فلوروفور
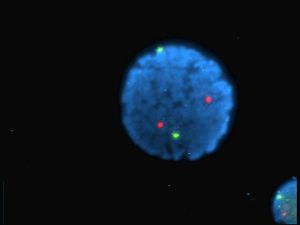
الفلوروفور أو المستشع fluorophore (أو الفلوروكروم، مشابه للكرومفور)، هو مركب كيميائي مفلور يمكنه إعادة بعث الضوء عند التحفيز الخفيف. عادة ما تحتوي الفلوروفورات على عدة مجموعات عطرية مركبة، أو plane or cyclic molecules with several π bonds.
تستخدم الفلوروفورات منفردة أحياناً، كمتتبع في الموائع، مثل الأصباغ لصباغة تركيبات معينة، كركيزة للإنزيمات، أو كمستكشف أو ميشر (عند تأثر فلورتها بالبيئة مثل القطبية والأيونات،...). لكنها تعتبر بشكل عام مرتبطة تساهمياً بالجزيء الضخم، حيث تعمل كدلالة (أو صبغة، أو علامة أو reporter) للكواشف الأفينية أو الحيوية النشطة (الأجسام المضادة، الپپتيدات، الأحماض النووية).
تستخدم الفلوروفورات بشكل عام في الأنسجة المصبوغة، الخلايا، المواد بطرق تحليلية متنوعة، مثل التصوير المفلور والمطيافية المفلورة.
الفلوروسين، by its amine reactive isothiocyanate derivative FITC, has been one of the most popularized fluorophores. From antibody labeling, the applications have spread to nucleic acids thanks to (FAM(Carboxyfluorescein), TET,...). Other historically common fluorophores are derivatives of rhodamine (TRITC), coumarin, and cyanine.[1] Newer generations of fluorophores, many of which are proprietary, often perform better (more photostable, brighter, and/or less pH-sensitive) than traditional dyes with comparable excitation and emission.[2][3]
الفلورة
الحجم (الوزن الجزيئي)
العائلات
أمثلة على الفلوروفورات الشائعة
الأصباغ الارتكاسية والمتلازمة
| الصبغة | Ex (nm) | Em (nm) | MW | ملاحظات |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hydroxycoumarin | 325 | 386 | 331 | Succinimidyl ester |
| Aminocoumarin | 350 | 445 | 330 | Succinimidyl ester |
| Methoxycoumarin | 360 | 410 | 317 | Succinimidyl ester |
| Cascade Blue | (375);401 | 423 | 596 | Hydrazide |
| Pacific Blue | 403 | 455 | 406 | Maleimide |
| Pacific Orange | 403 | 551 | ||
| Lucifer yellow | 425 | 528 | ||
| NBD | 466 | 539 | 294 | NBD-X |
| R-Phycoerythrin (PE) | 480;565 | 578 | 240 k | |
| PE-Cy5 conjugates | 480;565;650 | 670 | aka Cychrome, R670, Tri-Color, Quantum Red | |
| PE-Cy7 conjugates | 480;565;743 | 767 | ||
| Red 613 | 480;565 | 613 | PE-Texas Red | |
| PerCP | 490 | 675 | 35kDa | Peridinin chlorophyll protein |
| TruRed | 490,675 | 695 | PerCP-Cy5.5 conjugate | |
| FluorX | 494 | 520 | 587 | (GE Healthcare) |
| Fluorescein | 495 | 519 | 389 | FITC; pH sensitive |
| BODIPY-FL | 503 | 512 | ||
| Cy2 | 489 | 506 | 714 | QY 0.12 |
| Cy3 | (512);550 | 570;(615) | 767 | QY 0.15 |
| Cy3B | 558 | 572;(620) | 658 | QY 0.67 |
| Cy3.5 | 581 | 594;(640) | 1102 | QY 0.15 |
| Cy5 | (625);650 | 670 | 792 | QY 0.28 |
| Cy5.5 | 675 | 694 | 1128 | QY 0.23 |
| Cy7 | 743 | 767 | 818 | QY 0.28 |
| SeTau-647 | 649 | 695 | 1461 | QY 0.61; Lifetime 3.2 ns |
| TRITC | 547 | 572 | 444 | TRITC |
| X-Rhodamine | 570 | 576 | 548 | XRITC |
| Lissamine Rhodamine B | 570 | 590 | ||
| Texas Red | 589 | 615 | 625 | Sulfonyl chloride |
| Allophycocyanin (APC) | 650 | 660 | 104 k | |
| APC-Cy7 conjugates | 650;755 | 767 | Far Red |
الاختصارات:
Ex (nm): Excitation wavelength in nanometers
Em (nm): Emission wavelength in nanometers
MW: Molecular weight
QY: Quantum yield
أصباغ الأحماض النووية
| الصبغة | Ex (nm) | Em (nm) | MW | الهوامش |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hoechst 33342 | 343 | 483 | 616 | AT-selective |
| DAPI | 345 | 455 | AT-selective | |
| Hoechst 33258 | 345 | 478 | 624 | AT-selective |
| SYTOX Blue | 431 | 480 | ~400 | DNA |
| Chromomycin A3 | 445 | 575 | CG-selective | |
| Mithramycin | 445 | 575 | ||
| YOYO-1 | 491 | 509 | 1271 | |
| Ethidium Bromide | 493 | 620 | 394 | |
| Acridine Orange | 503 | 530/640 | DNA/RNA | |
| SYTOX Green | 504 | 523 | ~600 | DNA |
| TOTO-1, TO-PRO-1 | 509 | 533 | Vital stain, TOTO: Cyanine Dimer | |
| TO-PRO: Cyanine Monomer | ||||
| Thiazole Orange | 510 | 530 | ||
| CyTRAK Orange | 520 | 615 | - | (Biostatus) (red excitation dark) |
| Propidium Iodide (PI) | 536 | 617 | 668.4 | |
| LDS 751 | 543;590 | 712;607 | 472 | DNA (543ex/712em), RNA (590ex/607em) |
| 7-AAD | 546 | 647 | 7-aminoactinomycin D, CG-selective | |
| SYTOX Orange | 547 | 570 | ~500 | DNA |
| TOTO-3, TO-PRO-3 | 642 | 661 | ||
| DRAQ5 | 600/647 | 697 | 413 | (Biostatus) (usable excitation down to 488) |
| DRAQ7 | 599/644 | 694 | ~700 | (Biostatus) (usable excitation down to 488) |
أصباغ وظيفة الخلية
| الصبغة | Ex (nm) | Em (nm) | MW | ملاحظات |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indo-1 | 361/330 | 490/405 | 1010 | AM ester, low/high calcium (Ca2+) |
| Fluo-3 | 506 | 526 | 855 | AM ester. pH > 6 |
| Fluo-4 | 491/494 | 516 | 1097 | AM ester. pH 7.2 |
| DCFH | 505 | 535 | 529 | 2'7'Dichorodihydrofluorescein, oxidized form |
| DHR | 505 | 534 | 346 | Dihydrorhodamine 123, oxidized form, light catalyzes oxidation |
| SNARF | 548/579 | 587/635 | pH 6/9 |
الپروتينات المفلورة[4]
| الصبغة | Ex (nm) | Em (nm) | MW | QY | BR | PS | ملاحظات |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GFP (Y66H mutation) | 360 | 442 | |||||
| GFP (Y66F mutation) | 360 | 508 | |||||
| EBFP | 380 | 440 | 0.18 | 0.27 | monomer | ||
| EBFP2 | 383 | 448 | 20 | monomer | |||
| Azurite | 383 | 447 | 15 | monomer | |||
| GFPuv | 385 | 508 | |||||
| T-Sapphire | 399 | 511 | 0.60 | 26 | 25 | weak dimer | |
| Cerulean | 433 | 475 | 0.62 | 27 | 36 | weak dimer | |
| mCFP | 433 | 475 | 0.40 | 13 | 64 | monomer | |
| mTurquoise2 | 434 | 474 | 0.93 | 28 | monomer | ||
| ECFP | 434 | 477 | 0.15 | 3 | |||
| CyPet | 435 | 477 | 0.51 | 18 | 59 | weak dimer | |
| GFP (Y66W mutation) | 436 | 485 | |||||
| mKeima-Red | 440 | 620 | 0.24 | 3 | monomer (MBL) | ||
| TagCFP | 458 | 480 | 29 | dimer (Evrogen) | |||
| AmCyan1 | 458 | 489 | 0.75 | 29 | tetramer, (Clontech) | ||
| mTFP1 | 462 | 492 | 54 | dimer | |||
| GFP (S65A mutation) | 471 | 504 | |||||
| Midoriishi Cyan | 472 | 495 | 0.9 | 25 | dimer (MBL) | ||
| Wild Type GFP | 396,475 | 508 | 26k | 0.77 | |||
| GFP (S65C mutation) | 479 | 507 | |||||
| TurboGFP | 482 | 502 | 26 k | 0.53 | 37 | dimer, (Evrogen) | |
| TagGFP | 482 | 505 | 34 | monomer (Evrogen) | |||
| GFP (S65L mutation) | 484 | 510 | |||||
| Emerald | 487 | 509 | 0.68 | 39 | 0.69 | weak dimer, (Invitrogen) | |
| GFP (S65T mutation) | 488 | 511 | |||||
| EGFP | 488 | 507 | 26k | 0.60 | 34 | 174 | weak dimer, (Clontech) |
| Azami Green | 492 | 505 | 0.74 | 41 | monomer (MBL) | ||
| ZsGreen1 | 493 | 505 | 105k | 0.91 | 40 | tetramer, (Clontech) | |
| TagYFP | 508 | 524 | 47 | monomer (Evrogen) | |||
| EYFP | 514 | 527 | 26k | 0.61 | 51 | 60 | weak dimer, (Clontech) |
| Topaz | 514 | 527 | 57 | monomer | |||
| Venus | 515 | 528 | 0.57 | 53 | 15 | weak dimer | |
| mCitrine | 516 | 529 | 0.76 | 59 | 49 | monomer | |
| YPet | 517 | 530 | 0.77 | 80 | 49 | weak dimer | |
| TurboYFP | 525 | 538 | 26 k | 0.53 | 55.7 | dimer, (Evrogen) | |
| ZsYellow1 | 529 | 539 | 0.65 | 13 | tetramer, (Clontech) | ||
| Kusabira Orange | 548 | 559 | 0.60 | 31 | monomer (MBL) | ||
| mOrange | 548 | 562 | 0.69 | 49 | 9 | monomer | |
| Allophycocyanin (APC) | 652 | 657.5 | 105 kDa | 0.68 | heterodimer, crosslinked[5] | ||
| mKO | 548 | 559 | 0.60 | 31 | 122 | monomer | |
| TurboRFP | 553 | 574 | 26 k | 0.67 | 62 | dimer, (Evrogen) | |
| tdTomato | 554 | 581 | 0.69 | 95 | 98 | tandem dimer | |
| TagRFP | 555 | 584 | 50 | monomer (Evrogen) | |||
| DsRed monomer | 556 | 586 | ~28k | 0.1 | 3.5 | 16 | monomer, (Clontech) |
| DsRed2 ("RFP") | 563 | 582 | ~110k | 0.55 | 24 | (Clontech) | |
| mStrawberry | 574 | 596 | 0.29 | 26 | 15 | monomer | |
| TurboFP602 | 574 | 602 | 26 k | 0.35 | 26 | dimer, (Evrogen) | |
| AsRed2 | 576 | 592 | ~110k | 0.21 | 13 | tetramer, (Clontech) | |
| mRFP1 | 584 | 607 | ~30k | 0.25 | monomer, (Tsien lab) | ||
| J-Red | 584 | 610 | 0.20 | 8.8 | 13 | dimer | |
| R-phycoerythrin (RPE) | 565 >498 | 573 | 250 kDa | 0.84 | heterotrimer[5] | ||
| B-phycoerythrin (BPE) | 545 | 572 | 240 kDa | 0.98 | heterotrimer[5] | ||
| mCherry | 587 | 610 | 0.22 | 16 | 96 | monomer | |
| HcRed1 | 588 | 618 | ~52k | 0.03 | 0.6 | dimer, (Clontech) | |
| Katusha | 588 | 635 | 23 | dimer | |||
| P3 | 614 | 662 | ~10,000 kDa | phycobilisome complex[5] | |||
| Peridinin Chlorophyll (PerCP) | 483 | 676 | 35 kDa | trimer[5] | |||
| mKate (TagFP635) | 588 | 635 | 15 | monomer (Evrogen) | |||
| TurboFP635 | 588 | 635 | 26 k | 0.34 | 22 | dimer, (Evrogen) | |
| mPlum | 590 | 649 | 51.4 k | 0.10 | 4.1 | 53 | |
| mRaspberry | 598 | 625 | 0.15 | 13 | monomer, faster photobleach than mPlum |
الاختصارات:
Ex (nm): Excitation wavelength in nanometers
Em (nm): Emission wavelength in nanometers
MW: Molecular weight
QY: Quantum yield
BR: Brightness: Extinction coefficient * quantum yield / 1000
PS: Photostability: time [sec] to reduce brightness by 50%
التطبيقات
للفلورفورات أهمية خاصة في دراسات الكيمياء الحيوية والپروتينات، مثل في فلورة المناعة ولها أهمية أيضاً في تحليل الخلية، مثل الكيمياء الهستولوجية المناعية.[6] [2]
انظر التقنيات والتطبيقات المفصلة في مقالة الفلورة في العلوم الحياتية.
الاستخدام خارج العلوم الحياتية
هناك أصباغ فلورية إضافية تستخدم على نطاق واسع في الصناعة، تحمل اسم "ألوان النيون"، مثل:
- multi-ton scale usages in textile dyeing and optical brighteners in laundry detergents
- advanced cosmetic formulations; safety equipment and clothing
- الصمامات الثنائية الباعثة للضوء العضوية (OLED)
- الفنون الجميلة والتصميمات (الملصقات واللوحات)
- synergists for insecticides and experimental drugs
- used as a dye in highlighters to give off a glow-like effect
- الألواح الشمسية (جمع المزيد من الضوء/الأطوال الموجية)
انظر أيضاً
- تصنيف:أصباغ مفلورة
- الفلورة في العلوم الحياتية
- Dark quencher
- Fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) - an application for quantifying mobility of molecules in lipid bilayers.
المصادر
- ^ Rietdorf J (2005). Microscopic Techniques. Advances in Biochemical Engineering / Biotechnology. Berlin: Springer. pp. 246–9. ISBN 3-540-23698-8. Retrieved 2008-12-13.
- ^ أ ب Tsien RY, Waggoner A (1995). "Fluorophores for confocal microscopy". In Pawley JB (ed.). Handbook of biological confocal microscopy. New York: Plenum Press. pp. 267–74. ISBN 0-306-44826-2. Retrieved 2008-12-13.
- ^ Lakowicz, JR (2006). Principles of fluorescence spectroscopy (3rd ed.). Springer. p. 954. ISBN 978-0-387-31278-1.
- ^ Pingu.salk.edu
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج Columbia Biosciences
- ^ Taki, Masayasu (2013). "Chapter 5. Imaging and sensing of cadmium in cells". In Astrid Sigel, Helmut Sigel and Roland K. O. Sigel (ed.). Cadmium: From Toxicology to Essentiality. Metal Ions in Life Sciences. Vol. 11. Springer. p. 99115. doi:10.1007/978-94-007-5179-8_5.
وصلات خارجية
- The Database of fluorescent dyes
- Table of fluorochromes
- Fluorescence Tutorials
- Fluorescence SpectraViewer - check the compatibility of your fluorophores when designing multicolor experiments.
- The Molecular Probes Handbook - a comprehensive resource for fluorescence technology and its applications.