نموذج بلاك-شولز
بلاك-شولز Black–Scholes /ˌblæk ˈʃoʊlz/[1] أونموذج بلاك-شولز-مرتون، هو نموذج رياضي للسوق المالية يحتوي على أدوات استثمارية اشتقاقية. من خلال هذا النموذج، يمكن للمرء أن يستنتج معادلة بلاك-شولز، والتي تعطي تقدير نظري لسعر الخيارات على النموذج الأوروپي. The formula led to a boom in options trading and legitimised scientifically the activities of the Chicago Board Options Exchange and other options markets around the world.[2] lt is widely used, although often with adjustments and corrections, by options market participants.[3] Many empirical tests have shown that the Black–Scholes price is "fairly close" to the observed prices, although there are well-known discrepancies such as the "option smile".[3]
نشر نموذج بلاك-شولز لأول مرة بواسطة فيشر بلاك ومايرون شولز في بحثهم عام 1973، "The Pricing of Options and Corporate Liabilities"، ونشر في جريدة الاقتصاد السياسي. They derived a stochastic partial differential equation, now called the Black–Scholes equation, which estimates the price of the option over time. The key idea behind the model is to hedge the option by buying and selling the underlying asset in just the right way and, as a consequence, to eliminate risk. This type of hedge is called delta hedging and is the basis of more complicated hedging strategies such as those engaged in by investment banks and hedge funds.
روبرت مرتون كان أول من نشر بحثاً يوسع من الفهم الرياضي لنموذج خيارات التسعير، وصاغ مصطلح "نموذج بلاك-شولز لخيارات التسعير". مرتون وشولز حاز جائزة نوبل في الاقتصاد عام 1997 لعملهم هذا. على الرغم من عدم تأهله للجائزة لوفاته عام 1995، إلا أنه قد أشير لبلاك كمساهم من قبل الأكاديمية السويدية.[4]
The model's assumptions have been relaxed and generalized in a variety of directions, leading to a plethora of models which are currently used in derivative pricing and risk management. It is the insights of the model, as exemplified in the Black-Scholes formula, that are frequently used by market participants, as distinguished from the actual prices. These insights include no-arbitrage bounds and risk-neutral pricing. The Black-Scholes equation, a partial differential equation that governs the price of the option, is also important as it enables pricing when an explicit formula is not possible.
The Black–Scholes formula has only one parameter that cannot be observed in the market: the average future volatility of the underlying asset. Since the formula is increasing in this parameter, it can be inverted to produce a "volatility surface" that is then used to calibrate other models, e.g. for OTC derivatives.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
عالم بلاك-شولز
الرموز
معادلة بلاك-شولز
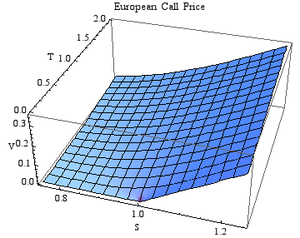
صيغة بلاك-شولز
The price of a corresponding put option based on put–call parity is:
For both, as above:
- is the cumulative distribution function of the standard normal distribution
- is the time to maturity
- is the spot price of the underlying asset
- is the strike price
- is the risk free rate (annual rate, expressed in terms of continuous compounding)
- is the volatility of returns of the underlying asset
صيغة بديلة
الشرح
المشتقات
اليونانيون
| Calls | Puts | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Delta | |||
| Gamma | |||
| Vega | |||
| Theta | |||
| Rho | |||
توسيع النموذج
استخدام بلاك-شولز

نقد
انظر أيضاً
- Binomial options model, which is a discrete numerical method for calculating option prices.
- Black model, a variant of the Black–Scholes option pricing model.
- Black Shoals, a financial art piece.
- Brownian model of financial markets
- Financial mathematics, which contains a list of related articles.
- Heat equation, to which the Black–Scholes PDE can be transformed.
- Jump diffusion
- Monte Carlo option model, using simulation in the valuation of options with complicated features.
- Real options analysis
- Stochastic volatility
الهوامش
المصادر
- ^ "Scholes". Retrieved March 26, 2012.
- ^ MacKenzie, Donald (2006). An Engine, Not a Camera: How Financial Models Shape Markets. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-13460-8.
- ^ أ ب Bodie, Zvi; Alex Kane; Alan J. Marcus (2008). Investments (7th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill/Irwin. ISBN 978-0-07-326967-2.
- ^ "Nobel Prize Foundation, 1997 Press release". October 14, 1997. Retrieved March 26, 2012.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
مصادر أساسية
- Black, Fischer (1973). "The Pricing of Options and Corporate Liabilities". Journal of Political Economy. 81 (3): 637–654. doi:10.1086/260062.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) [1] (Black and Scholes' original paper.) - Merton, Robert C. (1973). "Theory of Rational Option Pricing". Bell Journal of Economics and Management Science. The RAND Corporation. 4 (1): 141–183. doi:10.2307/3003143. JSTOR 3003143. [2]
- Hull, John C. (1997). Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives. Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-601589-1.
أوجه تاريخية واجتماعية
- Bernstein, Peter (1992). Capital Ideas: The Improbable Origins of Modern Wall Street. The Free Press. ISBN 0-02-903012-9.
- MacKenzie, Donald (2003). "An Equation and its Worlds: Bricolage, Exemplars, Disunity and Performativity in Financial Economics". Social Studies of Science. 33 (6): 831–868. doi:10.1177/0306312703336002. [3]
- MacKenzie, Donald (2003). "Constructing a Market, Performing Theory: The Historical Sociology of a Financial Derivatives Exchange". American Journal of Sociology. 109 (1): 107–145. doi:10.1086/374404.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help) [4] - MacKenzie, Donald (2006). An Engine, not a Camera: How Financial Models Shape Markets. MIT Press. ISBN 0-262-13460-8.
- Szpiro, George G. Pricing the Future: Finance, Physics, and the 300-Year Journey to the Black-Scholes Equation; A Story of Genius and Discovery (New York: Basic, 2011) 298 pp.
قراءات إضافية
- Haug, E. G (2007). "Option Pricing and Hedging from Theory to Practice". Derivatives: Models on Models. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-01322-9. The book gives a series of historical references supporting the theory that option traders use much more robust hedging and pricing principles than the Black, Scholes and Merton model.
- Triana, Pablo (2009). Lecturing Birds on Flying: Can Mathematical Theories Destroy the Financial Markets?. Wiley. ISBN 978-0-470-40675-5. The book takes a critical look at the Black, Scholes and Merton model.
وصلات خارجية
مناقشة النموذج
- Ajay Shah. Black, Merton and Scholes: Their work and its consequences. Economic and Political Weekly, XXXII(52):3337–3342, December 1997
- The mathematical equation that caused the banks to crash by Ian Stewart in The Observer, February 12, 2012
- When You Cannot Hedge Continuously: The Corrections to Black–Scholes, Emanuel Derman
- The Skinny On Options TastyTrade Show (archives)
الاشتقاق والحل
- Derivation of the Black–Scholes Equation for Option Value, Prof. Thayer Watkins
- Solution of the Black–Scholes Equation Using the Green's Function, Prof. Dennis Silverman
- Solution via risk neutral pricing or via the PDE approach using Fourier transforms (includes discussion of other option types), Simon Leger
- Assumptions for Black Scholes Model, black-scholes.co.uk
- Step-by-step solution of the Black–Scholes PDE, planetmath.org.
- The Black–Scholes Equation Expository article by mathematician Terence Tao.
تطبيقات الحاسوب
- Calculator for vanilla call and put based on Black-Sholes model
- Black–Scholes in Multiple Languages
- Chicago Option Pricing Model (Graphing Version)
- Black-Scholes-Merton Implied Volatility Surface Model (Java)
- Black-Scholes Calculator
- Online Black-Scholes Calculator
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
تاريخية
- Trillion Dollar Bet—Companion Web site to a Nova episode originally broadcast on February 8, 2000. "The film tells the fascinating story of the invention of the Black–Scholes Formula, a mathematical Holy Grail that forever altered the world of finance and earned its creators the 1997 Nobel Prize in Economics."
- BBC Horizon A TV-programme on the so-called Midas formula and the bankruptcy of Long-Term Capital Management (LTCM)
- BBC News Magazine Black–Scholes: The maths formula linked to the financial crash (April 27, 2012 article)
![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}C(S,t)&=N(d_{1})S-N(d_{2})Ke^{-r(T-t)}\\d_{1}&={\frac {1}{\sigma {\sqrt {T-t}}}}\left[\ln \left({\frac {S}{K}}\right)+\left(r+{\frac {\sigma ^{2}}{2}}\right)(T-t)\right]\\d_{2}&={\frac {1}{\sigma {\sqrt {T-t}}}}\left[\ln \left({\frac {S}{K}}\right)+\left(r-{\frac {\sigma ^{2}}{2}}\right)(T-t)\right]\\&=d_{1}-\sigma {\sqrt {T-t}}\end{aligned}}}](https://www.marefa.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f737b9bf99a4cd480d66fe454cda43e63c2ada5a)



















