مفاصلة
المفاصلة[5] أو الابتعاد الاجتماعي Social distancing، هي مجموعة من التدابير الغير صيدلانية لادارة العدوى تهدف لإيقاف أو إبطاء انتشار الأمراض المعدية. الهدف من الابتعاد الاجتماعي هو الحد من إحتمالية الاتصال بين الأشخاص الحاملين للعدوى، والآخرين الغير المصابين، ومن ثم التقليل من انتقال الأمراض، وفي النهاية الحد من أعداد الوفيات.[6][7]
يكون الابتعاد الاجتماعي أكثر فعالية عند احتمالية انتقال العدوى عن طريق السعال أو العطس؛ الاتصال الجسدي المباشر، بما في ذلك الاتصال الجنسي؛ الاتصال الجسدي غير المباشر (عن طريق لمس الأسطح الحاملة للعدوى أي أدوات العدوى)؛ أو الانتقال عن طريق الهواء (إذا كان بإمكان العضيات الدقيقة المعيشة في الهواء لفترات طويلة).[8]
قد يكون الابتعاد الاجتماعي أقل فعالية في حالات العدوى المنقولة بصفة رئيسية عن طريق الماء أو الطعام الذي يحمل العدوى أو عن طريق عوامل مثل الناموس أو الحشرات الأخرى، والأقل تواتراً من شخص لآخر..[9]
قد تتضمن مساويء الابتعاد الاجتماعي الشعور بالعزلة، انخفاض الانتاجية، وفقدان الفوائد الأخرى المرتبطة بالتفاعل البشري.
ترجع أولى الإشارات للابتعاد الاجتماعي إلى القرن السابع عشر قبل الميلاد والتي وردت في سفر اللاويين، 13:46: "كُلَّ الأَيَّامِ الَّتِي تَكُونُ الضَّرْبَةُ فِيهِ يَكُونُ نَجِسًا. إِنَّهُ نَجِسٌ. يُقِيمُ وَحْدَهُ. خَارِجَ الْمَحَلَّةِ يَكُونُ مُقَامُهُ."[10]
تاريخياً، بُنيت مستعمرات الجذام والمحاجر البحرية كوسيلة لمنع انتشار الجذام والأمراض المعدية الأخرى عن طريق الابتعاد الاجتماعي،[11] حتى تم اخترعت التدابير والعلاجات الأخرى الفعالة للحيلولة دون انتقال هذه الأمراض أو علاجها.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
أمثلة
من أمثلة وسائل الابتعاد الاجتماعي لمنع انتشار الأمراض المعدية:[12][13][بحاجة للاستشهاد الطبي]
- اغلاق المدارس، التعليم أونلاين[14]
- إغلاق أماكن العمل[15] ويشمل ذلك إغلاق الشركات والخدمات الاجتماعية "الغير أساسية" (الغير أساسية أي المرافق التي لا تؤدي المهام الأساسية في المجتمع، على عكس الخدمات الأساسية[16])
- العزل
- الحجر الصحي
- الحزام الصحي
- العزل الوقائي
- إلغاء التجمعات العامة مثل الفعاليات الرياضية، العروض السينمائية والموسيقية[17]
- إغلاق أو تقليل النقل العام
- إغلاق المرافق الترفيهية (حمامات السباحة، نوادي الشباب، صالات الألعاب الرياضية)[18]
- تدابير شخصية مثل الحفاظ على مسافة كافية بين الأشخاص، عدم استخدام الهواتف العامة، تجنب التواجد في الأماكن العامة المزدحمة وتقليل السفر الغير ضروري[19][20]
- عدم التصافح بالأيدي والتقليل من العناق والقبلات للتحية بين الأشخاص[21]
الفاعلية
إغلاق المدارس
بيـَّنت النمذجة الرياضية أن انتقال وتفشي مرض يمكن إبطاؤه بإغلاق المدارس. إلا أن النجاعة تعتمد على الاتصالات التي يقوم بها الأطفال خارج المدرسة. فكثيراً ما يُضطر أحد الوالدين لأخذ إجازة من العمل، كما أن إغلاق المدارس لفترات طويلة قد يكون مطلوباً، وهذا قد يؤدي إلى اضطراب اجتماعي واقتصادي.[23][24]
School closures were shown to reduce morbidity from the Asian Flu by 90% during the 1957-58 outbreak,[25] and up to 50% in controlling influenza in the US, 2004–2008.[26] Similarly, mandatory school closures and other social distancing measures were associated with a 29% to 37% reduction in influenza transmission rates during the 2009 flu epidemic in Mexico.[27]
During the swine flu outbreak in 2009 in the UK, in an article titled "Closure of schools during an influenza pandemic" published in the Lancet Infectious Diseases, a group of epidemiologists endorsed the closure of schools in order to interrupt the course of the infection, slow further spread and buy time to research and produce a vaccine.[28] Having studied previous influenza pandemics including the 1918 flu pandemic, the influenza pandemic of 1957 and the 1968 flu pandemic, they reported on the economic and workforce effect school closure would have, particularly with a large percentage of doctors and nurses being women, of whom half had children under the age of 16. They also looked at the dynamics of the spread of influenza in France during French school holidays and noted that cases of flu dropped when schools closed and re-emerged when they re-opened. They noted that when teachers in Israel went on strike during the flu season of 1999–2000, visits to doctors and the number of respiratory infections dropped by more than a fifth and more than two fifths respectively.[29]
إغلاق أماكن العمل
الحجر الصحي للأماكن المشتبه بها
الحزام الصحي
 مقالة مفصلة: الحزام الصحي
مقالة مفصلة: الحزام الصحي

العزل الوقائي

إلغاء التجمعات العامة
القيود على السفر
انظر أيضاً
المصادر
- ^ Wiles, Siouxsie (9 March 2020). "The three phases of Covid-19 – and how we can make it manageable". The Spinoff. Retrieved 9 March 2020.
- ^ Anderson, Roy M; Heesterbeek, Hans; Klinkenberg, Don; Hollingsworth, T Déirdre (March 2020). "How will country-based mitigation measures influence the course of the COVID-19 epidemic?". The Lancet. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30567-5.
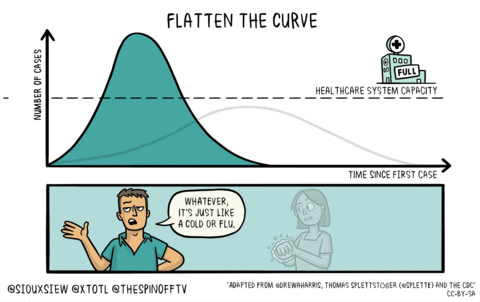
A key issue for epidemiologists is helping policy makers decide the main objectives of mitigation—e.g., minimising morbidity and associated mortality, avoiding an epidemic peak that overwhelms health-care services, keeping the effects on the economy within manageable levels, and flattening the epidemic curve to wait for vaccine development and manufacture on scale and antiviral drug therapies.
- ^ Wiles, Siouxsie (14 March 2020). "After 'Flatten the Curve', we must now 'Stop the Spread'. Here's what that means". The Spinoff. Retrieved 13 March 2020.
- ^ Anderson RM, Heesterbeek H, Klinkenberg D, Hollingsworth TD (March 2020). "How will country-based mitigation measures influence the course of the COVID-19 epidemic?". Lancet. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30567-5. PMID 32164834.
- ^ Hassan Hassan (2020-03-18). "مفاصلة". تويتر.
- ^ Johnson, Carolyn Y.; Sun, Lena; Freedman, Andrew (2020-03-10). "Social distancing could buy U.S. valuable time against coronavirus". Washington Post. Retrieved 2020-03-11.
- ^ Pandemic Planning - Social Distancing Fact Sheet
- ^ "Information about Social Distancing," Santa Clara Public Health Department.
- ^ "Interim Pre-Pandemic Planning Guidance: Community Strategy for Pandemic Influenza Mitigation in the United States—Early, Targeted, Layered Use of Nonpharmaceutical Interventions," CDC, Feb 2007
- ^ Bible Gateway, Authorized King James Version, Leviticus 13:46
- ^ Charles Léon Souvay, "Leprosy," Catholic Encyclopedia (1913), Volume 9.
- ^ Kathy Kinlaw, Robert Levine, "Ethical Guidelines on Pandemic Influenza," CDC, December 2006
- ^ Pueyo, Tomas (2020-03-12). "Coronavirus: Why You Must Act Now". Medium (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 2020-03-12.
- ^ Cauchemez S, Ferguson NM, Wachtel C, Tegnell A, Saour G, Duncan B, Nicoll A (2009). "Closure of schools during an influenza pandemic". The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 9 (8): 473–481. doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(09)70176-8. PMID 19628172.
- ^ Kumar S, Crouse Quinn S, Kim KH, Daniel LH, Freimuth VS (2012). "The Impact of Workplace Policies and Other Social Factors on Self-Reported Influenza-Like Illness Incidence During the 2009 H1N1 Pandemic". American Journal of Public Health. 102 (1): 134–140. doi:10.2105/AJPH.2011.300307. PMC 3490553. PMID 22095353.
- ^ "Social Distancing Support Guidelines," Colorado Dept. of Public Health and Environment, March 2008.
- ^ R. Booy and J. Ward, "Evidence compendium and advice on social distancing and other related measures for response to an influenza pandemic," National Centre for Immunisation Research and Surveillance.
- ^ "Flu Pandemic Mitigation - Social Distancing"
- ^ Glass RJ, Glass LM, Beyeler WE, Min HJ. "Targeted Social Distancing Designs for Pandemic Influenza." Emerg Infect Dis. 2006;12(11):1671-1681. https://dx.doi.org/10.3201/eid1211.060255
- ^ "Social Distancing Guidelines (for workplace communicable disease outbreaks)"
- ^ "Guidance on Preparing Workplaces for an Influenza Pandemic," OSHA 3327-02N 2007
- ^ "2009 Press Releases". Health Protection Agency. 24 December 2009. Archived from the original on 24 December 2009. Retrieved 24 December 2009.
- ^ Zumla, Alimuddin; Yew, Wing-Wai; Hui, David S. C. (2010). Emerging Respiratory Infections in the 21st Century, An Issue of Infectious Disease Clinics (in الإنجليزية). Vol. 24. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 614. ISBN 978-1-4557-0038-7.
- ^ Cauchemez, Simon; Ferguson, Neil M; Wachtel, Claude; Tegnell, Anders; Saour, Guillaume; Duncan, Ben; Nicoll, Angus (2009). "Closure of schools during an influenza pandemic". The Lancet Infectious Diseases. 9 (8): 473–481. doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(09)70176-8. ISSN 1473-3099. PMID 19628172.
- ^ Chin TD, Foley JF, Doto IL, Gravelle CR, Weston J (1960). "Morbidity and mortality characteristics of Asian strain influenza". Public Health Rep. 75 (2): 148–58. doi:10.2307/4590751. JSTOR 4590751. PMC 1929395. PMID 19316351.
- ^ Wheeler CC, Erhart LM, Jehn ML (2010). "Effect of school closure on the incidence of influenza among school -age children in Arizona". Public Health Reports. 125 (6): 851–859. doi:10.1177/003335491012500612. PMC 2966666. PMID 21121230.
- ^ Flu Pandemic Study Supports Social Distancing," NIH Research Matters, June 6, 2011.
- ^ Wardrop, Murray (21 July 2009). "Swine flu: schools should close to halt spread of virus, ministers told". The Telegraph (in الإنجليزية البريطانية). ISSN 0307-1235. Retrieved 17 March 2020.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ Walsh, Eric, ed. (20 July 2009). "Closing schools won't stop pandemics: study". Reuters (in الإنجليزية). Retrieved 17 March 2020.
{{cite news}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link)
وصلات خارجية
- Why outbreaks like coronavirus spread exponentially, and how to “flatten the curve”, by Harry Stevens, Washington Post, March 14 2020, "These simulations show how to flatten the coronavirus growth curve"