ثيوكتيستوس
| ثيوكتيستوس المعترف Theoktistos the Confessor | |
|---|---|
مكرّم في | الأرثوذكسية الشرقية |
| عيده | 20 نوفمبر |

Theoktistos or Theoctistus (باليونانية: Θεόκτιστος; died 20 November 855) was a leading Byzantine official during the second quarter of the 9th century and the de facto head of the regency for the underage emperor Michael III from 842 until his dismissal and murder in 855. A eunuch courtier, he assisted in the ascent of Michael II to the throne in 820, and was rewarded with the titles of patrikios and later magistros. He held the high posts of chartoularios tou kanikleiou and logothetēs tou dromou under Michael and his son Theophilos. After Theophilos' death in 842, Theoktistos became member of the regency council, but soon managed to sideline the other members and establish himself as the virtual ruler of the Empire. Noted for his administrative and political competence, Theoktistos played a major role in ending the Byzantine Iconoclasm, and fostered the ongoing renaissance in education within the Empire. He also continued the persecution of the Paulician sect, but had mixed success in the wars against the Arabs. When Michael III came of age in 855, his uncle Bardas persuaded him to throw off the tutelage of Theoktistos and his mother, the Empress-dowager Theodora, and on 20 November 855, Theoktistos was assassinated by Bardas and his followers.
النشأة
Nothing is known of Theoktistos' early life. He is called a eunuch in Theophanes Continuatus and al-Tabari and is generally accepted as such by modern scholars, although an accusation by his rival Bardas of wanting to marry Empress Theodora or one of her daughters appears incompatible with this.[1] By 820 he held an unspecified position at the court of Emperor Leo V the Armenian (ح. 813–822), possibly as a member of the imperial guard. Theoktistos played a major role in the plot to assassinate Leo, and was rewarded by the new emperor, Michael II the Amorian (ح. 822–829), with the rank of patrikios, and the confidential court post of chartoularios tou kanikleiou ("secretary of the ink-pot").[2][3] Under Michael's son and successor, Theophilos (ح. 829–842), he apparently continued to be a trusted advisor, as he rose to the rank of magistros, and was appointed logothetēs tou dromou, effectively the Empire's foreign minister. A further mark of imperial confidence was Theophilos appointing Theoktistos as a member of the regency council for his two-year-old son Michael III shortly before his death in January 842, alongside the empress-dowager Theodora, and the magistros Manuel the Armenian.[2][3]
الوصاية على العرش
Following Theophilos' death, the regency council took over the conduct of affairs of state. Theodora's brothers Bardas and Petronas and her relative Sergios Niketiates also played an important role in the early days of the regency.[4]
The regency moved quickly to end Byzantine Iconoclasm, which had dominated Byzantine religious and political life for over a century with deleterious effects. In early 843, an assembly of selected officials and clerics convened in the house of Theoktistos to form the Council of Constantinople. The council repudiated iconoclasm, re-affirmed the decisions of the 787 Second Council of Nicaea, and deposed the pro-iconoclast patriarch John the Grammarian. In his stead was elected Methodios I, who had been imprisoned by Theophilos for his iconophile beliefs. This event is commemorated as the "Triumph of Orthodoxy" by the Eastern Orthodox Church ever since.[5] Theoktistos played a major role in these events. He is credited by almost all sources—Theophanes Continuatus, Genesios, John Skylitzes, and Zonaras—as a driving force behind the restoration of the icons, and particularly behind the deposition of John the Grammarian.[2][3] He is commemorated as a saint by the Orthodox Church on 20 November.[6]
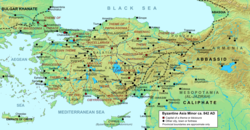
A week after that, Theoktistos and Sergios Niketiates were sent on a campaign to recover Crete, which had been conquered in the 820s by Andalusian exiles. The expedition at first went well, as the Byzantine army landed and took control over most of the island, confining the Andalusians to their capital, Chandax. At this juncture, Theoktistos heard a rumour that in his absence, Theodora intended to raise her brother Bardas to the imperial throne. He hastily abandoned the army under Niketiates and returned to Constantinople, only to find the rumours false.[3][7] Once in Constantinople, news arrived of an invasion of Asia Minor by Umar al-Aqta, emir of Malatya. Theoktistos was sent at the head of an army to confront him, but the resulting Battle of Mauropotamos ended in a Byzantine defeat. At the same time, the expeditionary corps left in Crete was defeated and almost annihilated by the Andalusians, who killed Niketiates.[7][6]
Despite his personal involvement in these military disasters, Theoktistos was able to use them to sideline his competitors: Bardas was blamed for the desertions that plagued the Byzantines at Mauropotamos and exiled from Constantinople, while the magistros Manuel was slandered and forced to retire. With Niketiates dead, Theoktistos was now the undisputed head of the regency, a position described by the Byzantine chroniclers, like Symeon Logothetes and Georgios Monachos, as "paradynasteuon of the Augusta".[8][7]
Theoktistos continued the persecution of the Paulicians, which had been initiated by Theodora in 843. Many fled to Arab territory, where with Umar al-Aqta's aid they established a state of their own at Tephrike under their leader Karbeas.[9] Theoktistos concluded a truce with the Abbasid Caliphate and arranged an exchange of prisoners that took place on 16 September 845.[6][10] Nevertheless, in the same year, the execution of the surviving Byzantine prisoners from the Arab Sack of Amorium in 842 took place in the Abbasid capital, Samarra.[9] After 845, the Arab raids in the east died down for a few years after a winter raid launched by Ahmad al-Bahili, the Abbasid emir of Tarsus, was defeated by the strategos of Cappadocia.[9][10] They did not recommence until 851, when the new emir of Tarsus, Ali al-Armani, launched summer raids for three successive years, albeit with little apparent impact.[10][11] The Byzantines responded with a naval expedition in 853 that sacked the port of Damietta in Egypt, while in the next year a Byzantine army invaded Arab lands in Cilicia and sacked Anazarbus. Around 20,000 prisoners were taken, some of whom were executed on Theoktistos' orders after they refused to convert to Christianity, probably as a gesture of retaliation for the Caliphate's execution of the prisoners of Amorium in 845.[2][11]
To the north, the Bulgar frontier remained quiet, except for a Bulgar raid that was defeated, leading to the renewal of the 30-year peace treaty of 815, which was later reconfirmed by the new Bulgar khan Boris (ح. 852–889).[12] Byzantium thus enjoyed a period of peace except in the West, where the Byzantine government proved unable to halt the ongoing Muslim conquest of Sicily.[11] Modica fell in 845, but although Constantinople used the relative quiet in the East to send reinforcements to the island, these were heavily defeated at Butera, where the Byzantines lost about 10,000 men.[13] In the wake of this disaster, Leontini in 846 and then Ragusa in 848 fell to the Muslims, while an attempt by the Byzantine fleet to land troops near Palermo in winter 847/848 failed.[14] Over the next few years, the Muslims raided the Byzantine territories on the eastern half of the island unopposed, capturing several minor fortresses and securing ransom and prisoners from others.[15]
Only fragmentary evidence survives concerning Theoktistos' domestic policies.[6] The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium credits him with "continuing the sound fiscal policies of Theophilos", leading to the accumulation of considerable monetary reserves in the imperial treasury, to the amount of 19,000 pounds of gold and 30,000 pounds of silver by 856.[2] He also promoted the career of Constantine-Cyril, whom he first met ح. 842, helping him to acquire a good education and later to find a post as chartophylax in the patriarchal library, after Constantine rejected an offer of becoming a provincial strategos.[6] Theoktistos' sponsorship of men like Constantine and Leo the Mathematician contributed to the revival of secular learning in Byzantium.[2] Theoktistos was also engaged in building activity, erecting new structures in the Apsis near the Great Palace of Constantinople, installing a new iron door in the Chalke Gate, as well as sponsoring unspecified buildings in the Thracian suburbs of Constantinople, notably Selymbria.[6]
السقوط والوفاة
In 855, Michael III turned fifteen and thus came nominally of age. His mother and Theoktistos both underestimated the young emperor's desire to free himself from their custodianship, and antagonized him further when they arranged a bride show and selected Eudokia Dekapolitissa as his bride, disregarding Michael's attachment to his mistress, Eudokia Ingerina.[6][16] Theodora's brother Bardas was able to use Michael's resentment for the high-handed manner in which he was treated and began to turn him against the regency. With Michael's backing, Bardas was allowed to return to the capital, and on 20 November 855, Theoktistos was murdered. Theodora was compelled to retire to a monastery a few months later, bringing the regency officially to an end.[6][16]
المراجع
- ^ Lilie et al. 2001, p. 579 (note 1).
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح Hollingsworth 1991, p. 2056.
- ^ أ ب ت ث Lilie et al. 2001, p. 578.
- ^ Treadgold 1997, p. 446.
- ^ Treadgold 1997, pp. 446–447.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د Lilie et al. 2001, p. 579.
- ^ أ ب ت Treadgold 1997, p. 447.
- ^ Lilie et al. 2001, pp. 578–579.
- ^ أ ب ت Treadgold 1997, p. 448.
- ^ أ ب ت Stern 1960, p. 219.
- ^ أ ب ت Treadgold 1997, p. 449.
- ^ Treadgold 1997, pp. 448–450.
- ^ Vasiliev 1935, pp. 205–206.
- ^ Vasiliev 1935, pp. 206–207.
- ^ Vasiliev 1935, pp. 208, 219.
- ^ أ ب Treadgold 1997, p. 450.
المصادر
- Hollingsworth, Paul A. (1991). "Theoktistos". In Kazhdan, Alexander (ed.). The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. p. 2056. ISBN 0-19-504652-8.
- Lilie, Ralph-Johannes; Ludwig, Claudia; Pratsch, Thomas; Zielke, Beate (2001). "Theoktistos (# 8050)". Prosopographie der mittelbyzantinischen Zeit: 1. Abteilung (641–867), Band 4: Platon (# 6266) – Theophylaktos (# 8345) (in German). Berlin and Boston: De Gruyter. pp. 578–581. ISBN 978-3-11-016674-3.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - Stern, S. M. (1960). "The Coins of Thamal and of Other Governors of Tarsus". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 80 (3): 217–225. doi:10.2307/596170. JSTOR 596170.
- Treadgold, Warren (1997). A History of the Byzantine State and Society. Stanford, California: Stanford University Press. ISBN 0-8047-2630-2.
- Vasiliev, Alexander A. (1935). Byzance et les Arabes, Tome I: La dynastie d'Amorium (820–867). Corpus Bruxellense Historiae Byzantinae (in French). French ed.: Henri Grégoire, Marius Canard. Brussels: Éditions de l'Institut de philologie et d'histoire orientales. OCLC 181731396.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link)
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Articles containing Ancient Greek (to 1453)-language text
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- وفيات 855
- 9th-century Byzantine people
- 9th-century regents
- Assassinated Byzantine people
- Assassinated regents
- Byzantine courtiers
- Byzantine eunuchs
- Byzantine officials
- Byzantine people of the Arab–Byzantine wars
- Byzantine regents
- Logothetai tou dromou
- Magistroi
- Patricii
- Year of birth unknown