سترويد ابتنائي
الستـِرويـْدات الابتنائية Anabolic steroids، أو anabolic-androgenic steroids (AAS), are a class of steroid hormones related to the hormone تستوسترون. They increase protein synthesis within cells, which results in the buildup of cellular tissue (anabolism), especially in muscles. Anabolic steroids also have androgenic and virilizing properties, including the development and maintenance of masculine characteristics such as the growth of the vocal cords and body hair. The word anabolic comes from the Greek anabolein, "to build up", and the word androgenic from the Greek andros, "man" + genein, "to produce".
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
تاريخ
Isolation of gonadal AAS

تطوير synthetic AAS
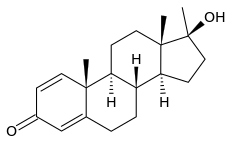
علم الأدوية
سبل التعاطي
آلية العمل

Anabolic and androgenic effects
| ||||||||||||||||
التأثيرات العكسية
Medical and ergogenic uses
الاستخدامات الطبية
الوضع في الرياضة
Anabolic steroids are banned by all major sports bodies including the Olympics,[4] the National Basketball Association,[5] the National Hockey League,[6] as well as the National Football League.[7] The World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA) maintains the list of performance-enhancing substances used by many major sports bodies and includes all anabolic agents, which includes all anabolic steroids and precursors as well as all hormones and related substances.[8][9] Spain has passed an anti-doping law creating a national anti-doping agency.[10] Italy passed a law in 2000 where penalties range up to three years in prison if an athlete has tested positive for banned substances.[11] In 2006, Russian President Vladimir Putin signed into law ratification of the International Convention Against Doping in Sport which would encourage cooperation with WADA. Many other countries have similar legislation prohibiting anabolic steroids in sports including Denmark,[12] France,[13] the Netherlands[14] and Sweden.[15]
التجار غير المشروع

. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
انظر أيضاً
- Prohormone
- سترويد
- Steroid stack
- Growth hormone treatment
- Selective androgen receptor modulator
- Ergogenic use of anabolic steroids
الهامش
- Hartgens F, Kuipers H (2004). "Effects of androgenic-anabolic steroids in athletes". Sports Med. 34 (8): 513–54. doi:10.2165/00007256-200434080-00003. PMID 15248788.
- ^ Grishkovskaya I, Avvakumov GV, Sklenar G, Dales D, Hammond GL, Muller YA (2000). "Crystal structure of human sex hormone-binding globulin: steroid transport by a laminin G-like domain". EMBO J. 19 (4): 504–12. doi:10.1093/emboj/19.4.504. PMID 10675319.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Pereira de Jésus-Tran K, Côté PL, Cantin L, Blanchet J, Labrie F, Breton R (2006). "Comparison of crystal structures of human androgen receptor ligand-binding domain complexed with various agonists reveals molecular determinants responsible for binding affinity". Protein Sci. 15 (5): 987–99. doi:10.1110/ps.051905906. PMC 2242507. PMID 16641486.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ خطأ استشهاد: وسم
<ref>غير صحيح؛ لا نص تم توفيره للمراجع المسماةChr - ^ "Olympic movement anti-doping code" (PDF). International Olympic Committee. 1999. Retrieved 2007-05-06.
- ^ "The nba and nbpa anti-drug program". NBA Policy. findlaw.com. 1999. Retrieved 2007-05-06.
- ^ "NHL/NHLPA performance-enhancing substances program summary". nhlpa.com. Retrieved 2007-05-06.
- ^ "List of Prohibited Substances" (PDF). nflpa.com. 2006. Retrieved 2007-05-06.
- ^ "World anti-doping code" (PDF). WADA. 2003. Retrieved 2007-07-10.
- ^ "Prohibited list of 2005" (PDF). WADA. 2005. Retrieved 2007-05-06.
- ^ "Spain's senate passes anti-doping law". Associated press. Herald Tribune. October 5, 2006. Retrieved 2007-05-06.
- ^ Johnson, Kevin (2006-02-20). "Italian anti-doping laws could mean 3 years in jail". USA Today. Retrieved 2007-05-06.
- ^ "Act on promotion of doping-free sport" (PDF). kum.dk. 2004. Retrieved 2007-05-06.
- ^ "Protection of health of athletes and the fight against doping" (PDF). WADA. 2006. Retrieved 2007-05-06.
- ^ "Anti-doping legislation in the netherlands" (PDF). WADA. 2006. Retrieved 2007-05-06.
- ^ "The Swedish Act prohibiting certain doping substances (1991:1969)" (PDF). WADA. 1991. Retrieved 2007-05-06.
للاستزادة
- D. Kochakian, Charles (2000). Anabolic Steroids in Sport and Exercise. Human Kinetics. ISBN 0880117869.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Daniels, R. C. (February 1, 2003). The Anabolic Steroid Handbook. Richard C Daniels. p. 80. ISBN 0-9548227-0-6.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Gallaway, Steve (January 15, 1997). The Steroid Bible. Belle Intl; 3rd Sprl edition. p. 125. ISBN 1-890342-00-9.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Llewellyn, William (January 28, 2007). ANABOLICS 2007 : Anabolic Steroid Reference Manual (6th Ed.). Body of Science. p. 988. ISBN 978-0967930466.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help) - Roberts, Anthony (2006). Anabolic Steroids: Ultimate Research Guide. Anabolic Books, LLC. p. 394. ISBN 1-59975-100-3.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|coauthors=ignored (|author=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - Yesalis, Charles E. (2000). Anabolic Steroids in Sport and Exercise. Human Kinetics Publishers; 2nd edition. p. 493. ISBN 0-88011-786-9.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|coauthors=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)