شلسفيج-هولشتاين
شلِسڤيگ-هولشتاين
| |
|---|---|
 | |
| الإحداثيات: 54°28′12″N 9°30′50″E / 54.47000°N 9.51389°E | |
| Country | Germany |
| Capital | Kiel |
| الحكومة | |
| • الكيان | Landtag of Schleswig-Holstein |
| • Minister-President | Daniel Günther (CDU) |
| • Governing parties | CDU / Bündnis 90/Die Grünen |
| • Bundesrat votes | 4 (of 69) |
| • Bundestag seats | 28 (of 736) |
| المساحة | |
| • Total | 15٬763٫17 كم² (6٬086٫19 ميل²) |
| التعداد (4 January 2022)[1] | |
| • Total | 2٬920٬850 |
| • الكثافة | 190/km2 (480/sq mi) |
| منطقة التوقيت | UTC+1 (CET) |
| • الصيف (التوقيت الصيفي) | UTC+2 (CEST) |
| ISO 3166 code | DE-SH |
| لوحة السيارة | formerly: S (1945–1947), SH (1947), BS (1948–1956)[2] |
| GRP (nominal) | €97,2 billion (2020)[3] |
| GRP per capita | €33.400 (2020) |
| NUTS Region | DEF |
| HDI (2018) | 0.924[4] very high · 13th of 16 |
| الموقع الإلكتروني | schleswig-holstein.de |
شلِسڤيگ-هولشتاين ( Schleswig-Holstein ؛ تـُنطق [ˌʃleːsvɪç ˈhɔlʃtaɪn] (![]() listen)؛ دنماركية: Slesvig-Holsten [ˌsle̝ːsvi ˈhʌlˌste̝ˀn]؛ Low German: Sleswig-Holsteen؛ North Frisian: Slaswik-Holstiinj) هي احدى ولايات ألمانيا الستة عشر. هولشتاين تشكل الجزء الجنوبي من الولاية، بينما تشكل شلسڤيگ الجنوبية الجزء الشمالي. وكانت شلسڤيگ قد قُسمت عام 1920 إلى جزئين جنوبي وشمالي بين ألمانيا والدنمارك.
listen)؛ دنماركية: Slesvig-Holsten [ˌsle̝ːsvi ˈhʌlˌste̝ˀn]؛ Low German: Sleswig-Holsteen؛ North Frisian: Slaswik-Holstiinj) هي احدى ولايات ألمانيا الستة عشر. هولشتاين تشكل الجزء الجنوبي من الولاية، بينما تشكل شلسڤيگ الجنوبية الجزء الشمالي. وكانت شلسڤيگ قد قُسمت عام 1920 إلى جزئين جنوبي وشمالي بين ألمانيا والدنمارك.
Historically, the name can also refer to a larger region, containing both present-day Schleswig-Holstein and the former South Jutland County (Northern Schleswig; now part of the Region of Southern Denmark) in Denmark. It covers an area of 15,763 km2 (6,086 sq mi), making it the 5th smallest German federal state by area (including the city-states).
Schleswig was under Danish control during the Viking Age, but in the 12th century it escaped full control and became a duchy. It bordered Holstein, which was a part of the Holy Roman Empire. Beginning in 1460, both Schleswig and Holstein were ruled together by the Danish king acting as duke of both Schleswig and Holstein, with the latter remaining part of Germany. In the 19th century, Danes and Germans each believed they had a claim to Schleswig-Holstein, the population of which was majority ethnic German. The resulting long-term political and territorial dispute was known as the Schleswig-Holstein Question. In 1848, Denmark tried to formally annex the area. Prussia responded by invading, thus beginning the First Schleswig War, which ended in a victory for Denmark and the signing of the 1852 London Protocol. But the fight broke out again in 1864 (the Second Schleswig War), and this time Prussia and Austria won and the territory was absorbed into Prussia in 1867. More than 50 years later, after the German defeat in World War I, the Allies required that the question of sovereignty over the territory be submitted to plebiscites (the 1920 Schleswig plebiscites), which resulted in the return of some of the territory to Denmark. After World War II, Schleswig-Holstein took in over a million refugees.
Today, Schleswig-Holstein's economy is known for its agriculture, such as its Holstein cows. Its position on the Atlantic Ocean makes it a major trade point and shipbuilding site; it is also the location of the Kiel Canal. Its offshore oil wells and wind farms produce significant amounts of energy. Fishing is a major industry, and the basis of its distinctive unique local cuisine. It is a popular tourist destination for Germans and tourists across the globe.
التاريخ

The term "Holstein" derives from Old Saxon Holseta Land, (Holz means wood in modern Standardized German; holt is a now-archaic English word for woods.) Originally, the term referred to the central of the three Saxon tribes north of the River Elbe: Tedmarsgoi (Dithmarschen), Holstein and Sturmarii (Stormarn). The area inhabited by the tribe of the Holsts lay between the Stör River and Hamburg; after Christianization, their main church was in Schenefeld. Saxon Holstein became a part of the Holy Roman Empire after Charlemagne's Saxon campaigns in the late eighth century. Beginning in 811, the northern border of Holstein (and thus of the Empire) was the River Eider.




The term "Schleswig" originally referred to the city of Schleswig. The city's name derives from Schlei "inlet" in the east and vik, which meant inlet in Old Norse and settlement in Old Saxon, and is cognate with the "-wick" and "-wich" elements in place-names in Britain.
The Duchy of Schleswig, or Southern Jutland, was originally an integral part of Denmark, but in medieval times was established as a fief under the control of the Kingdom of Denmark, having the same relationship with the Danish Crown as, for example, Brandenburg or Bavaria had with the Holy Roman Emperor. Around 1100, the Duchy of Saxony gave Holstein to Count Adolf I of Schauenburg.
دوقيات في الأملاك الدنماركية
Schleswig and Holstein have at different times belonged in part or completely to either Denmark or Germany, or have been virtually independent of both nations. Schleswig was never part of Germany until after the Second Schleswig War in 1864. But for many centuries, the king of Denmark was both a Danish Duke of Schleswig and a German Duke of Holstein. Essentially, Schleswig was either integrated into Denmark or was a Danish fief, and Holstein was a German fief and once, long before that, a sovereign state. Both were ruled for several centuries by the kings of Denmark. In 1721, all of Schleswig was united into a single duchy under the king of Denmark, and the great powers of Europe confirmed in an international treaty that all future kings of Denmark should automatically become dukes of Schleswig: consequently, Schleswig would always follow the order of succession that applied in the Kingdom of Denmark. Government business in both duchies was conducted in the German language, even though for a long time they were governed from Copenhagen. (Beginning in 1523, however, they were governed by the German Chancellery, which in 1806 was renamed the Schleswig-Holstein Chancellery). After the Protestant Reformation, church services were conducted in German in the southern part of Schleswig, and in Danish in the northern part. This difference would later contribute strongly to shaping the inhabitants' national sentiments, as would the different languages spoken in different schools after 1814, when mandatory schooling was instituted.
مسألة شلِسڤيگ-هولشتاين
The German national awakening that followed the Napoleonic Wars gave rise to a strong popular movement in Holstein and Southern Schleswig for unification with a new Prussian-dominated Germany. This development was paralleled by an equally strong Danish national awakening in Denmark and Northern Schleswig. This movement called for the complete reintegration of Schleswig into the Kingdom of Denmark and demanded an end to discrimination against Danes in Schleswig. The ensuing conflict is sometimes called the Schleswig-Holstein Question. In 1848, King Frederick VII of Denmark declared that he would grant Denmark a liberal constitution and the immediate goal of the Danish national movement was to ensure that this constitution would give rights to all Danes, i.e. not only to those in the Kingdom of Denmark, but also to Danes (and Germans) living in Schleswig. Furthermore, they demanded protection for the Danish language in Schleswig (the dominant language in almost a quarter of Schleswig had changed from Danish to German since the beginning of the 19th century).
A liberal constitution for Holstein was not seriously considered in Copenhagen, since it was well known that the political élite of Holstein were more conservative than Copenhagen's. Representatives of German-minded Schleswig-Holsteiners demanded that Schleswig and Holstein be unified and allowed its own constitution and that Schleswig join Holstein as a member of the German Confederation. These demands were rejected by the Danish government in 1848, and the Germans of Holstein and Southern Schleswig rebelled. This began the First Schleswig War (1848–51), which ended in a Danish victory at Idstedt.
In 1863, conflict broke out again when Frederick VII died without legitimate issue. According to the order of succession of Denmark and Schleswig, the crowns of both Denmark and Schleswig would pass to Duke Christian of Duchy of Glücksburg, who became Christian IX. The transmission of the duchy of Holstein to the head of the (German-oriented) branch of the Danish royal family, the House of Augustenborg, was more controversial. The separation of the two duchies was challenged by the Augustenborg heir, who claimed, as in 1848, to be rightful heir of both Schleswig and Holstein. The promulgation of a common constitution for Denmark and Schleswig in November 1863 prompted Otto von Bismarck to intervene and Prussia and Austria declared war on Denmark. This was the Second War of Schleswig, which ended in Danish defeat. British attempts to mediate in the London Conference of 1864 failed, and Denmark lost Schleswig (Northern and Southern Schleswig), Holstein, and Lauenburg to Prussia and Austria.
مقاطعة پروسيا
Contrary to the hopes of German Schleswig-Holsteiners, the area did not gain its independence, but was annexed as a province of Prussia in 1867. Also following the Austro-Prussian War in 1866, section five of the Peace of Prague stipulated that the people of Northern Schleswig would be consulted in a referendum on whether to remain under Prussian rule or return to Danish rule. This condition, however, was never fulfilled by Prussia. During the decades of Prussian rule within the German Empire, authorities attempted a Germanisation policy in the northern part of Schleswig, which remained predominantly Danish. The period also meant increased industrialisation of Schleswig-Holstein and the use of Kiel and Flensburg as important Imperial German Navy locations. The northernmost part and west coast of the province saw a wave of emigration to America, while some Danes of North Schleswig emigrated to Denmark.
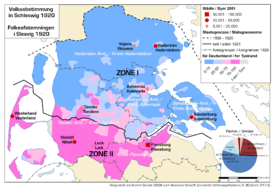
استفتاء 1920
| الدائرة الانتخابية |
الاسم الألماني |
الاسم الدنماركي |
لألمانيا | للدنمارك | ||
| النسبة | الأصوات | النسبة | الأصوات | |||
| المنطقة 1 (شمال شلسڤيگ)، 10 فبراير 1920 | 25.1 % | 25,329 | 74.9 % | 75,431 | ||
| منطقة | Hadersleben | Haderslev | 16.0% | 6,585 | 84.0% | 34,653 |
| بلدة | Hadersleben | Haderslev | 38.6% | 3,275 | 61.4% | 5,209 |
| منطقة | Apenrade | Aabenraa | 32.3% | 6,030 | 67.7% | 12,653 |
| بلدة | Apenrade | Aabenraa | 55.1% | 2,725 | 44.9% | 2,224 |
| منطقة | Sonderburg | Sønderborg | 22.9% | 5,083 | 77.1% | 17,100 |
| بلدة | Sonderburg | Sønderborg | 56.2% | 2,601 | 43.8% | 2,029 |
| بلدة | Augustenburg | Augustenborg | 48.0% | 236 | 52.0% | 256 |
| الجزء الشمالي من المنطقة |
Tondern | Tønder | 40.9% | 7,083 | 59.1% | 10,223 |
| بلدة | Tondern | Tønder | 76.5% | 2,448 | 23.5% | 750 |
| بلدة | Hoyer | Højer | 72.6% | 581 | 27.4% | 219 |
| بلدة | Lügumkloster | Løgumkloster | 48.8% | 516 | 51.2% | 542 |
| الجزء الشمالي من المنطقة |
Flensburg | Flensborg | 40.6% | 548 | 59.4% | 802 |
| المنطقة 2 (وسط شلسڤيگ)، 14 مارس 1920 | 80.2 % | 51,742 | 19.8 % | 12,800 | ||
| الجزء الجنوبي من المنطقة |
Tondern | Tønder | 87.9% | 17,283 | 12.1% | 2,376 |
| الجزء الجنوبي من المنطقة |
Flensburg | Flensborg | 82.6% | 6,688 | 17.4% | 1,405 |
| بلدة | Flensburg | Flensborg | 75.2% | 27,081 | 24.8% | 8,944 |
| الجزء الشمالي من المنطقة |
Husum | Husum | 90.0% | 672 | 10.0% | 75 |
الجغرافيا
شلسڤيگ-هولشتاين تقع في أقصى شمال ألمانيا وتطل من الشرق على بحر البلطيق بينما من الغرب على بحر الشمال. تحدها من الشمال الدانمارك ومن الجنوب مكلنبورگ-فورپومرن، هامبورگ وساكسونيا السفلى.
معظم أراضي الولاية سهلة، أعلى مرتفع هو بونگسبرگ (168 متر). هناك العديد من البحيرات خاصة في شرق هولسشتاين، حيث أنها تسمى سويسرا الهولشتاينية. مجموعة جزر فريزن تقع على الشاطئ الغربي وجزيرة أخرى تدعى هيلگولاند تقع أبعد إلى الشمال الغربي. هناك جزيرة واحدة في الشرق، هي جزيرة فيمارن Fehmarn. أهم الأنهار: إلبه وآيدر.
التقسيم الاداري وأهم المدن
تقسم الولاية إلى 11 دائرة قروية و 4 دوائر مدنية. Schleswig-Holstein is divided into eleven Kreise (sg. Kreis; district):
|
Furthermore, there are four urban districts that do not belong to any district:
كيل هي العاصمة وأكبر مدينة بالولاية، عدد سكانها يبلغ 229,000 نسمة. أهم المدن الأخرى: لوبك، فلنزبورگ ونويمونستر.
الاقتصاد والبنية التحتية
يعتمد اقتصاد الولاية بشكل عام على الزراعة وصيد الأسماك. هناك 3 مناطق اقتصادية كبيرة: المنطقة المحيطة بهامبورگ (صناعات ثقيلة وخدمات)، الساحل الغربي (سياحة وطاقة الرياح) و في المدن على الساحل الشرقي.
يوجد بكيل ولوبك مطارات دولية. تملك الولاية عدة موانئ بحرية أهمها موجود بكيل و لوبك أيضاً. هناك خطوط ملاحية تجارية مهمة مع دول اسكندينافيا، روسيا ودول البلطيق.
التعليم و الثقافة
تملك شلسڤيگ-هولشتاين 3 جامعات، 8 معاهد تطبيقية، معهد عالي للفنون ومعهد عالي آخر للادارة.
هناك أربع لغات رسمية بالولاية: الفريزية، الدانماركية، ألمانية سفلى (Plattdeutsch) والألمانية (الفصحى).
المصادر
- ^ "Zahlen zur Bevölkerung". Schleswig-Holstein.de (in الألمانية). Archived from the original on 17 April 2022. Retrieved 17 April 2022.
- ^ By the federal vehicle registration reform of 1 July 1956 distinct prefixes were given for every district.
- ^ "Zahlen zur Wirtschaft". Schleswig-Holstein.de (in الألمانية). Landesregierung Schleswig-Holstein. Archived from the original on 17 April 2022. Retrieved 17 April 2022.
- ^ "Sub-national HDI – Area Database – Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org (in الإنجليزية). Archived from the original on 23 September 2018. Retrieved 13 September 2018.
وصلات خارجية
- CS1 الألمانية-language sources (de)
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Articles containing دنماركية-language text
- Articles containing Low German-language text
- Articles containing North Frisian-language text
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- Pages using Lang-xx templates
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- شلسڤيگ-هولشتاين
- أقاليم التصنيف الأول في الاتحاد الأوروپي
- دول وأقاليم تأسست في 1946
- تأسيسات 1946 في ألمانيا الغربية
- صفحات مع الخرائط