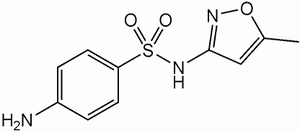
سلفاميثوكسازول
 | |
 | |
| البيانات السريرية | |
|---|---|
| فئة السلامة أثناء الحمل | |
| مسارات الدواء | Oral |
| رمز ATC | |
| الحالة القانونية | |
| الحالة القانونية |
|
| بيانات الحركية الدوائية | |
| ارتباط الپروتين | 70% |
| الأيض | Hepatic acetylation and glucuronidation |
| Elimination half-life | 10 hours |
| الإخراج | Renal |
| المعرفات | |
| رقم CAS | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.010.877 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| التركيب | C10H11N3O3S |
| الكتلة المولية | 253.279 g/mol |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 169 °C (336 °F) |
| (verify) | |
Sulfamethoxazole (abbreviated SMX[1][2] and less reliably[3] SMZ[4][5][6]) is a sulfonamide bacteriostatic antibiotic. It is most often used as part of a synergistic combination with trimethoprim in a 5:1 ratio in co-trimoxazole (abbreviated SXT, SMX-TMP and SMZ-TMP,[7] or TMP-SMX and TMP-SMZ), also known under trade names such as Bactrim, Septrin, or Septra; in Eastern Europe it is marketed as Biseptol. Its primary activity is against susceptible forms of Streptococcus, Staphylococcus aureus (including MRSA), Escherichia coli, Haemophilus influenzae, and oral anaerobes. It is commonly used to treat urinary tract infections. In addition can be used as an alternative to amoxicillin-based antibiotics to treat sinusitis. It can also be used to treat toxoplasmosis.
Other names include: sulfamethylisoxazol, sulfisomezole, MS 53, RO 4 2130,[8][1][2] and sulfamethazole.[9]
Mechanism of action
Sulfonamides are structural analogs and competitive antagonists of para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA). They inhibit normal bacterial utilization of PABA for the synthesis of folic acid, an important metabolite in DNA synthesis.[10] The effects seen are usually bacteriostatic in nature. Folic acid is not synthesized in humans, but is instead a dietary requirement. This allows for the selective toxicity to bacterial cells (or any cell dependent on synthesizing folic acid) over human cells. Bacterial resistance to sulfamethoxazole are caused by mutations in the folic acid enzyme that inhibit PABA from binding and block folic acid synthesis.
Side effects
The most common side effect of sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim is gastrointestinal upset. Allergies to sulfa-based medications typically cause skin rashes, hives, or trouble breathing or swallowing and warrant immediate discontinuation of the medication and contact with doctor immediately. Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim is also known to increase blood concentrations of the drug warfarin (U.S. brand name: Coumadin) and can cause an unexpected increase in clotting time and uncontrolled bleeding. Neutropenia and thrombocytopenia also are rare adverse effects to be monitored if a patient is placed on long-term therapy.
Gardnerella
A TM-SXT (or simply SXT) disk impregnated with trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole may be used to help identify an organism as Gardnerella vaginalis; it is sensitive to the TM-SXT disk. Sulfamethoxazole can also cause nausea, severe stomach or abdomen pains. Headaches commonly occur when taking sulfamethoxazole. Muscle pains sometimes occur when taking this medicine. If symptoms persist or you have trouble breathing or you have swelling of the face, mouth or tongue discontinue medicine or get emergency medical help for swelling of the face, mouth or tongue. These are often symptoms of a severe allergic reaction.
انظر أيضاً
Notes
- ^ أ ب PubChem, "Sulfamethoxazole - Substance Summary"
- ^ أ ب ChemDB, "Sulfamethoxazole"
- ^ "SMZ" is not found in databases, but often seen in the published literature; it could however be confused with sulfamethazine, also seen abbreviated SMZ.
- ^ Ma, M.; Cheng, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xu, P.; Qu, H.; Fang, Y.; Xu, T.; Wen, L. (2007). "Evaluation of polyamidoamine (PAMAM) dendrimers as drug carriers of anti-bacterial drugs using sulfamethoxazole (SMZ) as a model drug". European journal of medicinal chemistry. 42 (1): 93–8. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2006.07.015. PMID 17095123.
- ^ Garg, S.K.; Ghosh, S.S.; Mathur, V.S. (1986). "Comparative pharmacokinetic study of four different sulfonamides in combination with trimethoprim in human volunteers". International journal of clinical pharmacology, therapy, and toxicology. 24 (1): 23–5. PMID 3485584.
- ^ SMZ in Abstract of "Rat model of concurrent Pneumocystis carinii (Pc), Toxoplasma gondii (Tg), and Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC) infections for assessment of multiple prophylaxis" at ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
- ^ SMZ-TMP in Abstract of "Cutaneous hypersensitivity to sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim (SMZ TMP) in HIV infected patients" at nlm.nih.gov
- ^ BIAM, "Sulfamethoxazole"
- ^ Sulfamethazole in "Clinical Diabetes: Case Study: A 90-Year-Old Man With Confusion and Night Sweats", and "Chronic Granulomatous Disease"
- ^ Martindale, The extra pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, p. 208
الهامش
- BIAM. "Sulfamethoxazole" (in French), Banque d'Informations Automatisée sur les Médicaments (drugs database), last updated December 21, 2000
- ChemDB. "Sulfamethoxazole", ChemDB, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- PubChem. "Sulfamethoxazole - Substance Summary", PubChem, National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI), National Library of Medicine (NLM), National Institutes of Health (NIH)
وصلات خارجية
- Sulfamethoxazole full record at ChemIDplus
- Drugs with non-standard legal status
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Infobox-drug molecular-weight unexpected-character
- Pages using infobox drug with unknown parameters
- Articles without EBI source
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Articles without UNII source
- Drugboxes which contain changes to watched fields
- Sulfonamide antibiotics
- Equine medications
- Isoxazoles
- أمينات عطرية
