نظام إحداثيات سماوية
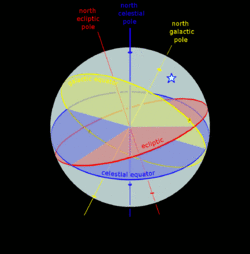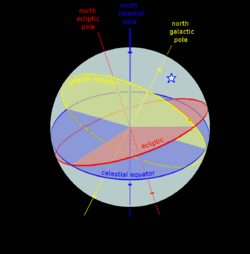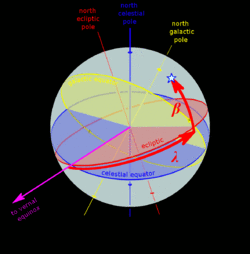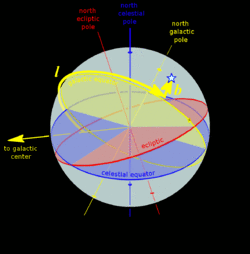 A star's galactic, ecliptic, and equatorial coordinates, as projected on the celestial sphere. Ecliptic and equatorial coordinates share the vernal equinox as the primary direction, and galactic coordinates are referred to the galactic center. The origin of coordinates (the "center of the sphere") is ambiguous; see celestial sphere for more information. |
نظام إحداثيات سماوية Celestial coordinate system مصطلح حديث لم يستخدم في تراثنا القديم استخدمه رياضيو العصر الحديث. والإحداثيات بشكل عام تعنى الابعاد التى يتعين بها موضع نقطة ما بالنسبة الى أساس الإسناد وتسمى لإحداثيات النقطة. ففى الجغرافيا نلجأالى الخرائط والأطالس لتحديد مواقع محددة على الأرض (بلدان ومدن وأماكن و------) معتمدين على خطوط الطول والعرض تسقطها على نموذج الكرة الارضية . وفى علم الفلك يلجأ الفلكيون الى وضع خرائط سماوية توفر إحداثيات مختلف الأجرام السماوية المعروفة بثباتتها على الزمان أسقطت على كرة رمزية وسميت كرة السماء.
وهى بمعنى أدق اى عدد من الإحداثيات كالبعد السمتى والارتفاع والطول السماوى والعرض السماوى والزاوية الساعية المحلية والسمت والميل والتى تستخدم لتحديد موقع نقطة على الكرة السماوية.
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
أنظمة الإحداثيات
| نظام الإحداثيات | المستوى الرئيسي | الأقطاب | الإحداثيات | الحقبة |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| أفقية (ويسمى أيضاً Alt/Az or Az/El) |
الأفق | سمت الرأس/النظير | الارتفاع - السمت - meridian | |
| إستوائية | خط الإستواء السماوي | الأقطاب السماوية | declination - right ascension أو hour angle | B1950, J2000 |
| الكسوفية | كسوفية | الأقطاب الكسوفية | ecliptic latitude - ecliptic longitude | |
| المجرّية | مستوى مجرّي | أقطاب مجرّية | ||
| Supergalactic | supergalactic plane |
نظام الإحداثيات الإستوائية
تحويل الإحداثيات
تحويل الإحداثيات الإستوائية إلى أفقية
Let δ be the declination and the hour angle.
Let φ be the observer's latitude.
Let El be the elevation angle and Az the azimuth angle.
Let θ be the zenith (or zenith distance, i.e. the 90° complement of Alt).
Then the equations of the transformation are:
Use the inverse trigonometric functions to get the values of the coordinates.
NOTE: Inverse cosine is dual valued, i.e. 160° and 200° both have the same cosine. The above needs to be corrected. If H < 180 (or Pi radians) then Az = 360 - Az as derived from the above equation.
انظر أيضا
المصادر
- مؤمن, عبد الأمير (2006). قاموس دار العلم الفلكي. بيروت، لبنان: دار العلم للملايين.
{{cite book}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|طبعة أولى coauthors=(help)
وصلات خارجية
| Celestial coordinate systems
]].- NOVAS, the U.S. Naval Observatory's Vector Astrometry Software, an integrated package of subroutines and functions for computing various commonly needed quantities in positional astronomy.
- SOFA, the IAU's Standards of Fundamental Astronomy, an accessible and authoritative set of algorithms and procedures that implement standard models used in fundamental astronomy.
- This article was originally based on Jason Harris' Astroinfo, which comes along with KStars, a KDE Desktop Planetarium for Linux/KDE.


