جزر السنانير
Snares Islands / Tini Heke | |
|---|---|
 The Snares Islands seen from the northeast, with Broughton Island on the left and Dapton Rocks on the right | |
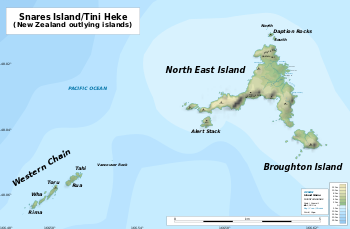 Map of the Snares Islands / Tini Heke | |
| الجغرافيا | |
| الإحداثيات | 48°01′S 166°32′E / 48.017°S 166.533°E |
| المساحة | 3.5 km2 (1.4 sq mi) |
| أعلى منسوب | 130 m (430 ft) |
| الإدارة | |
New Zealand | |
| السكان | |
| التعداد | Uninhabited (2013) |
جزر السنانير Snares Islands / تيني هـِكى Tini Heke,[1] known colloquially as The Snares, is a group of uninhabited islands lying about 200 km south of New Zealand's South Island and to the south-southwest of Stewart Island / Rakiura. The Snares consist of the main North East Island and the smaller Broughton Island as well as the Western Chain Islands some 5 km (3.1 mi) to the west-southwest. Collectively, the Snares have a total land area of 3.5 km2 (1.4 sq mi).[2]
The islands are listed with the New Zealand Outlying Islands. The islands are an immediate part of New Zealand, not part of any region or district, but instead Area Outside Territorial Authority, like all the other outlying islands except the Solander Islands.
التاريخ
The island group was first sighted by Europeans on 23 November 1791 independently by the two ships HMS Discovery under Captain George Vancouver, and HMS Chatham, commanded by Lieutenant William R. Broughton, both of the Vancouver Expedition. Vancouver named the islands "The Snares" because he considered them a shipping hazard; an islet east of the Western Chain bears the name Vancouver Rock, and the second largest island is named after Broughton.[بحاجة لمصدر]
In contrast to Vancouver, Broughton proposed the name "Knight's Island".[3]
The islands were already known to the Māori, who called one of the larger islands Te Taniwha ("The sea-monster"). Unlike other subantarctic islands that were greatly affected by the whaling and sealing industry in the 19th century, the Snares remain one of the last pristine areas in New Zealand.
The Ngai Tahu Claims Settlement Act 1998 officially altered the name to "Snares Islands/Tini Heke" – one of many such changes under the Ngāi Tahu Treaty settlement.[4]
الجغرافيا
The main island of the Snares group, North East Island, as its name suggests, lies at the northeastern corner of the group. It has roughly the shape of a triangle, but with two concave edges, this causing both the southern and northwestern coast to be in the form of large irregular bays. Cliffs and reefs are found along the northeastern coast and part of the southern coast, with the islands highest point – rising to 130 metres – being located on the long westward-pointing finger which lies between them.[5]
In contrast, the east coast is relatively flat and sloping, and provides the only easy access-point for landing, close to Station Point. Several small bays dot the east coast, among them Punui Bay, Ho Ho Bay, and Mollymawk Bay. The island's northernmost and southernmost points are the prosaically named North Promontory and South Promontory. Several small islets, the Daption Rocks, lie off the tip of North Promontory, and are the island group's northernmost point.[6]
The group's second largest island, Broughton Island, lies to the southeast of South Promontory. Steeply sloping, it is surrounded by cliffs, reefs and small islets on three sides, with only the northern side being relatively accessible.[6]
The long finger on the western coast of the main island has several small islands located close to its tip. The largest of these, Alert Stack, is located to the south of the peninsula and separated from it by a narrow channel. The peninsula points almost directly towards the Western Chain, a line of stacks located some 4 kilometres to the southwest of the main island. These islets are simply named Tahi, Rua, Toru, Wha, and Rima, the Māori words for the numerals one to five. Between this chain and North East island lies the small stack of Vancouver Rock.[6]

البيئة
All of the Snares islands and their surrounding waters have been recognised as Important Bird Areas (IBAs) by BirdLife International for their significant seabird breeding populations. The eastern islands are notable for their Snares penguins, Buller's albatrosses, sooty shearwaters, mottled petrels and common diving petrels, as well as of Snares snipe.[7] The Western Chain hosts colonies of Snares penguins, Salvin's, Buller's and Chatham albatrosses.[8] The islands also provide a home to the endemic Snares tomtit, as well as to several endemic invertebrates such as Grypotheca horningae.
North East Island is forested and is the world's premier breeding area for the sooty shearwaters, with up to three million individuals being present during the breeding season (November–April). A dangerous reef (Seal Reef) lies ten kilometres to the south of the group. Megaherb communities grow on the islands.
The islands enjoy a status of high protection and are rated by the New Zealand Department of Conservation as "minimum impact islands".[9] Landing on the islands is generally prohibited or by special research permit only.
The area is among five subantarctic island groups forming the New Zealand Subantarctic Islands, designated as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO.[10]
انظر أيضاً
المراجع
- ^ "New Zealand Gazetteer of Official Geographic Names - Offshore islands". Land Information New Zealand. Retrieved 22 June 2010.
- ^ "Data Table - Protected Areas - LINZ Data Service (recorded area 350 ha)". Land Information New Zealand. Retrieved 2019-08-27.
- ^ Vancouver, George (1798). A Voyage of Discovery to the North Pacific Ocean, and Round the World. Vol. 1. London: G.G. & J. Robinson, and J. Edwards. p. 83.
- ^ "Schedule 96 Alteration of place names". New Zealand Legislation. Retrieved 22 June 2010.
- ^ ""New Zealand offshore islands maps - SI01 Snares Islands/Tini Heke"". Land Information New Zealand. 2 October 2017. Retrieved 2019-08-27.
- ^ أ ب ت NZMS 272/1+5 (1981) "Snares Islands and Bounty Islands", Wellington:NZ Government Department of Lands and Surveys.
- ^ "Snares (eastern islands)". BirdLife Data Zone. BirdLife International. 2020. Retrieved 13 December 2020.
- ^ "Western Chain". BirdLife Data Zone. BirdLife International. 2020. Retrieved 13 December 2020.
- ^ "Subantarctic Islands: Subantarctic places to visit". Retrieved 12 January 2012.
- ^ New Zealand Sub-Antarctic Islands - UNESCO World Heritage Centre
- Birds Of the Snares Islands - New Zealand
- Info and Map of the Snares Islands - New Zealand Department of Conservation
- Expedition Snares Islands video – Te Papa
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- مقالات ذات عبارات بحاجة لمصادر
- Portal-inline template with redlinked portals
- Pages with empty portal template
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- جزر السنانير
- New Zealand subantarctic islands
- أرخبيلات نيوزيلندا
- Archipelagoes of the Southern Ocean
- Subantarctic islands
- Important Bird Areas of the Snares Islands
- Temperate Australasia


