خيتون
| خيتون | |
|---|---|

| |
| Lined chiton, Tonicella lineata. The anterior end of the animal is to the right | |
| التصنيف العلمي | |
| أصنوفة غير معروفة (أصلحها): | الحياة |
| مملكة: | الحيوانية |
| Phylum: | رخويات |
| Class: | عديدات الصدف Blainville, 1816 |
خيتون (Chitons؛ ![]() /ˈkaɪtənz/) هي رخويات بحرية تتراوح في الحجم من صغيرة إلى كبيرة في صف عديدة الأصداف Polyplacophora، والتي كانت تُعرف من قبل بإسم مزدوجات الأعصاب Amphineura صف من الرخويات Mollusca يضم الخيتونات (أو الدرقيات) Chiton. وهي حيوانات مسطحة مضغوطة ظهرياً بطنياً، وجهها الظهري المحدب مغطى بثماني صفائح كلسية متمفصلة، متراكبة جزئياً الواحدة فوق الأخرى، الأمر الذي دعا إلى تسميتها عديدات الصفائح Polyplacophora إضافة إلى مزدوجات الأعصاب، التي قسمت إلى ثلاث رتب هي عديمات الصفائح Aplacophora ووحيدات الصفائح Monoplacophora وعديدات الصفائح، والتي يعد اليوم كل منها بمنزلة صف قائم بذاته.
/ˈkaɪtənz/) هي رخويات بحرية تتراوح في الحجم من صغيرة إلى كبيرة في صف عديدة الأصداف Polyplacophora، والتي كانت تُعرف من قبل بإسم مزدوجات الأعصاب Amphineura صف من الرخويات Mollusca يضم الخيتونات (أو الدرقيات) Chiton. وهي حيوانات مسطحة مضغوطة ظهرياً بطنياً، وجهها الظهري المحدب مغطى بثماني صفائح كلسية متمفصلة، متراكبة جزئياً الواحدة فوق الأخرى، الأمر الذي دعا إلى تسميتها عديدات الصفائح Polyplacophora إضافة إلى مزدوجات الأعصاب، التي قسمت إلى ثلاث رتب هي عديمات الصفائح Aplacophora ووحيدات الصفائح Monoplacophora وعديدات الصفائح، والتي يعد اليوم كل منها بمنزلة صف قائم بذاته.
معظم الخيتونات صغير يراوح طول الواحد منها بين 2 و5سم، لكن قد يصل طول أضخمها ـ وهو الخيتون الخفي Cryptochiton ـ إلى نحو 30 سم. وهي تعيش على شواطئ البحر متثبتة بين جذوع الأشجار وأوراقها المتساقطة على السطوح الصخرية في المناطق بين المد والجزر، لكن بعضها يألف الحياة في الأعماق السحيقة من البحر.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
الشكل
شكلها الخارجي
| جزء من سلسلة عن |
| القواقع البحرية |
|---|
 |
| قواقع الرخويات |
| عن قواقع الرخويات |
| قواقع بحرية أخرى |
الخيتونات حيوانات داكنة اللون (الشكل 1)، صغيرة الرأس الذي يحمل أعضاء تتحسس بالضوء تشبه العيون. وهي تتغذى بِـ«كشط» الطحالب المترسبة على الصخور بفضل مبشرة radula موجودة في فمها.
تتثبت الخيتونات على الصخور بشدة بفضل القدم المسطحة العريضة (الشكل 2)، وتتكور على نفسها مثل الكرة إذا ما فقدت مرتكزها.

The most anterior plate is crescent shaped, and is known as the cephalic plate (sometimes called a "head plate", despite the absence of a complete head). The most posterior plate is known as the anal plate (sometimes called the "tail plate", although chitons do not have a tail.)
يغطي ظهر الحيوان رداء mantle أو pallium، يتدلى على محيط الحيوان تاركاً بينه وبين القدم المركزية ميزابةً دائريةً pallial groove تسمى الجوف الردائي pallial cavity، تتدلى فيه ـ وعلى جانبي الحيوان ـ مجموعة من الغلاصم التنفسية. فعندما يتثبت الحيوان على الصخر وترتكز حافة الرداء على المرتكز؛ تتشكل الميزابة التي تحبس فيها كمية من الماء يتم منه استخلاص الأكسجين الضروري للحيوان عبر جدار الغلاصم التي تتدلى فيه. وفي أثناء الجزر تنضغط حافة الرداء على الأرض؛ لتحبس الماء في الميزابة؛ لتحافظ عليه تعزيزاً للتنفس.
الأجهزة الداخلية
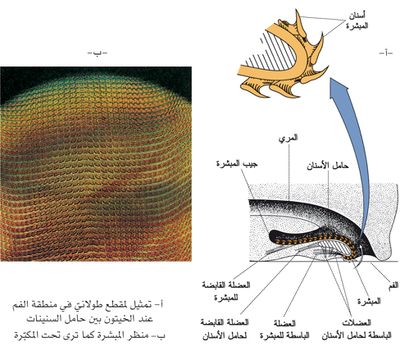
يبدأ جهاز الهضم بالفم الذي ينفتح على الوجه السفلي من الرأس، ويؤدي إلى بلعوم يبرز في أرضه ما يشبه اللسان الذي تدعمه صفيحة غضروفية تسمى حامل السنينات odontophore؛ لأنه تغطيه صفيحة عليها مجموعة من السنينات المتجهة إلى الخلف تشكل ما يسمى المبشرة radula يستخدمها الحيوان في التغذي بـ «بَشْرِ» الغذاء (الشكل 3)، وتوجه الناتج إلى معدة تحف بها غدد هضمية، وتنتهي بأمعاء تطرح الفضلات الغذائية بفوهة شرج في نهاية الميزابة الردائية.
يتألف جهاز الدوران من قلب ثلاثي الأجواف يوجد في النهاية الخلفية للحيوان، يحيط به جوف حول القلب pericardium، يؤدي إلى شريان أبهر aorta وجَيْبَيْن sinuses دمويين توجه الدم نحو الغلاصم للتنقية.
ويتكون جهاز الإطراح من شفع من الكُلَيّات التالية metanephridia تنفتح كل منهما بفوهة في الجوف حول القلب طارحةً الفضلات في الميزابة الردائية بفوهتي إطراح على جانبي الحيوان.
ويتكون الجهاز العصبي في مزدوجات الأعصاب من طوق عصبي حول البلعوم يعصب المنطقة الأمامية من جسم الحيوان، ينطلق منه شفعان من الحبال العصبية على طول الحيوان (ومن هنا أتت التسمية بمزدوجات الأعصاب) تعصب القدم والرداء.
الأجناس منفصلة في معظم الخيتونات، وتفقس البيضة الملقحة؛ لتعطي يرقة حاملة للدولاب trochophore larva (الشكل 4) التي تتحول شكلياً مباشرة إلى خيتونات فتية.
الحواس
الاستخدامات الططعام
Chitons are eaten in many islands in the Caribbean, including Trinidad, Tobago and Barbados. They were also eaten by native Americans of the Pacific coasts of both North and South America. The foot of the chiton is prepared in a manner similar to abalone.
عادات الحياة
A chiton creeps along slowly on a muscular foot. They have considerable power of adhesion and can cling to rocks very powerfully, like a limpet.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
التكاثر ودورة الحياة

المفترسون
Animals which prey on chitons include humans, seagulls, seastars, crabs, lobster and fish.
أكبر أنواع
The largest chiton (up to 33 cm in length) is the brick-red gumboot chiton of the Pacific Northwest. In this species the valves are completely internal.
الأصول التطورية
Chitons have a relatively good fossil record, stretching back [2] to the Devonian. Before this, some organisms have been interpreted (tentatively) as stem-group polyplacophora; the record of polyplacophora stretches back to the Ordovician.[3]

تاريخ الاستقصاء العلمي للخيتونات
Chitons were first studied by Carolus Linnaeus in 1758. Since his description of the first four species, chitons have been variously classified. They were called Cyclobranchians ("round arm") in the early 19th century, and then grouped with the aplacophorans in the subphylum Amphineura in 1876. The class Polyplacophora was named by de Blainville 1816.
أصل الاسم
The English name "chiton" originates from the Latin word chitōn, which means "mollusc", and in turn is derived from the Greek word "khitōn", meaning tunic (which also is the source of the word chitin). The Greek word "khitōn" can be traced to the Central Semitic word "*kittan", which is from the Akkadian words "kitû" or "kita’um", meaning flax or linen, and originally the Sumerian word "gada" or "gida".
The Greek-derived name Polyplacophora comes from the words poly- (many), plako- (tablet), and -phoros (bearing), a reference to the chiton's eight shell plates.
التصنيف
Most classification schemes in use today are based, at least in part, on Pilsbry's Manual of Conchology (1892–1894), extended and revised by Kaas and Van Belle (1985–1990).
The most recent classification (Sirenko 2006) is based not only on shell morphology, as usual, but also other important features including aesthetes, girdle, radula, gills, glands, egg hull projections and spermatozoids. It includes all the living and extinct genera of chitons.
This system is now generally accepted.
- Class Polyplacophora de Blainville, 1816
- Subclass Paleoloricata Bergenhayn, 1955
- Order Chelodida Bergenhayn, 1943
- Family Chelodidae Bergenhayn, 1943
- Chelodes Davidson et King, 1874
- Euchelodes Marek, 1962
- Calceochiton Flower, 1968
- Family Chelodidae Bergenhayn, 1943
- Order Septemchitonida Bergenhayn, 1955
- Family Gotlandochitonidae Bergenhayn, 1955
- Gotlandochiton Bergenhayn, 1955
- Family Helminthochitonidae Van Belle, 1975
- Kindbladochiton Van Belle, 1975
- Diadelochiton Hoare, 2000
- Helminthochiton Salter in Griffith et M'Coy, 1846
- Echinochiton Pojeta, Eernisse, Hoare et Henderson, 2003
- Family Septemchitonidae Bergenhayn, 1955
- Septemchiton Bergenhayn, 1955
- Paleochiton A. G. Smith, 1964
- Thairoplax Cherns, 1998
- Family Gotlandochitonidae Bergenhayn, 1955
- Order Chelodida Bergenhayn, 1943
- Subclass Loricata Shumacher, 1817
- Order Lepidopleurida Thiele, 1910
- Suborder Cymatochitonina Sirenko et Starobogatov, 1977
- Family Acutichitonidae Hoare, Mapes et Atwater, 1983
- Acutichiton Hoare, Sturgeon et Hoare, 1972
- Elachychiton Hoare, Sturgeon et Hoare, 1972
- Harpidochiton Hoare et Cook, 2000
- Arcochiton Hoare, Sturgeon et Hoare, 1972
- Kraterochiton Hoare, 2000
- Soleachiton Hoare, Sturgeon et Hoare, 1972
- Asketochiton Hoare et Sabattini, 2000
- Family Cymatochitonidae Sirenko et Starobogatov, 1977
- Cymatochiton Dall, 1882
- Compsochiton Hoare et Cook, 2000
- Family Gryphochitonidae Pilsbry, 1900
- Gryphochiton Gray, 1847
- Family Lekiskochitonidae Smith et Hoare, 1987
- Lekiskochiton Hoare et Smith, 1984
- Family Permochitonidae Sirenko et Starobogatov, 1977
- Permochiton Iredale et Hull, 1926
- Family Acutichitonidae Hoare, Mapes et Atwater, 1983
- Suborder Lepidopleurina Thiele, 1910
- Family Ferreiraellidae Dell’ Angelo et Palazzi, 1991
- Glaphurochiton Raymond, 1910
- ?Pyknochiton Hoare, 2000
- ?Hadrochiton Hoare, 2000
- Ferreiraella Sirenko, 1988
- Family Glyptochitonidae Starobogatov et Sirenko, 1975
- Glyptochiton Konninck, 1883
- Family Leptochitonidae Dall, 1889
- Colapterochiton Hoare et Mapes, 1985
- Coryssochiton DeBrock, Hoare et Mapes, 1984
- Proleptochiton Sirenko et Starobogatov, 1977
- Schematochiton Hoare, 2002
- Pterochiton (Carpenter MS) Dall, 1882
- Leptochiton Gray, 1847
- Parachiton Thiele, 1909
- Terenochiton Iredale, 1914
- Trachypleura Jaeckel, 1900
- Pseudoischnochiton Ashby, 1930
- Lepidopleurus Risso, 1826
- Hanleyella Sirenko, 1973
- Family Camptochitonidae Sirenko, 1997
- Camptochiton DeBrock, Hoare et Mapes, 1984
- Pedanochiton DeBrock, Hoare et Mapes, 1984
- Euleptochiton Hoare et Mapes, 1985
- Pileochiton DeBrock, Hoare et Mapes, 1984
- Chauliochiton Hoare et Smith, 1984
- Stegochiton Hoare et Smith, 1984
- Family Nierstraszellidae Sirenko, 1992
- Nierstraszella Sirenko, 1992
- Family Mesochitonidae Dell’ Angelo et Palazzi, 1989
- Mesochiton Van Belle, 1975
- Pterygochiton Rochebrune, 1883
- Family Protochitonidae Ashby, 1925
- Protochiton Ashby, 1925
- Deshayesiella (Carpenter MS) Dall, 1879
- Oldroydia Dall, 1894
- Family Hanleyidae Bergenhayn, 1955
- Hanleya Gray, 1857
- Hemiarthrum Dall, 1876
- Family Ferreiraellidae Dell’ Angelo et Palazzi, 1991
- Suborder Cymatochitonina Sirenko et Starobogatov, 1977
- Order Chitonida Thiele, 1910
- Suborder Chitonina Thiele, 1910
- Superfamily Chitonoidea Rafinesque, 1815
- Family Ochmazochitonidae Hoare et Smith, 1984
- Ochmazochiton Hoare et Smith, 1984
- Family Ischnochitonidae Dall, 1889
- Ischnochiton Gray, 1847
- Stenochiton H. Adams et Angas, 1864
- Stenoplax (Carpenter MS) Dall, 1879
- Lepidozona Pilsbry, 1892
- Stenosemus Middendorff, 1847
- Subterenochiton Iredale et Hull, 1924
- Thermochiton Saito et Okutani, 1990
- Connexochiton Kaas, 1979
- Tonicina Thiele, 1906
- Family Callistoplacidae Pilsbry, 1893
- Ischnoplax Dall, 1879
- Callistochiton Carpenter MS, Dall, 1879
- Callistoplax Dall, 1882
- Ceratozona Dall, 1882
- Calloplax Thiele, 1909
- Family Chaetopleuridae Plate, 1899
- Chaetopleura Shuttleworth, 1853
- Dinoplax Carpenter MS, Dall, 1882[4]
- Family Loricidae Iredale et Hull, 1923
- Family Callochitonidae Plate, 1901
- Callochiton Gray, 1847
- Eudoxochiton Shuttleworth, 1853
- Vermichiton Kaas, 1979
- Family Chitonidae Rafinesque, 1815
- Subfamily Chitoninae Rafinesque, 1815
- Chiton Linnaeus, 1758
- Amaurochiton Thiele, 1893
- Radsia Gray, 1847
- Sypharochiton Thiele, 1893
- Nodiplax Beu, 1967
- Rhyssoplax Thiele, 1893
- Teguloaplax Iredale & Hull, 1926
- Mucrosquama Iredale, 1893
- Subfamily Toniciinae Pilsbry, 1893
- Tonicia Gray, 1847
- Onithochiton Gray, 1847
- Subfamily Acanthopleurinae Dall, 1889
- Acanthopleura Guilding, 1829
- Liolophura Pilsbry, 1893
- Enoplochiton Gray, 1847
- Squamopleura Nierstrasz, 1905
- Superfamily Schizochitonoidea Dall, 1889
- Family Schizochitonidae Dall, 1889
- Incissiochiton Van Belle, 1985
- Schizochiton Gray, 1847
- Family Ochmazochitonidae Hoare et Smith, 1984
- Suborder Acanthochitonina Bergenhayn, 1930
- Superfamily Mopalioidea Dall, 1889
- Family Tonicellidae Simroth, 1894
- Subfamily Tonicellinae Simroth, 1894
- Lepidochitona Gray, 1821
- Particulazona Kaas, 1993
- Boreochiton Sars, 1878
- Tonicella Carpenter, 1873
- Nuttallina (Carpenter MS) Dall, 1871
- Spongioradsia Pilsbry, 1894
- Oligochiton Berry, 1922
- Subfamily Juvenichitoninae Sirenko, 1975
- Juvenichiton Sirenko, 1975
- Micichiton Sirenko, 1975
- Nanichiton Sirenko, 1975
- Family Schizoplacidae Bergenhayn, 1955
- Schizoplax Dall, 1878
- Family Mopaliidae Dall, 1889
- Subfamily Heterochitoninae Van Belle, 1978
- Heterochiton Fucini, 1912
- Allochiton Fucini, 1912
- Subfamily Mopaliinae Dall, 1889
- Aerilamma Hull, 1924
- Guildingia Pilsbry, 1893
- Frembleya H. Adams, 1866
- Diaphoroplax Iredale, 1914
- Plaxiphora Gray, 1847
- Placiphorina Kaas & Van Belle, 1994
- Nuttallochiton Plate, 1899
- Mopalia Gray, 1847
- Maorichiton Iredale, 1914
- Placiphorella (Carpenter MS) Dall, 1879
- Katharina Gray, 1847
- Amicula Gray, 1847
- Superfamily Cryptoplacoidea H. et A. Adams, 1858
- Family Acanthochitonidae Pilsbry, 1893
- Subfamily Acanthochitoninae Pilsbry, 1893
- Acanthochitona Gray, 1921
- Craspedochiton Shuttleworth, 1853
- Spongiochiton (Carpenter MS) Dall, 1882
- Notoplax H. Adams, 1861
- Pseudotonicia Ashby, 1928
- Bassethullia Pilsbry, 1928
- Americhiton Watters, 1990
- Choneplax (Carpenter MS) Dall, 1882
- Cryptoconchus (de Blainville MS) Burrow, 1815
- Subfamily Cryptochitoninae Pilsbry, 1893
- Cryptochiton Middendorff, 1847
- Family Hemiarthridae Sirenko, 1997
- Hemiarthrum Carpenter in Dall, 1876
- Weedingia Kaas, 1988
- Family Choriplacidae Ashby, 1928
- Family Cryptoplacidae H. et A. Adams, 1858
- Cryptoplax de Blainville, 1818
- Order Lepidopleurida Thiele, 1910
- Incertae sedis
- Family Scanochitonidae Bergenhayn, 1955
- Scanochiton Bergenhayn, 1955
- Family Olingechitonidae Starobogatov et Sirenko, 1977
- Olingechiton Bergenhayn, 1943
- Family Haeggochitonidae Sirenko et Starobogatov, 1977
- Haeggochiton Bergenhayn, 1955
- Family Ivoechitonidae Sirenko et Starobogatov, 1977
- Ivoechiton Bergenhayn, 1955
- Family Scanochitonidae Bergenhayn, 1955
- Subclass Paleoloricata Bergenhayn, 1955
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
الهامش
- ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةRunnegar1974 - ^ أ ب خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةSerb2008 - ^ DOI:10.1098/rspb.2007.0701
This citation will be automatically completed in the next few minutes. You can jump the queue or expand by hand - ^ http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php search term Dinoplax accessed 7 April 2010
- Sirenko BI. New outlook on the system of chitons (Mollusca: Polyplacophora). Venus, 65 (1-2): 27-49, 2006