قلب وعائي
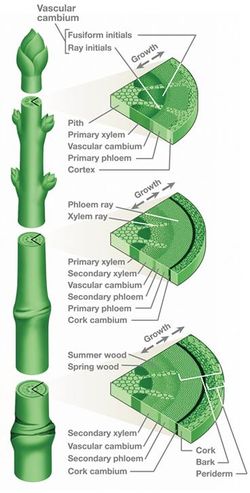
كامبيوم Cambium ، الطبقة الداخلية في لحاء خشب الأشجار، وتمثل مكان النمو في النبات.[2] وتعطي provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. It is found in the area between xylem and phloem. A cambium can also be defined as a cellular plant tissue from which phloem, xylem, or cork grows by division, resulting (in woody plants) in secondary thickening. It forms parallel rows of cells, which result in secondary tissues.[3]
There are several distinct kinds of cambium found in plant stems and roots:
- Cork cambium, a tissue found in many vascular plants as part of the periderm.
- Unifacial cambium, which ultimately produces cells to the interior of its cylinder.
- Vascular cambium, a lateral meristem in the vascular tissue of plants.
الاستخدامات
The cambium of many species of woody plants are edible;[4] however, due to its vital role in the homeostasis and growth of woody plants, this may result in death of the plant if enough cambium is removed at once. The cambium can generally be eaten raw or cooked, and can be ground to flour for use in baking.
الأصل
مرادفات
- Wood cambium
- Main cambium
- Bifacial cambium
انظر أيضا
المصادر
- ^ Winterborne J, 2005. Hydroponics - Indoor Horticulture [1]
- ^ عبد الجليل هويدي، محمد أحمد هيكل (2004). أساسيات الجيولوجيا التاريخية. مكتبة الدار العربية للكتب.
- ^ "Cambium". Dictionary of Botany.
- ^ Holmes, Tao Tao (2016-05-20). "So You Want to Eat a Tree". Atlas Obscura (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2022-05-08.
وصلات خارجية
- Pictures of Vascular cambium
- Detailed description - James D. Mauseth
- Review: Risopatron JPM, Sun YQ, Jones BJ (2010) The vascular cambium: Molecular control of cellular structure. Protoplasma 247 (3-4):145-161. DOI:10.1007/s00709-010-0211-z PMID 20978810
