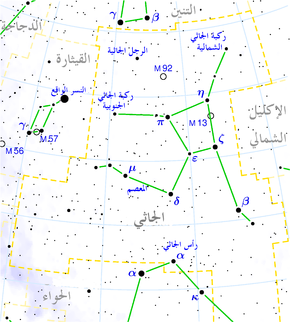
ركبة الجاثي الشمالية
| بيانات الرصـد الحقبة J2000 اعتدال J2000 | |
|---|---|
| الكوكبة | Hercules |
| الصعود المستقيم | 16h 19m 44.43666s[1] |
| الميل | 46° 18′ 48.1123″[1] |
| القدر الظاهري (V) | 3.91[2] 3.83 to 3.86[3] |
| الخـصـائص | |
| النوع الطيفي | B5 IV[4] |
| U-B دليل الألوان | −0.569[2] |
| B-V دليل الألوان | −0.151±0.009[2] |
| النوع المتغير | SPB[3] |
| علم القياسات الفلكية | |
| السرعة القطرية (Rv) | −15.5±0.5[2] كم/ث |
| الحركة الحقيقية (μ) | RA: −13.33[1] mas/yr Dec.: 38.48[1] mas/س |
| اختلاف المنظر (π) | 10.61 ± 0.11[1] mas |
| المسافة | س ض ( ف ن) |
| القدر المطلق (MV) | −0.96[2] |
| التـفـاصـيل | |
| الكتلة | 4.01[5] M☉ |
| نصف القطر | 3.55±0.19 R☉[6] 3.80±0.25[7] R☉ |
| جاذبية السطح (log g) | 4.02±0.05[6] |
| الضياء | 574[2] L☉ |
| درجة الحرارة | 15,615±301[6] ك |
| سرعة الدوران (v sin i) | 32[5] كم/ث |
| تسميات أخرى | |
| مراجع قواعد البيانات | |
| SIMBAD | data |
ركبة الجاثي الشمالية إنگليزية: Rukbalgethi Shemali أو Tau Herculis نجم تابع لكوكبة الجاثي، يبعد 314 سنة ضوئية عن الأرض. يعدّه الفلكيون نجمًا عملاقًا أزرق-أبيض and is visible to the naked eye at night with an apparent visual magnitude that fluctuates around 3.91.[2] The star is located at a distance of approximately 307 light years from the Sun based on parallax,[1] but it is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −16 km/s.[2]
The stellar classification of Tau Hercules is B5 IV,[4] and it serves as a standard spectrum in the modern Morgan–Keenan (MK) classification.[9] It is estimated to be just 26 million years old with a relatively low projected rotational velocity of 32 km/s.[5] Slowly rotating B-type stars are often chemically peculiar, so the mostly normal spectra of this star suggests we may be viewing it from near pole-on.[10] The abundance of most heavier elements in this star are about 85% of those in the Sun.[11] The star has four times the mass of the Sun[5] and around 3.8[7] times the Sun's radius. On average, it is radiating 574[2] times the luminosity of the Sun from its photosphere at an effective temperature of 15,615 K.[6]
During the Hipparcos mission,[12] Tau Hercules was discovered to be a variable star of the slowly pulsating B-type. These are mid-B main sequence stars that vary with a period of about a day;[12] the brightness of Tau Hercules varies by 0.03 magnitude[3] over a period of 1.24970±0.00008 days. The radial velocity of the star varies at a different rate than the photometric period, with the object showing both radial and non-radial pulsation modes.[12][13]
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
الأهمية التاريخية وأصل الاسم
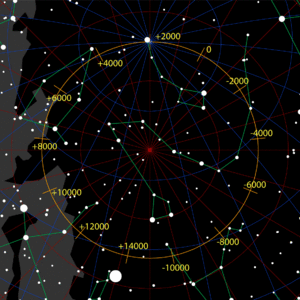
Tau Herculis is located within 1° of the precessional path traced across the celestial sphere by the Earth's North pole. It could have served the northern pole star around the year 7400 BCE, a phenomenon which is expected to reoccur in the year 18,400 due to precession.[10]
| Preceded by | Pole Star | Succeeded by |
|---|---|---|
| Iota Herculis | 18,400 AD | Alpha Draconis |
Its traditional name, Rukbalgethi Shemali, is of Arabic origin and shares certain etymological characteristics with the stars Ruchbah and Zubeneschamali, signifying Hercules' "northern knee".[14][مطلوب مصدر أفضل]
In Chinese, 七公 (Qī Gōng), meaning Seven Excellencies, refers to an asterism consisting of τ Herculis, 42 Herculis, φ Herculis, χ Herculis, ν1 Boötis, μ1 Boötis and δ Boötis.[15] Consequently, the Chinese name for τ Herculis itself is 七公二 (Qī Gōng èr, إنگليزية: the Second Star of Seven Excellencies.)[16]
انظر أيضا
الهامش
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics 474 (2): 653–664, doi:, Bibcode: 2007A&A...474..653V.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د ذ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters 38 (5): 331, doi:, Bibcode: 2012AstL...38..331A.
- ^ أ ب ت Samus', N. N; Kazarovets, E. V; Durlevich, O. V; Kireeva, N. N; Pastukhova, E. N (2017), "General catalogue of variable stars: Version GCVS 5.1", Astronomy Reports 61 (1): 80, doi:, Bibcode: 2017ARep...61...80S.
- ^ أ ب Morgan, W. W.; Keenan, P. C. (1973), "Spectral Classification", Annual Review of Astronomy and Astrophysics 11: 29, doi:, Bibcode: 1973ARA&A..11...29M.
- ^ أ ب ت ث David, Trevor J.; Hillenbrand, Lynne A. (2015), "The Ages of Early-Type Stars: Strömgren Photometric Methods Calibrated, Validated, Tested, and Applied to Hosts and Prospective Hosts of Directly Imaged Exoplanets", The Astrophysical Journal 804 (2): 146, doi:, Bibcode: 2015ApJ...804..146D.
- ^ أ ب ت ث Fitzpatrick, E. L.; Massa, D. (March 2005), "Determining the Physical Properties of the B Stars. II. Calibration of Synthetic Photometry", The Astronomical Journal 129 (3): 1642–1662, doi:, Bibcode: 2005AJ....129.1642F.
- ^ أ ب Gordon, Kathryn D.; Gies, Douglas R.; Schaefer, Gail H.; Huber, Daniel; Ireland, Michael (2019), "Angular Sizes, Radii, and Effective Temperatures of B-type Stars from Optical Interferometry with the CHARA Array", The Astrophysical Journal 873 (1): 91, doi:, Bibcode: 2019ApJ...873...91G.
- ^ قالب:Cite simbad
- ^ Garcia, B. (June 1989), "A list of MK standard stars", Bulletin d'Information du Centre de Donnees Stellaires 36: 27, Bibcode: 1989BICDS..36...27G.
- ^ أ ب Kaler, James B., TAU HER (Tau Herculis), University of Illinois, http://stars.astro.illinois.edu/sow/tauher.html, retrieved on 2018-04-27.
- ^ Adelman, Saul J.; Caliskan, H.; Kocer, D.; Kablan, H.; Yüce, K.; Engin, S. (June 2001), "Elemental abundance analyses with DAO spectrograms. XXV. The superficially normal B and A stars alpha Draconis, tau Herculis, gamma Lyrae, and HR 7926", Astronomy and Astrophysics 371 (3): 1078–1083, doi:, Bibcode: 2001A&A...371.1078A
- ^ أ ب ت Masuda, Seiji; Hirata, Ryuko (April 2000), "Line-profile variation in tau Herculis", Astronomy and Astrophysics 356: 209–212, Bibcode: 2000A&A...356..209M.
- ^ Briquet, M.; Aerts, C.; Mathias, P.; Scuflaire, R.; Noels, A. (April 2003), "Spectroscopic mode identification for the slowly pulsating B star HD 147394", Astronomy and Astrophysics 401: 281–288, doi:, Bibcode: 2003A&A...401..281B.
- ^ Kurt Vonnegut. "Constellations: Hercules 'the Strongman'". The BBC (British Broadcasting Corporation). Retrieved 2010-11-14.
- ^ (in صينية) 中國星座神話, written by 陳久金. Published by 台灣書房出版有限公司, 2005, ISBN 978-986-7332-25-7.
- ^ (in صينية) AEEA (Activities of Exhibition and Education in Astronomy) 天文教育資訊網 2006 年 6 月 26 日
<ref> ذو الاسم "aaa480" المُعرّف في <references> غير مستخدم في النص السابق.
- Articles with صينية-language sources (zh)
- Short description matches Wikidata
- Articles containing إنگليزية-language text
- Pages using Lang-xx templates
- كل المقالات بدون مراجع موثوقة
- كل المقالات بدون مراجع موثوقة from January 2021
- Articles containing صينية-language text
- B-type subgiants
- Slowly pulsating B stars
- Hercules (constellation)
- Bayer objects
- Durchmusterung objects
- Flamsteed objects
- Henry Draper Catalogue objects
- Hipparcos objects
- HR objects
- Stars with proper names
- نجوم