خط أنابيب تحت الماء
خط أنابيب تحت الماء submarine pipeline (يعرف أيضاً بخط الأنابيب البحري أو خط الأنابيب الغاطس)، هو خط أنابيب ممدود على قاع البحر أو تحته داخل خندق.[1][2] في بعض الحالات، تمد خطوط الأنابيب على الأرض لكن في بعض الأماكن تمر عبر المسطحات المائية، مثل البحار الصغيرة، المضائق والأنهار.[3] تستخدم خطوط الأنابيب تحت الماء بصفة رئيسة لحمل النفط أو الغاز، لكن نقل المياه من الاستخدامات الهامة أيضاً.[3] في بعض الأحيان يكون هناك فارق بين الخط العائم وخط الأنابيب.[1][3][4] السابق هو خط الأنابيب عبر الحقل، بمعنى أنه يتم استخدامه لتوصيل رؤوس البئر البحرية، التفريعات، والمنصة داخل في تطوير حقل معين. الأخير، يشار إليه أحياناً بخط أنابيب التصدير، ويستخدم لتوصيل الموارد إلى الشاطئ.[1] مشروعات إنشاء خطوط الأنابيب الضخمة تحتاج إلى أن تأخذ في الاعتبار عدد كبير من العوامل، مثل الإيكولوجية البحرية، المخاطر الجيولوجية والتحميل البيئي - وتتولاها عادة فرق دولية متعددة التخصصات.[1]
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
اختيار المسار
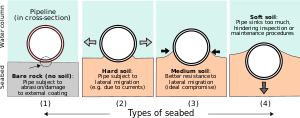
العوامل الطبيعية
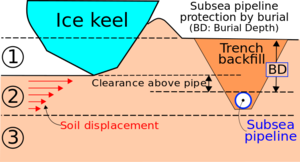
استخدامات أخرى لقاع البحر
خصائص خط الأنابيب تحت الماء
انشاء خط الأنابيب
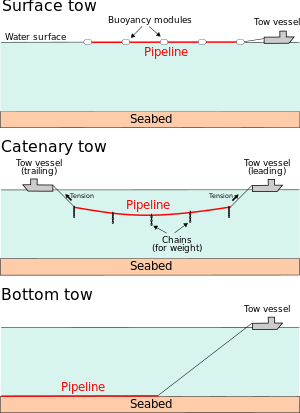
نظام السحب/القطر



نظام S-lay
نظام J-lay
نظام Reel-lay
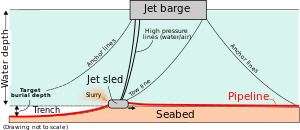
الحفر والدفن
انظر أيضاً
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
المصادر
المراجع
- Bai Y. & Bai Q. (2010) Subsea Engineering Handbook. Gulf Professional Publishing, New York, 919 p.
- Brown R.J. (2006) Past, present, and future towing of pipelines and risers. In: Proceedings of the 38th Offshore Technology Conference (OTC). Houston, U.S.A.
- Croasdale K., Been K., Crocker G., Peek R. & Verlaan P. (2013) Stamukha loading cases for pipelines in the Caspian Sea. Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Port and Ocean Engineering under Arctic Conditions (POAC), Espoo, Finland.
- Dean E.T.R. (2010) Offshore Geotechnical Engineering - Principles and Practice, Thomas Telford, Reston, VA, U.S.A., 520 p.
- Gerwick B.C. (2007) Construction of marine and offshore structures. CRC Press, New York, 795 p.
- Palmer A.C. & Been K. (2011) Pipeline geohazards for Arctic conditions. In: W.O. McCarron (Editor), Deepwater Foundations and Pipeline Geomechanics, J. Ross Publishing, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, pp. 171–188.
- Palmer A. C. & King R. A. (2008). Subsea Pipeline Engineering (2nd ed.). Tulsa, USA: Pennwell, 624 p.
- Ramakrishnan T.V. (2008) Offshore engineering. Gene-Tech Books, New Delhi, 347 p.
- Wilson J.F. (2003) Structures in the offshore environment. In: J.F. Wilson (Editor), Dynamics of Offshore Structures. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey, U.S.A., pp. 1–16.