خنت
خنت Ghent
| |
|---|---|
 | |
| الإحداثيات: 51°03′13″N 03°43′31″E / 51.05361°N 3.72528°E | |
| البلد | بلجيكا |
| Community | Flemish Community |
| المنطقة | المنطقة الفلمنكية |
| المقاطعة | East Flanders |
| Arrondissement | Ghent |
| الحكومة | |
| • العمدة (قائمة) | Mathias De Clercq |
| • الحزب الحاكم | sp.a-Groen, Open VLD, CD&V |
| المساحة | |
| • الإجمالي | 156٫18 كم² (60٫30 ميل²) |
| التعداد (2018-01-01) | |
| • الإجمالي | 260٬341 |
| • الكثافة | 1٬700/km2 (4٬300/sq mi) |
| Postal codes | 9000–9052 |
| Area codes | 09 |
| الموقع الإلكتروني | www.gent.be |
خنت (بالهولندية Gent ، بالفرنسية Gand) مدينة وبلدية بلجيكا، عاصمة مقاطعة فلاندر الشرقية في الإقليم الفلمنكي . بلغ عدد قاطنيها في سنة 2005 230 951 ساكن (ثالث أكبر مدينة في بلجيكا). و تغطي مساحة 156.18 كيلومتر مربع.
غِنت مدينة بلجيكية تقع على بعد حوالي 50كم شمال غربي مدينة بروكسل، ويبلغ عدد سكانها 228,490 نسمة. تقع المدينة في الجزء الذي يتحدث اللغة الهولندية، عند ملتقى نهري شيلدي ولييه. وهي ميناء مهم، حيث تربط قناة حفرت في عام 1886م المدينة ببحر الشَّمال. تشتهر مدينة غنت بالمنتجات الكيميائية ومحالج القطن والكتان والأزهار، وتمتد أكثر من 200 جسر فوق المجاري المائية التي تتقاطع عبر المدينة. ودار بلدية المدينة التي شيدت في القرن السادس عشر الميلادي مثال رائع للفن المعماري القوطي.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
التاريخ
نشأت المدينة في البداية كمستوطنة عند التقاء نهري شلت وليس وأصبحت في العصور الوسطى واحدة من أكبر وأغنى مدن شمال أوروبا. وهي اليوم مدينة مزدحمة بميناء وجامعة.
أصبحت غنت مدينة مهمة في العصور الوسطى. وبلغت قمة الأهمية في القرن الخامس عشر الميلادي، إلا أن الثورات والحروب مزقت المدينة عدة سنوات بعد ذلك. وقد احتلها الأسبان والفرنسيون والنمساويون في فترات مختلفة قبل استقلال بلجيكا. كما احتلت القوات الأَلمانيَّة مدينة غنت في الحربين العالميتين الأُولى والثانية.
الجغرافيا
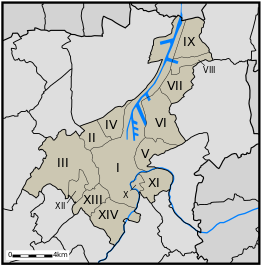
بعد اندماجات البلديات في 1965 و 1977، فإن المدينة تتكون من:
- I خنت
- II Mariakerke
- III Drongen
- IV Wondelgem
- V Sint-Amandsberg
- VI Oostakker
- VII Desteldonk
- VIII Mendonk
- IX Sint-Kruis-Winkel
- X Ledeberg
- XI Gentbrugge
- XII Afsnee
- XIII Sint-Denijs-Westrem
- XIV Zwijnaarde
البلديات المجاورة
المناخ
The climate in this area has mild differences between highs and lows, and there is adequate rainfall year-round. According to the Köppen climate classification system, Ghent has a marine west coast climate, abbreviated "Cfb" on climate maps.[1]
| Climate data for خنت (1981–2010 normals, sunshine 1984–2013) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 6.2 (43.2) |
7.0 (44.6) |
10.8 (51.4) |
14.5 (58.1) |
18.1 (64.6) |
20.6 (69.1) |
23.0 (73.4) |
22.9 (73.2) |
19.7 (67.5) |
15.3 (59.5) |
10.1 (50.2) |
6.5 (43.7) |
14.7 (58.5) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 3.4 (38.1) |
3.8 (38.8) |
6.8 (44.2) |
9.4 (48.9) |
13.2 (55.8) |
15.9 (60.6) |
18.1 (64.6) |
17.9 (64.2) |
14.9 (58.8) |
11.2 (52.2) |
7.0 (44.6) |
4.0 (39.2) |
10.6 (51.1) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 0.7 (33.3) |
0.4 (32.7) |
2.7 (36.9) |
4.5 (40.1) |
8.3 (46.9) |
11.1 (52.0) |
13.2 (55.8) |
12.8 (55.0) |
10.2 (50.4) |
7.2 (45.0) |
3.9 (39.0) |
1.5 (34.7) |
6.4 (43.5) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 70.7 (2.78) |
56.2 (2.21) |
61.5 (2.42) |
50.6 (1.99) |
63.1 (2.48) |
74.3 (2.93) |
77.4 (3.05) |
84.2 (3.31) |
74.2 (2.92) |
81.7 (3.22) |
82.7 (3.26) |
82.2 (3.24) |
858.8 (33.81) |
| Average precipitation days | 12.6 | 10.8 | 12.0 | 10.1 | 11.1 | 10.5 | 10.3 | 10.0 | 10.9 | 12.1 | 13.4 | 13.0 | 136.8 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 61 | 79 | 123 | 172 | 204 | 196 | 209 | 196 | 144 | 118 | 66 | 50 | 1٬618 |
| Source: Royal Meteorological Institute [2] | |||||||||||||
السياحة
العمارة
 Historical centre of Ghent - from left to right: Old post office, Saint-Nicholas Church, Belfry, and Saint Bavo Cathedral. |
أشهر أبنائها

- القديس باڤو, القديس الحامي لخنت (589-654)
- هنري من خنت, scholastic philosopher (c. 1217-1293)
- ياكوب ڤان أرتڤلده, statesman and political leader (c. 1290-1345)
- John of Gaunt, 1st Duke of Lancaster (1340-1399)
- يان ڤان أيك, رسام (ح. 1385-1441)
- Hugo van der Goes, painter (c. 1440-1482)
- Jacob Obrecht, composer of the عصر النهضة (c. 1457-1505)
- شارل الخامس، الامبراطور الروماني المقدس, Karel V, Charles Quint (1500-1558)
- Cornelius Canis, composer of the Renaissance, music director for the chapel of Charles V in the 1540s-1550s
- Daniel Heinsius, scholar of the Dutch عصر النهضة (1580-1655)
- Caspar de Crayer, painter (1582-1669)
- Frans de Potter, writer, (1834-1904)
- Jan Frans Willems, writer (1793-1846)
- Joseph Guislain, physician (1797-1860)
- Hippolyte Metdepenningen, lawyer and politician (1799-1881)
- لويس الثامن عشر من فرنسا نـُفي إلى خنت أثناء المائة يوم في 1815
- Charles John Seghers, Jesuit clergyman and missionary (1839-1886)
- Victor Horta، معماري أرت نوڤو (1861-1947)
- موريس ميترلينك، شاعر، كاتب مسرحي، كاتب مقالات، حاصل على جائزة نوبل في الأدب (1862-1949)
- Frans Rens, writer, (1805-1874)
- Leo Baekeland, chemist and inventor of Bakelite (1863-1944)
- Pierre Louÿs, poet and romantic writer (1870-1925)
- Marthe Boël, feminist (1877-1956)
- كورني جان فرانسوا هيمانز, فسيولوجي حاصل على جائزة نوبل في الفسيولوجيا أو الطب (1892-1968)
- Suzanne Lilar, essayist, novelist, and playwright (1901-1992)
- جان داسكاليدس، طبيب أمراض نساء ومؤسس شوكولاتات ليونيداس (1922-1992)
- جاك روگه، رئيس اللجنة الاولمپية الدولية (1942-)
- Gabriel Rios, musician
- Kristof Ongenaet, basketball player
- Jan Robbe, electronic musician and founder of Entity
- Soulwax, electronic/rock band: brothers David and Stephen Dewaele
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
المدن الشقيقة
|
معرض الصور
City palace Hotel d'Hane-Steenhuyse
Ruins of Saint Bavo's Abbey
انظر أيضاً
الهامش
- ^ "Climate Summary for Ghent, Belgium". weatherbase.com. Retrieved 18 May 2015.
- ^ "Klimaatstatistieken van de Belgische gemeenten" (PDF) (in الهولندية). Royal Meteorological Institute. Retrieved 29 May 2018.
- ^ أ ب ت ث ج ح خ د "Twin cities". Stad Gent. City of Ghent. Retrieved 29 March 2020.
- ^ "Wiesbaden's international city relations". Retrieved 24 December 2012.
- ^ "European networks and city partnerships". Nottingham City Council. Archived from the original on 25 June 2012. Retrieved 20 July 2013.
وصلات خارجية
- Official website
 (in هولندية)
(in هولندية) - Official Tourist website (in هولندية, إنگليزية, فرنسية, ألمانية, and إسپانية)
- Flanders Tourism Website (in هولندية, فرنسية, ألمانية, إسپانية, سويدية, دنماركية, إيطالية, تشيكية, يابانية, and صينية)
- Pages using gadget WikiMiniAtlas
- CS1 الهولندية-language sources (nl)
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- Articles with hatnote templates targeting a nonexistent page
- Articles containing هولندية-language text
- Articles containing فرنسية-language text
- Coordinates on Wikidata
- Articles with هولندية-language sources (nl)
- Articles with إنگليزية-language sources (en)
- Articles with فرنسية-language sources (fr)
- Articles with ألمانية-language sources (de)
- Articles with إسپانية-language sources (es)
- Articles with سويدية-language sources (sv)
- Articles with دنماركية-language sources (da)
- Articles with إيطالية-language sources (it)
- Articles with تشيكية-language sources (cs)
- Articles with يابانية-language sources (ja)
- Articles with صينية-language sources (zh)
- مدن بلجيكا
- خنت
- Municipalities of East Flanders
- Port cities and towns in Belgium
- Provincial capitals of Flanders