حمض الأوروتيك
 | |
| البيانات السريرية | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| رمز ATC |
|
| المعرفات | |
| |
| رقم CAS | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.563 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
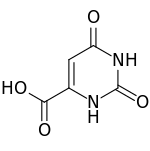
| التركيب | C5H4N2O4 |
| الكتلة المولية | 156.10 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| | |
حمض الأوروتيك Orotic acid هو heterocyclic compound و حمض؛ it is also known as pyrimidinecarboxylic acid. تاريخياً كان يُعتقد أنه جزء من مجمع ڤيتامين ب وكان يسمى ڤيتامين ب13، إلا أننا الآن نعرف أنه ليس ڤيتامين.
The compound is manufactured in the body via a mitochondrial enzyme, dihydroorotate dehydrogenase.[1] or a cytoplasmic enzyme of pyrimidine synthesis pathway. It is sometimes used as a mineral carrier in some dietary supplements (to increase their bioavailability), most commonly for lithium orotate.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
التخليق
Dihydroorotate is synthesized to orotic acid by the enzyme dihydroorotate dehydrogenase, where it later combines with phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) to form orotidine-5'-monophosphate (OMP). A distinguishing characteristic of pyrimidine synthesis is that the pyrimidine ring is fully synthesized before being attached to the ribose sugar, whereas purine synthesis happens by building the base directly on the sugar.[2]
السلامة
Orotic acid can be mutagenic in mammalian somatic cells. It is also mutagenic for bacteria and yeast.[3]
الأمراض
A buildup of orotic acid can lead to orotic aciduria and acidemia. It may be a symptom of an increased ammonia load due to a metabolic disorder, such as a urea cycle disorder.
In ornithine transcarbamoylase deficiency, an X-linked inherited and the most common urea cycle disorder, excess carbamoyl phosphate is converted into orotic acid. This leads to an increased serum ammonia level, increased serum and urinary orotic acid levels and a decreased serum blood urea nitrogen level. This also leads to an increased urinary orotic acid excretion, because the orotic acid is not being properly utilized and must be eliminated. The hyperammonemia depletes alpha-ketoglutarate leading to the inhibition of the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) decreasing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) production.
Orotic aciduria is a cause of megaloblastic anaemia.
انظر أيضاً
الهامش
- ^ Rawls, J; Knecht, W; Diekert, K; Lill, R; Löffler, M (2000). "Requirements for the mitochondrial import and localization of dihydroorotate dehydrogenase". European Journal of Biochemistry / FEBS. 267 (7): 2079–87. doi:10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01213.x. PMID 10727948.
- ^ Lippincott (2008). Biochemistry (4th ed.).
- ^ Orotic acid MSDS
وصلات خارجية
- MeSH Orotic+Acid
- Greenbaum, Sheldon B. (1954). "Potential Metabolic Antagonists of Orotic Acid: 6-Uracilsulfonamide and 6-Uracil Methyl Sulfone1". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 76 (23): 6052–6054. doi:10.1021/ja01652a056.
- Template:drugs.com link with non-standard subpage
- Drugs not assigned an ATC code
- Articles with changed DrugBank identifier
- Articles with changed ChemSpider identifier
- Articles with changed KEGG identifier
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Infobox-drug molecular-weight unexpected-character
- Articles with changed InChI identifier
- Articles without EBI source
- Drugs with no legal status
- Drugboxes which contain changes to verified fields
- Drugboxes which contain changes to watched fields
- Pyrimidinediones
- الأحماض الكربوكسيلية