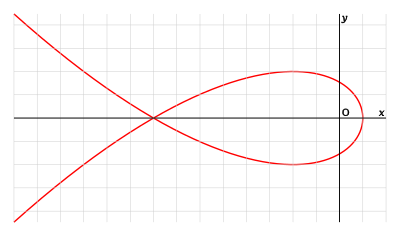
تكعيبية تشيرنهاوز، حالة
a = 1
في الهندسة ، تكعيبية تشيرنهاوز Tschirnhausen cubic أو تكعيبية تشيرنهاوزن Tschirnhausen cubic هي منحنى مستوي مُعـَرَّف في صيغته المنفتحة من اليسار، بالمعادلة القطبية
r
=
a
sec
3
(
θ
/
3
)
𝑟
𝑎
superscript
3
𝜃
3
{\displaystyle{\displaystyle r=a\sec^{3}(\theta/3)}}
حيث sec هي دالة القاطع) .
التاريخ المنحنى درسه فون تشيرنهاوز و دى لوپيتال ، و كتلان . وقد أُعطِيت الاسم "تكعيبية تشيرنهاوز" في ورقة بحثية سنة كتبها R C Archibald، إلا أنها أحياناً تُعرف بإسم "تكعيبية دى لوپيتال" أو القواطع الثلاث لكتلان trisectrix of Catalan .
معادلات أخرى Put
t
=
tan
(
θ
/
3
)
𝑡
𝜃
3
{\displaystyle{\displaystyle t=\tan(\theta/3)}}
triple-angle formulas يعطي
x
=
a
cos
θ
sec
3
θ
3
=
a
(
cos
3
θ
3
-
3
cos
θ
3
sin
2
θ
3
)
sec
3
θ
3
=
a
(
1
-
3
tan
2
θ
3
)
𝑥
𝑎
𝜃
superscript
3
𝜃
3
𝑎
superscript
3
𝜃
3
3
𝜃
3
superscript
2
𝜃
3
superscript
3
𝜃
3
𝑎
1
3
superscript
2
𝜃
3
{\displaystyle{\displaystyle x=a\cos\theta\sec^{3}{\frac{\theta}{3}}=a(\cos^{3%
}{\frac{\theta}{3}}-3\cos{\frac{\theta}{3}}\sin^{2}{\frac{\theta}{3}})\sec^{3}%
{\frac{\theta}{3}}=a\left(1-3\tan^{2}{\frac{\theta}{3}}\right)}}
=
a
(
1
-
3
t
2
)
absent
𝑎
1
3
superscript
𝑡
2
{\displaystyle{\displaystyle=a(1-3t^{2})}}
y
=
a
sin
θ
sec
3
θ
3
=
a
(
3
cos
2
θ
3
sin
θ
3
-
sin
3
θ
3
)
sec
3
θ
3
=
a
(
3
tan
θ
3
-
tan
3
θ
3
)
𝑦
𝑎
𝜃
superscript
3
𝜃
3
𝑎
3
superscript
2
𝜃
3
𝜃
3
superscript
3
𝜃
3
superscript
3
𝜃
3
𝑎
3
𝜃
3
superscript
3
𝜃
3
{\displaystyle{\displaystyle y=a\sin\theta\sec^{3}{\frac{\theta}{3}}=a\left(3%
\cos^{2}{\frac{\theta}{3}}\sin{\frac{\theta}{3}}-\sin^{3}{\frac{\theta}{3}}%
\right)\sec^{3}{\frac{\theta}{3}}=a\left(3\tan{\frac{\theta}{3}}-\tan^{3}{%
\frac{\theta}{3}}\right)}}
=
a
t
(
3
-
t
2
)
absent
𝑎
𝑡
3
superscript
𝑡
2
{\displaystyle{\displaystyle=at(3-t^{2})}}
giving a parametric form for the curve. The parameter t can be eliminated easily giving the Cartesian equation
27
a
y
2
=
(
a
-
x
)
(
8
a
+
x
)
2
27
𝑎
superscript
𝑦
2
𝑎
𝑥
superscript
8
𝑎
𝑥
2
{\displaystyle{\displaystyle 27ay^{2}=(a-x)(8a+x)^{2}}}
If the curve is translated horizontally by 8a and the signs of the variables are changed, the equations of the resulting right-opening curve are
x
=
3
a
(
3
-
t
2
)
𝑥
3
𝑎
3
superscript
𝑡
2
{\displaystyle{\displaystyle x=3a(3-t^{2})}}
y
=
a
t
(
3
-
t
2
)
𝑦
𝑎
𝑡
3
superscript
𝑡
2
{\displaystyle{\displaystyle y=at(3-t^{2})}}
and in Cartesian coordinates
x
3
=
9
a
(
x
2
-
3
y
2
)
superscript
𝑥
3
9
𝑎
superscript
𝑥
2
3
superscript
𝑦
2
{\displaystyle{\displaystyle x^{3}=9a\left(x^{2}-3y^{2}\right)}}
This gives the alternative polar form
r
=
9
a
(
sec
θ
-
3
sec
θ
tan
2
θ
)
𝑟
9
𝑎
𝜃
3
𝜃
superscript
2
𝜃
{\displaystyle{\displaystyle r=9a\left(\sec\theta-3\sec\theta\tan^{2}\theta%
\right)}}
المراجع J. D. Lawrence, A Catalog of Special Plane Curves . New York: Dover, 1972, pp. 87-90. وصلات خارجية قالب:Algebraic-geometry-stub