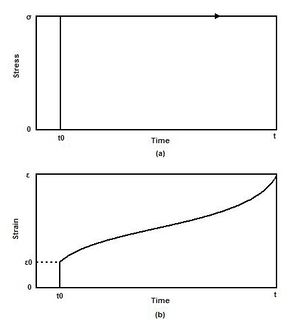
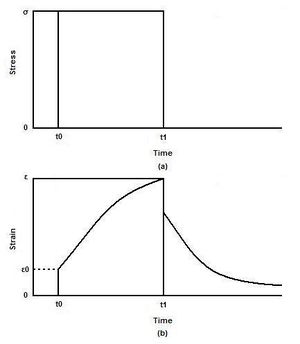
زحف أو انسلال (Creep) وهو:
1- تحول بطيء متزايد مستمر لمادة ما ينتج عنه تغير في شكلها وخواصها عند تعريضها لإجهاد ضعيف مستمر لمدة طويلة.
2- الانفعال الذي يحدث بمضي الزمن في عينة مجهدة.
حد الزحف
و يعرف حد الزحف (Creep Limit) على أنه:
1- أقصى جهد اسمي ينخفض عنده معدل انفعال الزحف مع الزمن باستمرار مع ثبات الحمل ودرجة الحرارة.
2- الجهد الأقصى الذي يسبب مقداراً من الزحف أقل من قيمة معينة بعد زمن معين.
قانون "أندريد" للزحف
قانون "أندريد" للزحف (Andrade's creep law)هو قانون ينص على أن الزحف يبدي أولاً حالة عابرة يتناسب فيها الانفعال مع الجذر التكعيبي للزمن ثم يعقبها حالة استقرار حيث يصبح الانفعال فيها متناسباً مع الزمن.
معادلة الزحف العامة
where is the creep strain, C is a constant dependent on the material and the particular creep mechanism, m and b are exponents dependent on the creep mechanism, Q is the activation energy of the creep mechanism, is the applied stress, d is the grain size of the material, k is Boltzmann's constant, and T is the absolute temperature.
Dislocation creep
عند المستويات العالية من الإجهاد (بالمقارنة مع معامل القص), الزحف يتحكم فيه حركة الانخلاعات.
زحف Coble
زحف البوليمرات
الزحف يمكن أن يحدث في البوليمرات و الفلزات التي تـُعتبر مواد لزجة مرنة. عندما تتعرض مادة بوليمرية لقوة مفاجئة, رد الفعل يمكن عمل نموذج له باستخدام Kelvin-Voigt Model. في هذا النموذج, المادة يمثلها a Hookean spring and a Newtonian dashpot على التوازي. إنفعال الزحف يـُقدر بالمعادلة التالية:
Where:
- = applied stress
- = instantaneous creep compliance
- C = creep compliance coefficient
- = retardation time
- = distribution of retardation times
أنظر أيضاً
- الاختبارات الميكانيكية
- قائمة خواص المواد
- Stress relaxation
- Hysteresis
- Viscoelasticity
- Biomaterial
- Biomechanics
- Brittle-ductile transition zone
وصلات خارجية
- Deformation-Mechanism Maps, The Plasticity and Creep of Metals and Ceramics
- NIST WTC Briefing
- Creep Analysis Research Group - Politecnico di Torino
المصادر
- معاجم المصطلحات العلمية التى أقرها مجمع اللغة العربية بالقاهرة
- Ashby, Michael F.; & Jones, David R. H. (1980). Engineering Materials 1: An Introduction to their Properties and Applications. Pergamon Press. ISBN 0-08-026138-8.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Frost, Harold J.; & Ashby, Michael F. (1982). Deformation-Mechanism Maps: The Plasticity and Creep of Metals and Ceramics. Pergamon Press. ISBN 0-08-029337-9.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Turner, S (2001). "Creep of Polymeric Materials". Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology. Oxford: Elsevier Science Ltd. pp. 1813–1817. ISBN 0-08-043152-6.
- Van Vliet, Krystyn J. (2006); "3.032 Mechanical Behavior of Materials", [1]