دراما، اليونان
Drama
Δράμα | |
|---|---|
 | |
| الإحداثيات: 41°9′00″N 24°8′48″E / 41.15000°N 24.14667°E | |
| البلد | |
| المنطقة الادارية | East Macedonia and Thrace |
| الوحدة المحلية | Drama |
| الحكومة | |
| • العمدة | Christodoulos Mamsakos |
| المساحة | |
| • البلدية | 840٫1 كم² (324٫4 ميل²) |
| • الوحدة البلدية | 488٫8 كم² (188٫7 ميل²) |
| المنسوب | 115 m (377 ft) |
| التعداد (2021) | |
| • البلدية | 58٬944 |
| • كثافة البلدية | 70/km2 (180/sq mi) |
| • الوحدة البلدية | 58٬532 |
| • كثافة الوحدة البلدية | 120/km2 (310/sq mi) |
| Community | |
| • التعداد | 50,252 (2021) |
| منطقة التوقيت | UTC+2 (EET) |
| • الصيف (التوقيت الصيفي) | UTC+3 (EEST) |
| Postal code | 661 00 |
| مفتاح الهاتف | 25210 |
| Vehicle registration | ΡΜ |
ذراما ( Drama ؛ باليونانية: Δράμα [ˈðrama])، وأيضاً تلفظ (دراما)، مدينة يونانية تقع في شمال شرق البلاد، وهي عاصمة مقاطعة ذراما في منطقة مقدونيا الشرقية و تراقيا الإدارية. يبلغ عدد سكان المدينة حوالي 55,593 نسمة في 2021 census)[1] is the economic center of the municipality (pop. 58,944), which in turn comprises 60 percent of the regional unit's population. The next largest communities in the municipality are Choristi (pop. 2,725), Χiropótamos (2,554), Kallífytos (1,282), Kalós Agrós (1,178), and Koudoúnia (996).
Built at the foot of mount Falakro, in a verdant area with abundant water sources, Drama has been an integral part of the Hellenic world since the classical era;[2] under the Byzantine Empire, Drama was a fortified city with a castle and rose to great prosperity under the Komnenoi as a commercial and military junction.[3]
During the Ottoman era, tobacco production and trade, the operation of the railway (1895) and improvement of the road network towards the port of Kavala, led to an increase in the population of the city and to the enhancement of commercial activity.[2]
Drama hosts the "Eleftheria", cultural events in commemoration of the city's liberation, at the end of June or beginning of July, and an annual film festival in September.
Name
Archaeological finds show that in the area of the modern city there used to be an ancient Greek settlement named Dyrama (Greek: Δύραμα) or alternatively Hydrama (Greek: Ύδραμα), both meaning "rich in water".[3] Some scholars associate Drama with the ancient Greek Drabescus (باليونانية: Δράβησκος).[4] Hydrama was notable as the place of worship for many gods of classical Greek mythology, especially Apollo and Artemis. With the passage of time Dyrama became Drama. In the South Slavic languages, the city is known as Драма which is itself a transliteration of the Greek name.[2]
الموقع
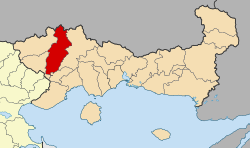
تقع ذراما في سهل غني بالمياه عند أقدام جبل فالاكرو وعلى ارتفاع 115 م عن مستوى سطح البحر.
التاريخ
تعود أولى آثار الإستيطان البشري في ذراما إلى الألف السادس قبل الميلاد، وهي عبارة عن آثار من العصر النيوليثي. أما في العصرين الإغريقي والروماني كانت المدينة تعرف باسم "درابيسكوس" كمحطة هامة على طريق إغناتيا والذي كان يربط روما بالقسطنطينية.
وفي العصر البيزنطي أصبحت تعرف باسم ذراما وتعود أقدم الوثائق التي تحمل هذا الإسم إلى العام 1172 م. وكانت المدينة وقتها ضمن المنطقة الإدارية لفيليبي التي تقع على بعد 20 كيلومتر إلى الجنوب.
احتلها الأتراك العثمانيون عام 1383 م. ومنذ ذلك الوقت أصبح في ذراما جالية مسلمة كبيرة بالإضافة إلى الأحياء المسيحية واليهودية.
عرفت المدينة نموا اقتصاديا هاما في القرن التاسع عشر نظرا لتوسع زراعة التبغ في السهول المحيطة بالمدينة.
حرر الجيش اليوناني هذه المدينة في عام 1913 بعد أكثر من 530 عام من السيطرة العثمانية، واكتسبت المينة طابعها اليوناني بعد سياسة الترحيل حسب اتفاقية لوزان عام 1923 حيث تم استبدال السكان الأتراك بيونانيي آسيا الصغرى.
Geography
Climate
Drama has a Mediterranean climate with hot, dry summers and chilly, wet winters.
| Climate data for Drama, Greece | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 8.3 (46.9) |
11.7 (53.1) |
14.9 (58.8) |
20.2 (68.4) |
25.1 (77.2) |
29.5 (85.1) |
32.3 (90.1) |
33.1 (91.6) |
28.0 (82.4) |
20.8 (69.4) |
15.7 (60.3) |
10.1 (50.2) |
20.8 (69.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 3.7 (38.7) |
6.6 (43.9) |
9.5 (49.1) |
13.7 (56.7) |
18.6 (65.5) |
22.8 (73.0) |
25.5 (77.9) |
25.9 (78.6) |
21.2 (70.2) |
14.8 (58.6) |
10.3 (50.5) |
5.0 (41.0) |
14.8 (58.6) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −0.2 (31.6) |
2.0 (35.6) |
4.3 (39.7) |
7.5 (45.5) |
12.0 (53.6) |
16.4 (61.5) |
18.5 (65.3) |
18.9 (66.0) |
14.8 (58.6) |
9.7 (49.5) |
5.6 (42.1) |
0.4 (32.7) |
9.2 (48.6) |
| Average rainfall mm (inches) | 71 (2.8) |
63 (2.5) |
74 (2.9) |
38 (1.5) |
53 (2.1) |
74 (2.9) |
32 (1.3) |
22 (0.9) |
45 (1.8) |
75 (3.0) |
42 (1.7) |
71 (2.8) |
660 (26.2) |
| Source: [5] | |||||||||||||
Municipality
The municipality Drama was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 2 former municipalities, that became municipal units (constituent communities in brackets):[6]
- Drama (Choristi, Drama, Kallifytos, Kalos Agros, Koudounia, Livadero, Makryplagio, Mavrovatos, Mikrochori, Monastiraki, Mylopotamos, Nikotsaras, Xiropotamos)
- Sidironero (Sidironero, Skaloti)
The municipality has an area of 840.103 km2, the municipal unit 488.830 km2.[7]
Population
| Year | City | Municipal community | Municipality |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1981 | 36,109 | 37,118 | 37,118 |
| 1991 | 37,604 | 38,546 | 47,925 |
| 2001 | 42,501 | 43,485 | 55,632 |
| 2011 | 44,823 | 45,828 | 58,944 |
Economy
In the recent past the economy of the Drama area relied heavily on the local paper and textile-clothing industries. However, these industries have either closed down or moved across the border to Bulgaria,[8] because of the low demands of the Bulgarian workforce,[9] with a negative impact on the local economy and employment. The situation worsened after 2007, when Bulgaria was admitted to the EU, and local Greek businessmen moved to expand their operations there. Other sources of revenue include agriculture, consisting mainly of tobacco plantations, small-scale mining (particularly of marble) and forestry. Recently, there have been efforts to exploit the rich local natural environment and to develop ecotourism.
There is a modern ski resort on Mount Falakro. Drama also hosts an annual short film festival.[10]
Transport
Rail transport
The town is served by Drama railway station on the Thessaloniki-Alexandroupoli line, with daily services to Thessaloniki and Alexandroupolis.
Culture
Since 1978, Drama has hosted the Drama International Short Film Festival. In 1987, the festival was recognized nationally. In 1995, it added the International competition section, where short films from all over the world visit the city every year.[11] In 1996, the festival was included in the National Cultural Network of Cities by the Greek Ministry of Culture.
المعالم الأساسية
- سور المدينة البيزنطية: ويعود إلى القرن التاسع والعاشر بعد الميلاد وهو يحيط بالمدينة القديمة.
- كنيسة أيا صوفيا: ويعود تاريخ بنائها إلى القرن التاسع بعد الميلاد.
- حجرة تاكسيارخي (باليونانية: Ταξιαρχή): وتعود غلى بدايات العصر المسيحي في القرن الخامس بعد الميلاد.
- مياه أيَا ڤارڤارا: وهي حديقة عامة مليئة بالينابيع الطبيعية الجارية، إلى الجنوب منها يقع موقع أركاذيكوس والذي يعود للعصر النيوليثي.
- متحف ذراما الأركيولوجي: وهو يضم اللقى الأثرية من كل مقاطعة ذراما بدءا من العصر النيوليثي وحتى مرحلة السيطرة العثمانية.
متفرقات
- منذ عام 1978 يقام في ذراما سنويا مهرجان عالمي للأفلام القصيرة.
- يعد نادي ذوكسا ذراماس أقدم نادي كرة قدم في المدينة ويعود تاريخ تأسيسه إلى عام 1918.
- لايوجد في ذراما جامعة ولكنها تحتوي على محطة لأبحاث التبغ ومعهد عالي للغابات.
- يعتمد اقتصاد المدينة على صناعة الورق والنسيج وأيضا زراعة التبغ، الغابات والسياحة البيئية.
Museums
Archaeological Museum
The Archaeological Museum of Drama covers human presence in the regional unit of Drama from the mid Paleolithic Period (50,000 years before present) with traces of life from Paleolithic hunts in the caves of the source of the Angitis, up to modern times (1913).
The exhibition space consists of three main halls. In the first archaeological finds from the cave of Maara give witness to the presence of nomadic hunters in the area from the mid Palaeolithic period, while other finds show us about the life of settled farmers and animal rearers from Neolithic villages and the passage of the Copper Age in the city of Drama and the village of Sitagri. The reproduction of a Neolithic house with finds which describe the activities of Neolithic man and his daily activities is the main centre of interest for visitors of all ages.
Bust of Dionysius, found in the area of Kali Vrysi. The same hall continues the journey through time to the Iron Age and later years where the main element was the worship of Dionysius at the city of Drama itself and at Kali Vrysi and other areas of the regional unit. In the second hall architectural sculptures, pottery and coins confirm that life continued in the city and throughout the whole regional unit during early Christian, Byzantine and post-Byzantine years.
The visitor is taken through modern recent history by a photographic exhibition relating to the city of Drama, the towns of the regional unit and the mountain villages. The exhibition covers the period from the beginning of the Ottoman period up to the middle of the 19th century. In the third hall which is roofed with an atrium, the visitor can admire sculptures arranged into three thematic groups. The first includes architectural sculptures dating from ancient times up to Turkish occupation. The second contains votive monuments connected with the worship of various gods in the Greco-Roman pantheon as well as local deities, with particular reference to Dionysius while the third group of sculptures focuses on funerary monuments from Hellenistic and Roman times.
Ecclesiastical Museum
The history of the Christian Church in Drama began during the Byzantine period and underwent difficult and troubled times. From the 14th century when the city was captured by the Ottomans until the 20th century with successive foreign occupations, the Greek Orthodox Church in Drama struggled without end, fed by the blood of many faithful, martyrs to the faith and to the Hellenic ideal and provided succor to its followers through difficult periods.
The collection of icons dating from Byzantine times to the 20th century forms the basic core of the museum's exhibits. The Museum of the Cathedral of Drama, founded during the reign of the honourable Bishop Dionysius 1st, is now housed in a recently restored five-storey wing of the Bishop of Drama's palace on Venizelou St. In the spacious and well-attended halls, ecclesiastical treasures of priceless spiritual and artistic value are on exhibition. The Icons of the Virgin Ηοdegetria and the Blessing Lord from the 13th century, icons from the 17th century and particularly from the 19th century decorate and sanctify the place. Moreover, the episcopal canonicals, holy vessels and their covers, many from the 19th century, relics of Chrysostomos of Drama and Smyrni, constitute the most important exhibits in the museum.
Many of the exhibits are relics brought by refugees from Asia Minor and Pontus in 1922 from the churches of their ancient homes to their new home, valuable reminders of who they were and where they came from. Organized groups of pilgrims and visitors to the city are advised to contact the office of the Diocese of Drama before visiting the museum to make arrangements.
Other museums
Sport
Drama hosts many sport teams in various sports. The most famous and most popular is Doxa Dramas, founded in 1918. Other successful clubs with presence in Greek national divisions are KAOD (basketball club), Pandramaikos FC, Drama 1986 and Amazones Dramas.
| Sport clubs based in Drama | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Club | Founded | Sports | Achievements |
| Doxa Dramas | 1918 | Football | Earlier long-time presence in A Ethniki |
| Pandramaikos FC | 1969 | Football | Earlier presence in Beta Ethniki |
| Drama 1986 | 1986 | Handball | Presence in A1 Ethniki |
| KAOD | 1989 | Basketball | Presence in A1 Ethniki |
| Titanes Dramas | 1990 | Basketball | Presence in A2 Ethniki women |
| Amazones Dramas | 2005 | Football | Panhellenic title in Greek women football |
Notable people
- Tabanıyassı Mehmed Pasha- Grand Vizier of the Ottoman Empire, (died 1637)
- Mahmud Dramali Pasha (1780–1822) - Ottoman General during the Greek Independence War
- Yesari Asım Arsoy (1900–1992), classical Turkish music composer - singer
- Koulis Stoligkas (1910–1984), actor
- Michael Athans (b. 1937), electrical engineer, retired MIT professor
- Apostolos Nikolaidis (1938–1999), Greek singer
- Basilis C. Xanthopoulos (1951–1990), theoretical physicist
- Nikos Sergianopoulos (1952–2008), television and stage actor
- Tania Tsanaklidou,(b. 1952) singer
- Athanassios Tsakiris (b. 1965), five-time Winter Olympian
- Petros Gaitanos (b. 1967), singer
- Natassa Theodoridou, (b. 1970), singer
- Paraskevas Antzas (b. 1977), footballer
- Charikleia Bouda (b. 1980), Olympic sprinter
- Stratos Perperoglou (b. 1984), basketball player
- Konstantinos Douvalidis (b. 1987), Olympic hurdler
- Dimitris Siovas (b. 1988), footballer
- Panagiota Tsakiri (b. 1990), Olympic biathlete and cross-country skier
- Ioannis Fetfatzidis (b. 1990), footballer
- Anna Korakaki (b. 1996), shooter, Gold medalist Women's 25m pistol, bronze medalist in the 10m air pistol at the 2016 Summer Olympics
Gallery
Grave stele of Tiberius Claudius Maximus, Archaeological Museum of Drama
See also
Cooperation with other cities
References
- ^ "Census 2022" (PDF). elstat-outsourcers.statistics.gr. Retrieved 15 May 2023.
- ^ أ ب ت "Παρουσιάστηκε πρόβλημα" (PDF). Retrieved 15 May 2023.
- ^ أ ب "Visit Greece | Δράμα". Archived from the original on 2014-05-17. Retrieved 2014-05-15.
- ^ James I. Porter (2002). Constructions of the Classical Body. University of Michigan Press. pp. 142–. ISBN 978-0-472-08779-2. Retrieved 3 March 2013.
- ^ (in en)Drama (drm) Monthly Climate Average, Drama, World Weather Online, October 2019
- ^ "ΦΕΚ B 1292/2010, Kallikratis reform municipalities" (in اليونانية). Government Gazette.
- ^ "Population & housing census 2001 (incl. area and average elevation)" (PDF) (in اليونانية). National Statistical Service of Greece. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-09-21.
- ^ "Job Creation and Enterprise Development Department (EMP/ENTERPRISE)" (PDF). Ilo.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2009-03-27. Retrieved 2013-03-26.
- ^ Αγγελιοφόρος, September 24, 2006
- ^ "Διεθνές Φεστιβάλ Ταινιών Μικρού Μήκους Δράμας | Official website". Φεστιβάλ Ταινιών Μικρού Μήκους Δράμας.
- ^ "Short Film Festival in Drama - History". Archived from the original on 6 August 2011. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
Bibliography
- Gaydarska, B. "Prehistoric Drama and its regional context," in Stoyanov, T., Angelova, S. & Lozanov (eds), Stephanos Archaeologicos in honorem Professoris Ludmilli Getov, Vol. I (Sofia: Sofia University Press, 2005), 116 – 133.
External links
 Drama travel guide from Wikivoyage
Drama travel guide from Wikivoyage- Official website of Drama regional unit
قالب:Drama div خطأ لوا في وحدة:Authority_control على السطر 278: attempt to call field '_showMessage' (a nil value).
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- CS1 اليونانية-language sources (el)
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- Articles containing Greek-language text
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Drama, Greece
- Wine regions of Greece
- Populated places in Drama (regional unit)
- مدن اليونان