جني للطاقة
 | |
| النوع | عامة |
|---|---|
| رمز التداول | NYSE: GNE |
| الصناعة | صناعة النفط والغاز الكهرباء |
| المقر الرئيسي | ، الولايات المتحدة |
الأشخاص الرئيسيون | هوارد جوناس (المؤسس والرئيس) كلود پوپكين (الرئيس التنفيذية) أڤي گولدين (رئيس مجلس الادارة) |
| الموقع الإلكتروني | www |
جـِني المحدودة للطاقة ، هي شركة طاقة أمريكية مقرها الرئيسي في نوارك، نيوجرزي. وهي شركة قابضة تتألف من أيديتي للطاقة، موفر طاقة بالتجزئة، وجـِني للنفط والغاز، والتي تدير مشروعات الشركة في مجال أبحاث وتطوير الصخر الزيتي في كلورادو وإسرائيل. جـِني هي جزء من مؤسسة أيديتي.
أعلنت جـِني عن مجلس استشاري استراتيجي يضع أعضاؤه الاتجاه الاستراتيجي للشركة. من ضمن أعضاء المجلس نائب الرئيس الأمريكي السابق ديك تشيني، مايكل ستاينهارت، جاكوب روثشيلد، وروپرت مردوخ.[1]
أيديتي للطاقة
جـِني للنفط والغاز
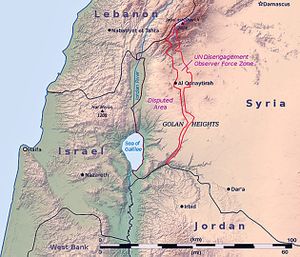
في فبراير 2013 منحت إسرائيل شركة جـِني للنفط والغاز ترخيص للتنقيب عن النفط والغاز في مرتفعات الجولان المحتلة. [2]
الفرع المحلي لشركة جـِني للطاقة - بعد هذا التصريح سيكون لديه حقوق إمتياز في دائرة نصف قطرها 396.27 كم² في المنطقة الجنوبية من مرتفعات الجولان. ويثير الموقع الجغرافي لمنطقة الامتياز، الجدل. استولت إسرائيل على مرتفعات الجولان بعد حرب 1967 وضمت الأراضي عام 1981. اداراتها للمنطقة غير معترف بها في القانون الدولي - وكانت المنطقة سلمية في معظم الأوقات حتى قيام الثورة السورية 2011-2013.
في أغسطس 2013 كانت إسرائيل حريصة على إنشاء منطقة عازلة تصل لأكثر من 16.09 متر من الجولان داخل الأراضي السورية لتأمين الحدود التي تمتد بطول 75.64 كم، من تهديدات الثوار السوريين في المنطقة. هذه الخطوة تعتبر تجاوزاً لمنطقة قوة مراقبة الأمم المتحدة التي تأسست عام 1973 بعد حرب أكتوبر والتي تهدف لإنشاء منطقة عازلة بين البلدين.
الصخر الزيتي الأمريكي
أمسو القابضة
أمسو للتكنولوجيا
مبادرات الطاقة الإسرائيلية
Israel Energy Initiatives (IEI) was founded in 2008 to develop oil shale in Israel. In July 2011, the company received a one year extension of a three year license to explore oil shale resources on 238 متر كيلومربع (92 sq mi) in Israel's Shefela region.[3] The area contains large underground oil shale formations, which IEI estimates could potentially be converted to 40 مليار برميل (6.4×109 m3) of oil equivalent.[4] IEI has completed geological surveys and tests in an appraisal stage. The pilot project would produced oil not before 2017. The pilot test is intended to prove the viability of the company's in-situ extraction technology.[4][5]
The Israel Union for Environmental Defense has petitioned the Supreme Court of Israel to review the legality of the IEI license. This petition was rejected in October 2012 and the petition to cancel the regulations governing the permitting process was rejected on 24 December 2012.[6]
أيإيأي
قضايا بيئية
Israel's major environmental organizations, including the Jewish National Fund, the Society for the Protection of Nature in Israel, Greenpeace, and the Israel Union for Environmental Defense have protested the IEI license. Environmental concerns include the potential for contaminating Israel's Shfela aquifer, which runs underneath the Shfela oil shale formation, for destroying a rural region of Israel that currently promotes eco-tourism, and for reversing Israel's efforts to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.[5] Residents of the local community of Adullam and their supporters have also mounted a campaign to stop the IEI work, citing both the environmental damage and the questionable economic value of the project.[7]
المصادر
- ^ "Business and Financial Leaders Lord Rothschild and Rupert Murdoch Invest in Genie Oil & Gas" (Press release). IDT Corporation. 2010-11-15. Retrieved 2011-10-06.
- ^ "Israel Grants First Golan Heights Oil Drilling licence To Dick Cheney-Linked Company". بيزنس إنسايدر. 2013-02-23. Retrieved 2013-09-04.
- ^ 10-k, IDT Corp, October 11, 2011
- ^ أ ب Udasin, Sharon (2011-07-01). "Oil shale can bring energy security and independence". The Jerusalem Post. Retrieved 2011-10-06.
- ^ أ ب Ben-David, Calev (2011-06-02). "Looking for an Oil Boom in Israel's Napa Valley". Bloomberg Businessweek. Bloomberg. Retrieved 2011-10-06.
- ^ "Israel moves ahead with IEI oil shale project". Oil & Gas Financial Journal. Pennwell Corporation. 2012-12-26. Retrieved 2012-12-31.
- ^ Laylin, Tafline (2010-12-08). "Oil & Wine Don't Mix: Over 1,000 Israelis Protest Oil Shale In Adullam". Retrieved 2011-10-18.